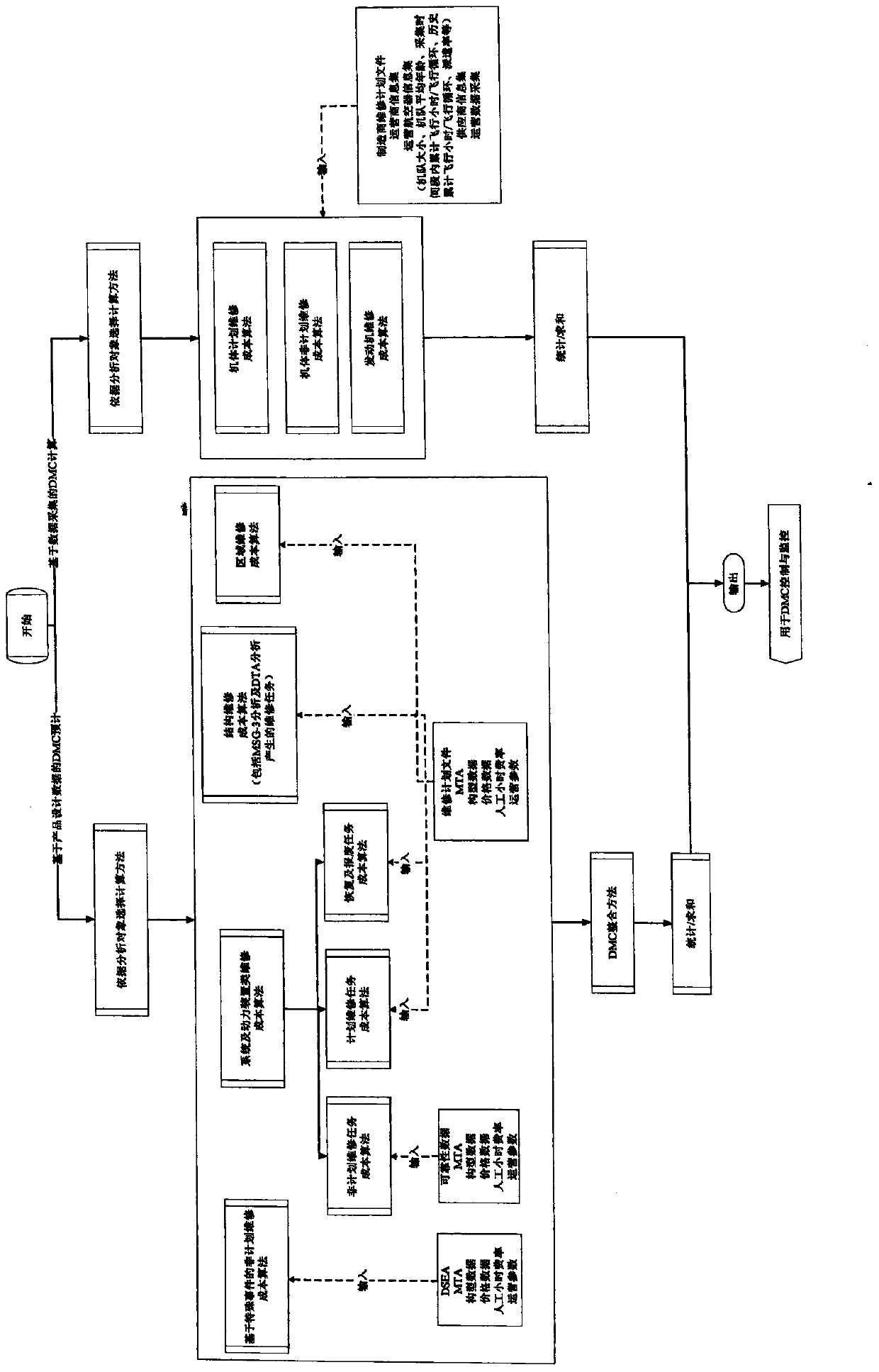
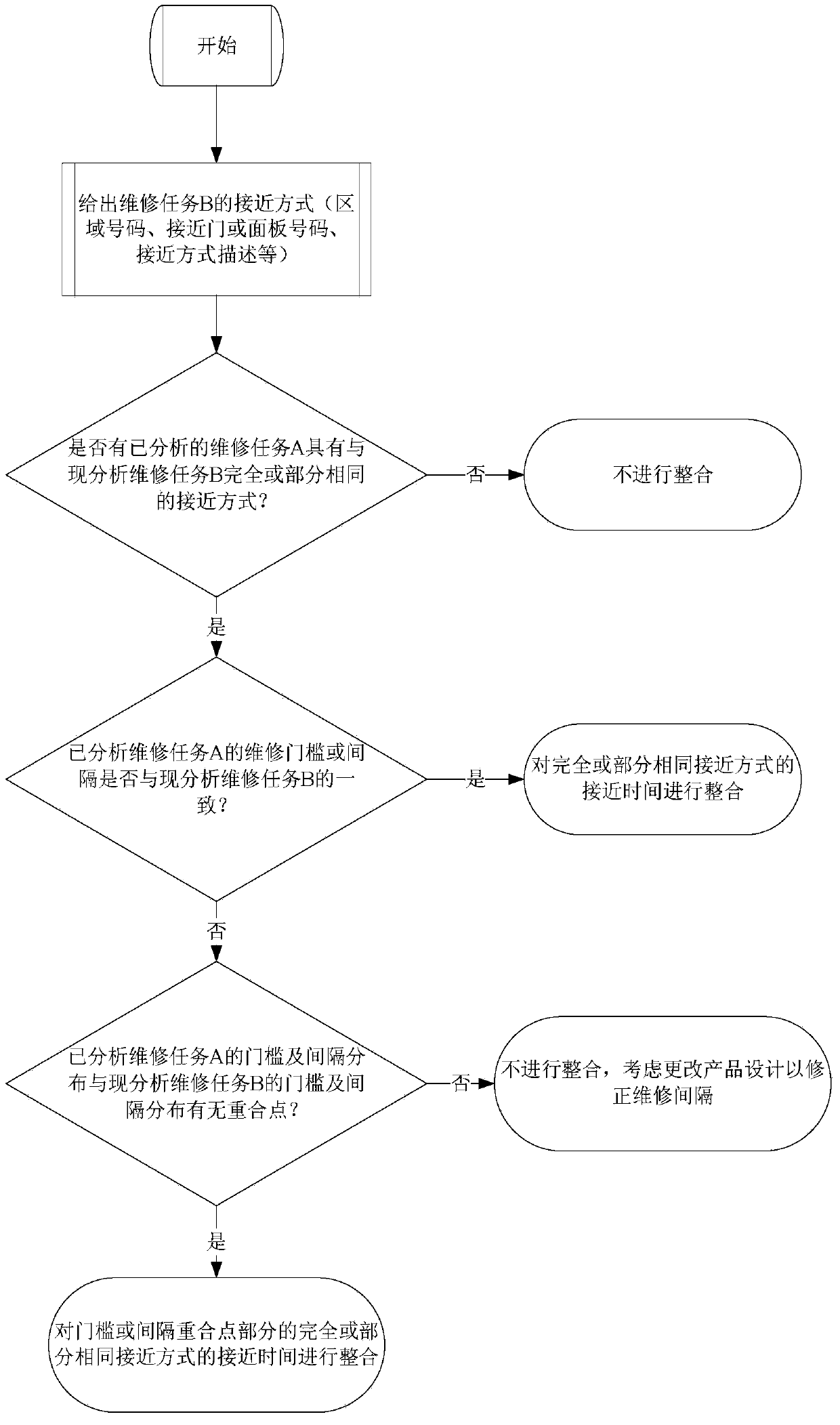
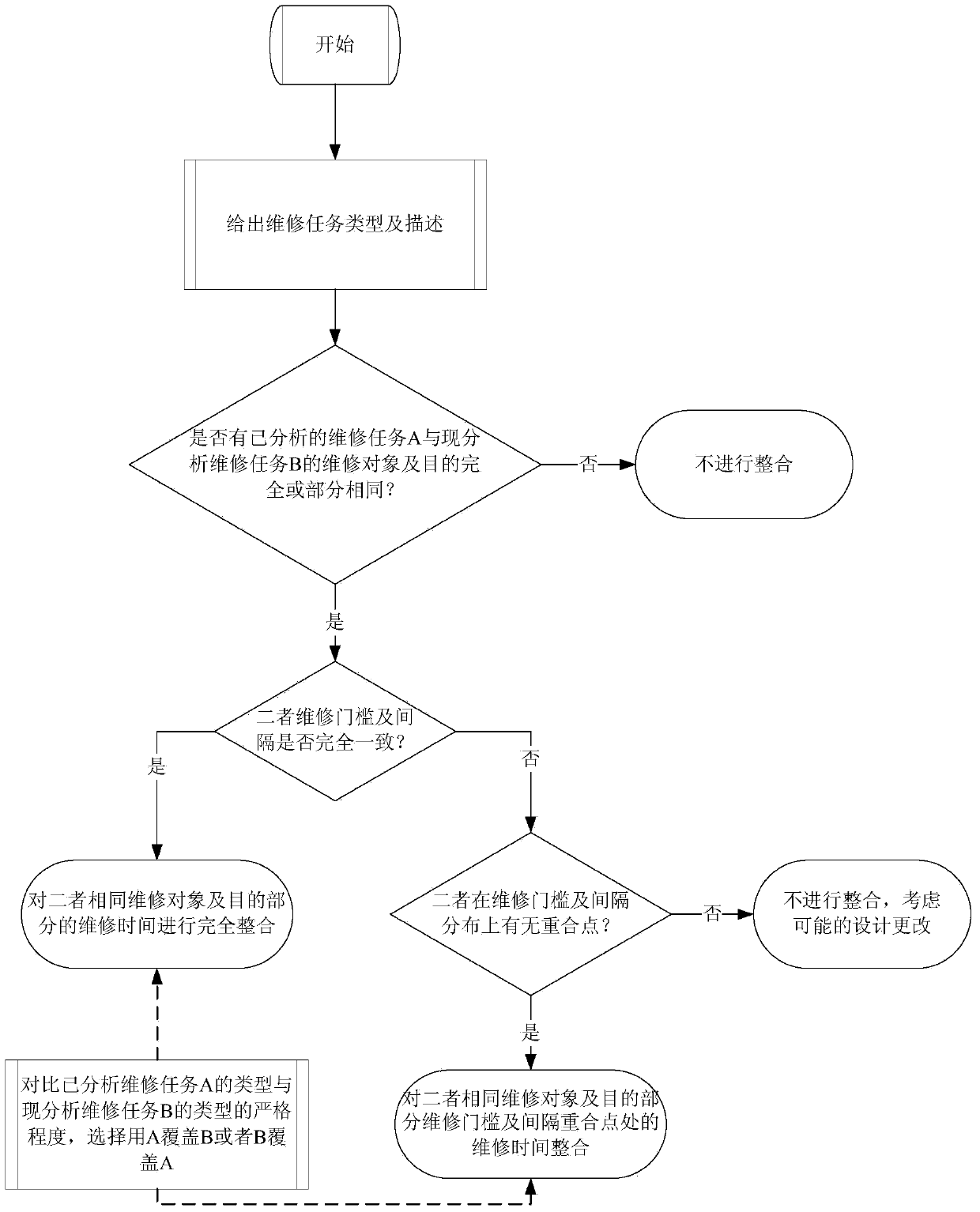
Calculation method for direct maintenance cost (DMC) of aircraft
A maintenance cost and calculation method technology, applied in the aviation field, can solve problems such as analysis and control problems that have not formed a mature set
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0232] Table 1 Example 1 - Proximity Time Integration
[0233]
[0234] according to image 3 , since the detailed visual inspection is more stringent than the general visual inspection, in actual operation, we can directly use the detailed visual inspection of DTA to cover the inspection requirements for cracks in the MSG-3 task (assumed to be 0.5 hours), by integrating We found that the total man-hours of maintenance tasks are: 0.5*2+1*4=5 hours, as shown in Table 2.
[0235] Table 2 Example 1 - Maintenance time integration
[0236]
[0237]
[0238] Step 3: Statistics and summation
