Sub-step flotation and detoxification method for incineration fly ash of medical garbage
A technology for incinerating fly ash and medical waste, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of waste liquid mixed with residual ash, long precipitation time, complicated process, etc., and achieve the effects of reduced treatment cost, simple operation and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
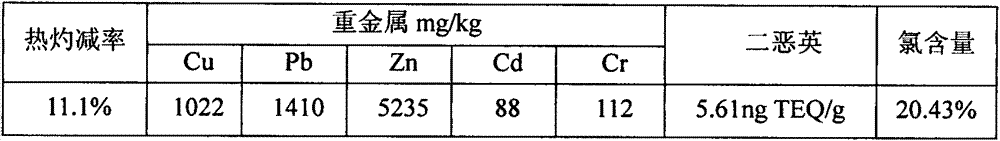
[0015] See Table 1 for the thermal loss rate, heavy metals, dioxins and chlorine contents of a certain medical waste incineration fly ash. Add 200g of medical waste incineration fly ash and 4 liters of deionized water into the slurry mixing tank at the same time, stir the mortar for 5 minutes to make the fly ash thoroughly wet, during this period, add hydrochloric acid to the mortar to make the pH of the mortar = 6, and add 2.4 grams The kerosene was stirred for several minutes to temper the slurry, during which time 0.6 grams of methyl isobutyl carbinol was added to the mortar and stirred for several minutes to temper the slurry.
[0016] Table 1 Thermal burn rate, heavy metal, dioxin and chlorine content of fly ash from medical waste incineration
[0017]
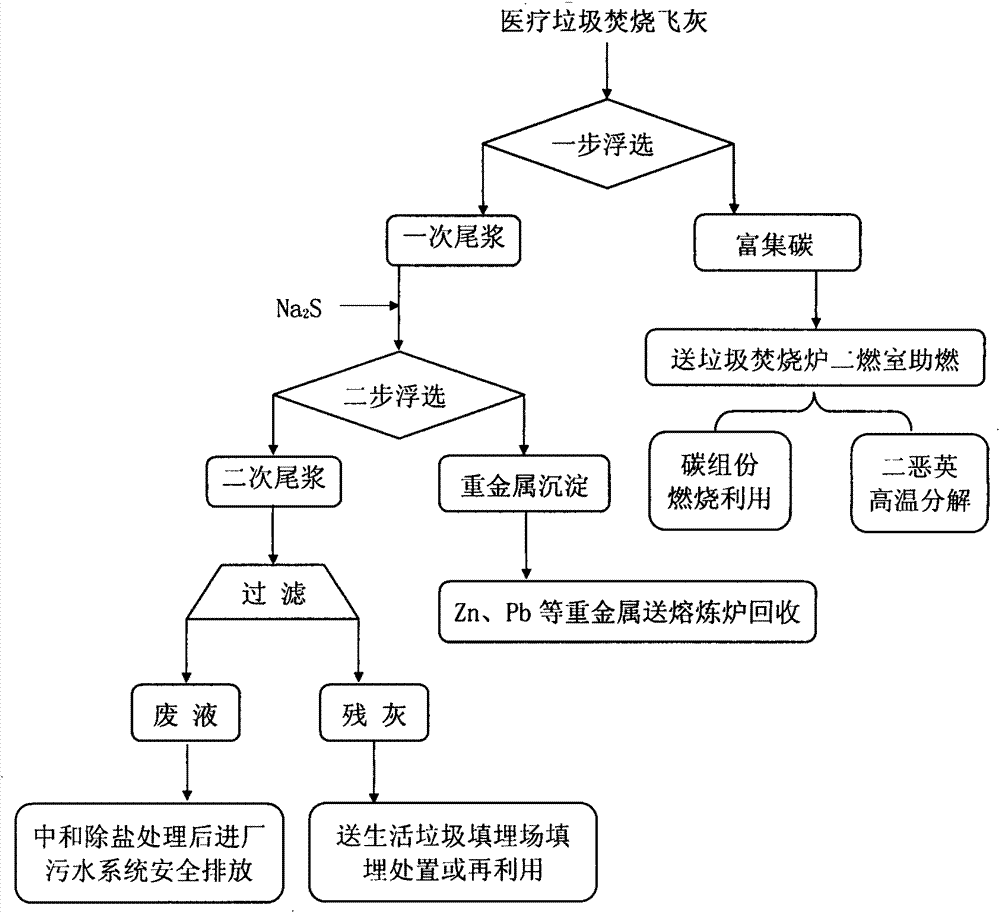
[0018] The above-mentioned slurry is sent to the flotation column for flotation for the first step of flotation. The hydrophobic carbon components (activated carbon and residual carbon) and dioxin in the slurry are att...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The medical waste incineration fly ash sample used is the same as that in Example 1, nitric acid is added to the mortar in the first step of flotation to make the pH of the mortar=5, and in the second step of flotation, press S 2- The number of moles is the number of moles of all heavy metal ions in the first tailing slurry and adding Na 2 S, other added flotation agents and operating parameters are the same as in Example 1.
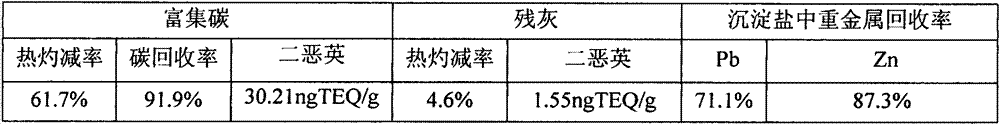
[0029] The flotation separation product was analyzed after dehydration and drying, and the results are shown in Table 5. The dioxin content in the residual ash met the dioxin limit required by GB16889-2008 (<3ng TEQ / g). At the same time, the dried residual ash was tested for the leaching concentration of heavy metals according to HJ / T300. The test results are shown in Table 6. The harmful concentration in the leaching solution is lower than the concentration limit of heavy metal pollutants in GB16889-2008, indicating that the residual ash can be d...
Embodiment 3
[0038] The medical waste incineration fly ash sample that adopts is identical with embodiment 1, in the first step flotation mortar pH=7, press S in the second step flotation 2- The number of moles is 3 times of the number of moles of all heavy metal ions in the first tailings and add Na 2 S, other added flotation agents and operating parameters are the same as in Example 1.
[0039] According to the above conditions, the flotation separation products (enriched carbon, residual ash, precipitated salt) were analyzed after dehydration and drying. The results are shown in Table 8. The dioxin content in the residual ash meets the dioxin limit required by GB16889-2008 (<3ngTEQ / g). At the same time, the dried residual ash was tested for heavy metal leaching concentration according to HJ / T300. The test results are shown in Table 9. The harmful concentration in the leaching solution is lower than the concentration limit of heavy metal pollutants in GB16889-2008, indicating that the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com