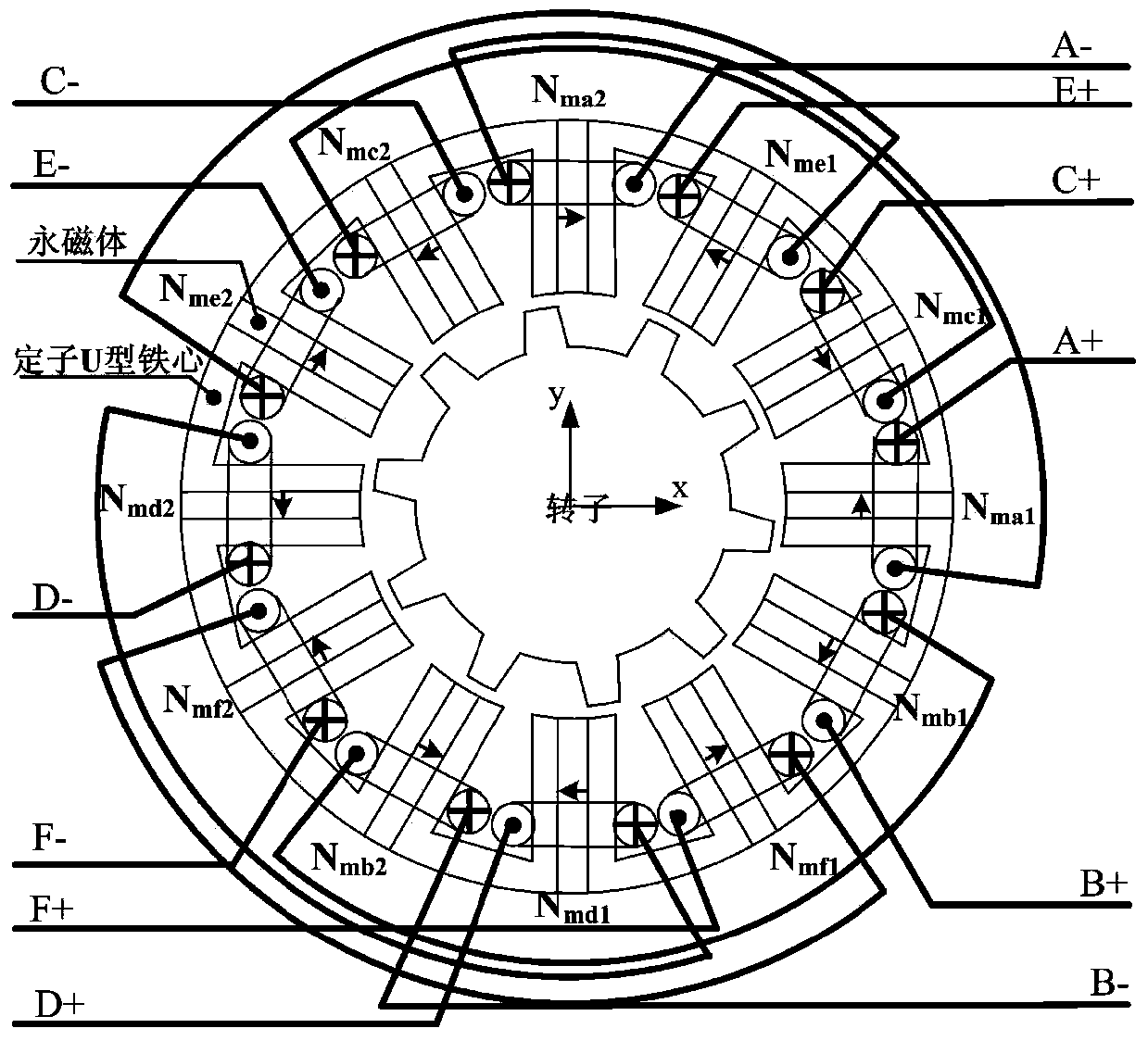
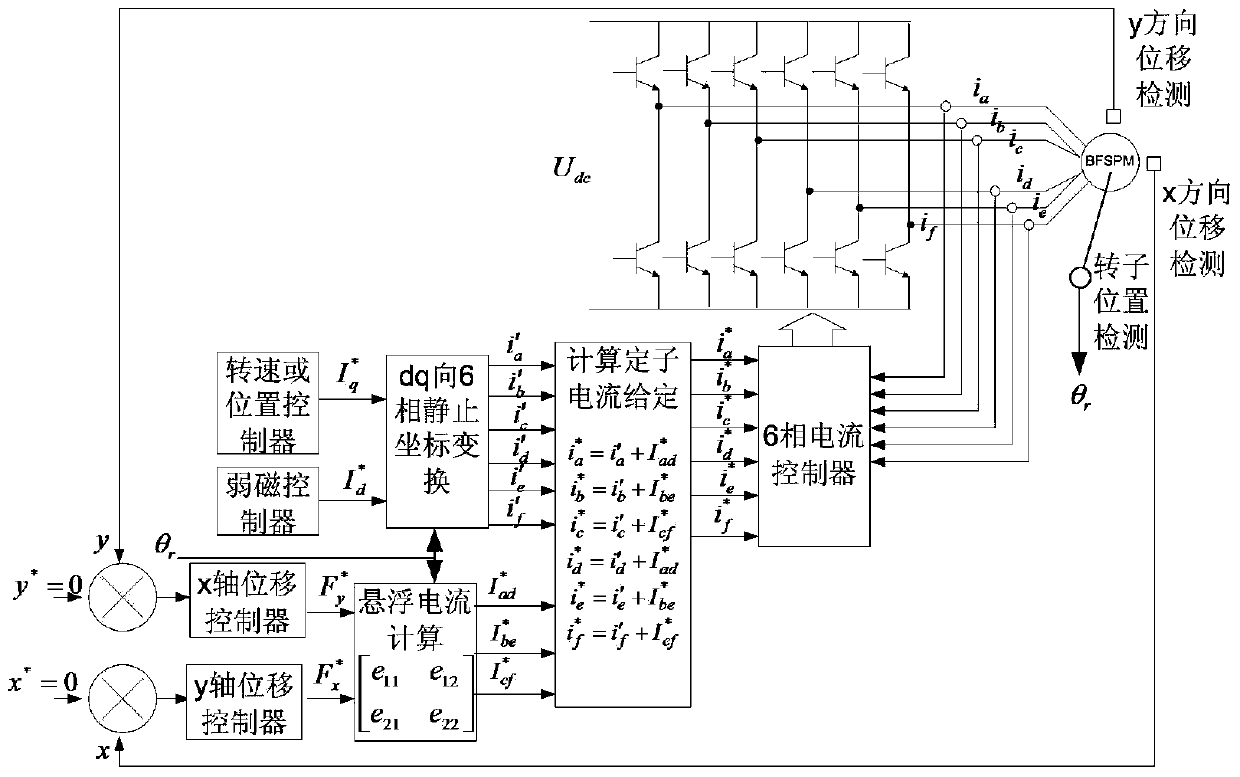
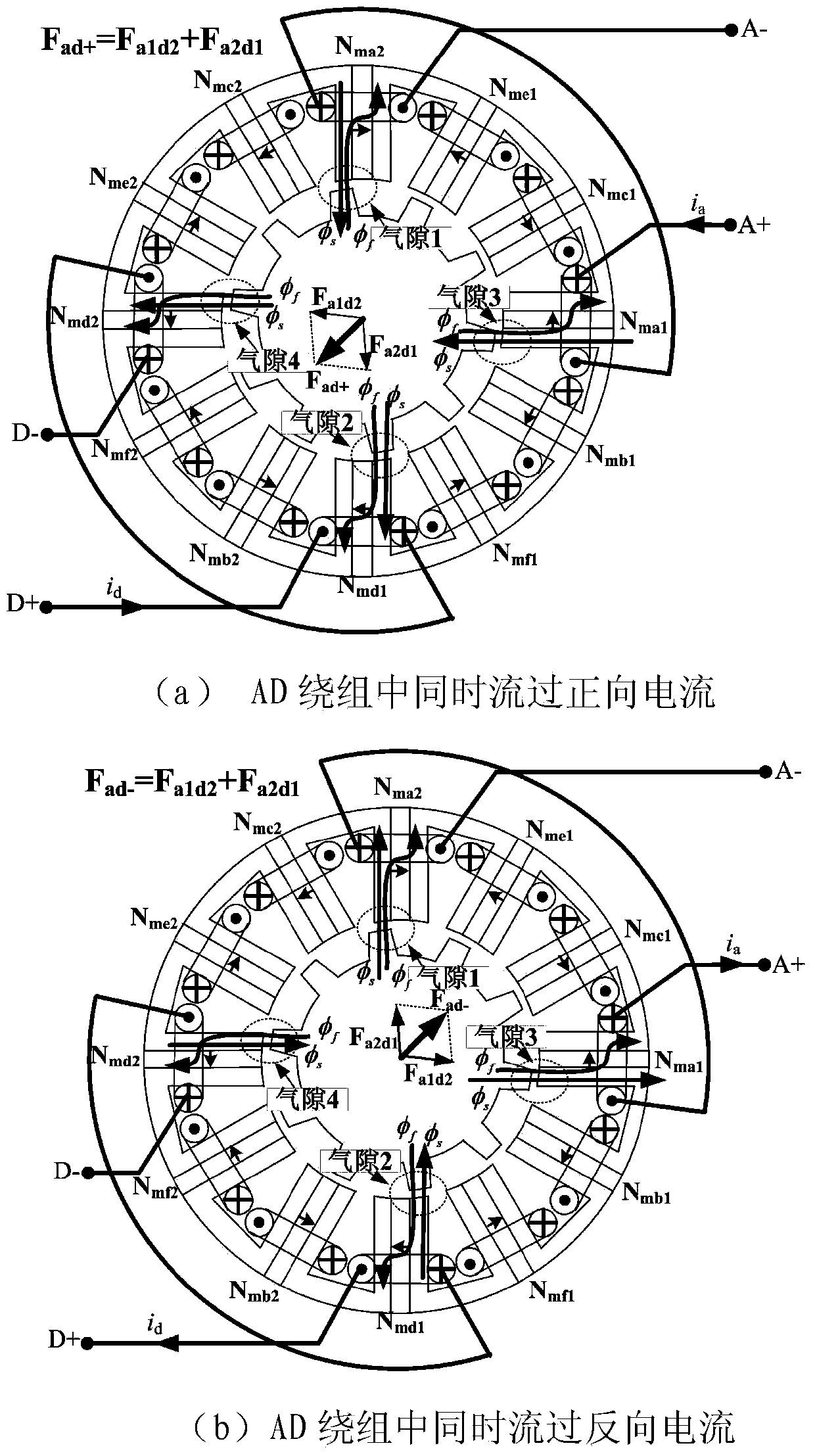
Rotor suspension control method for stator permanent magnet type bearingless synchronous motor
A synchronous motor and suspension control technology, applied in the field of electric motors, can solve the problems of difficult heat dissipation of rotor permanent magnets, pollution of mechanical bearings, complex rotor structure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] Certain terms are used, for example, in the description and claims to refer to particular components. Those skilled in the art should understand that hardware manufacturers may use different terms to refer to the same component. The specification and claims do not use the difference in name as a way to distinguish components, but use the difference in function of components as a criterion for distinguishing. As mentioned throughout the specification and claims, "comprising" is an open term, so it should be interpreted as "including but not limited to". "Approximately" means that within an acceptable error range, those skilled in the art can solve the technical problem within a certain error range and basically achieve the technical effect. In addition, the term "coupled" herein includes any direct and indirect electrical coupling means. Therefore, if it is described that a first device is coupled to a second device, it means that the first device may be directly elect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com