[0239] After the integration of approach time and repair time, the sum of the actual direct repair costs of these two repair tasks is: C Str =60×[(1+3)×4+(0.5×2+1×4)] / 60000=0.021$ / FH. This value is 0.003$ / FH lower than before integration.
Embodiment 2
[0240] Example 2: This example estimates the unplanned maintenance cost of an aircraft under research due to a special event, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0241] Step 1: Determine the category of the calculation object
[0242] Through selection, the cost of unplanned maintenance of an aircraft under development due to a special event should belong to the "unplanned maintenance cost based on special events" in the "DMC estimate based on product design".
[0243] Collect input data as follows:
[0244] ·Average segment: 2 hours;
[0245] ·Special event type: bird strike;
[0246] · Labor hour rate: 60$ / FH;
[0247] Each maintenance man-hour is: 1 hour;
[0248] ·Special event probability: the probability of encountering bird strikes is 1.67×10 -8 / flight, and the distribution of bird strikes on various parts of the aircraft is: engine 21%, wing 19%, windshield 17%, radome 16%, fuselage 11%, landing gear 5%, and more than one part 11%;
[0249] ·Material cost: 5...
Embodiment 3
[0259] Embodiment 3: In this example, the maintenance cost of a single engine of an aircraft in service is calculated as follows, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0260] Step 1: Determine the category of the calculation object
[0261] Through selection, the cost incurred by the maintenance of a single engine of an in-service aircraft should belong to the "engine maintenance cost" in the "DMC calculation based on data collection".
[0262] Collect input data as follows:
[0263] ·Engine model: YYYxx-xx;
[0264] Reasons for maintenance: mechanical failure and oil leakage, etc.;
[0265] ·Maintenance method: workshop maintenance;
[0266] ·Send it for repair twice during the collection period;
[0267] · Maintenance times: 1st time;
[0268] ◇Labor cost: 20000$;
[0269] ◇Material cost (excluding time control): 40000$;
[0270] ◇Outsourcing repair cost: 60000$;
[0271] ◇Time control fee: 30000$;
[0272] ◇Time from last maintenance: 12000FH;
[0273] ·Mainten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com