Starch microsphere slow-release fertilizer and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of slow-release fertilizers and starch microspheres, which is applied in application, fertilizer mixtures, fertilization devices, etc., can solve the problems of short fertilizer effect period, weak adsorption capacity, and accelerated soil acidification, so as to achieve prolonged slow-release effect, improved adsorption capacity, The effect of improving the adsorption speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
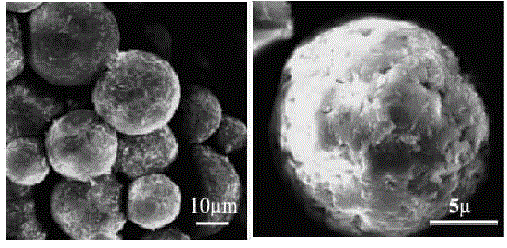
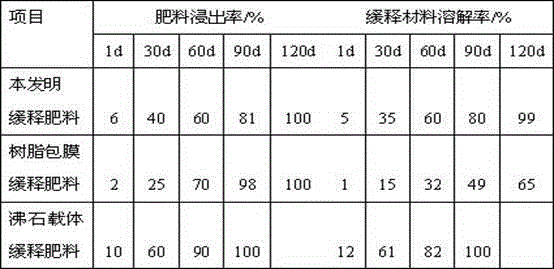
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
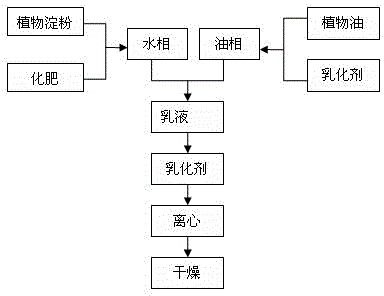
[0037] (1) Put 30 parts by weight of urea, 10 parts by weight of ammonium bicarbonate, 10 parts by weight of superphosphate, 10 parts by weight of potassium chloride, 5 parts by weight of trace element fertilizer, and 15 parts by weight of cornstarch into the In the stirred reactor, add 100 parts by weight of distilled water to mix and dissolve, heat at 70°C and stir at a stirring speed of 500r / min, react for 30min, cool to 50°C, and set aside;
[0038] (2) Measure 140 parts by weight of vegetable oil into a vertical emulsifier, add 0.5 parts by weight of emulsifier Span40, heat at 60°C and stir for 1 hour at a stirring speed of 500r / min to completely dissolve it;
[0039] (3) Add the starch solution obtained in step (1) dropwise to the system in step (2), disperse for 1 min at a stirring speed of 10000 r / min, so that the starch droplets are evenly dispersed in the oil phase, and add 0.5 parts by weight of Combined agent epichlorohydrin, stirred at a constant temperature of 50...
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Put 20 parts by weight of ammonium sulfate, 10 parts by weight of ammonium nitrate, 10 parts by weight of monoammonium phosphate, 10 parts by weight of diammonium phosphate, 10 parts by weight of potassium sulfate, and 20 parts by weight of tapioca starch into stirring In the mixer, add 120 parts by weight of distilled water to mix and dissolve, heat at 65°C and stir at a stirring speed of 500r / min, react for 40min, cool to 50°C, and set aside;
[0042] (2) Measure 150 parts by weight of cyclohexane into a vertical emulsifier, add 0.5 parts by weight of Span20 and 0.5 parts by weight of Span80, heat at 60°C and stir for 1.5 hours at a stirring speed of 500r / min to dissolve completely;
[0043] (3) Add the starch solution obtained in step (1) dropwise to the system of step (2), and disperse for 1.5 minutes at a stirring speed of 10000r / min, so that the starch droplets are evenly dispersed in the oil phase, and add 0.6 parts by weight of Cross-linking agent epichloro...
Embodiment 3
[0045] (1) 20 parts by weight of sodium nitrate, 10 parts by weight of ammonium nitrate, 20 parts by weight of superphosphate, 10 parts by weight of potassium chloride, 5 parts by weight of potassium monohydrogen phosphate, 15 parts by weight of wheat Starch was put into a stirred reactor, 120 parts by weight of distilled water was added to mix and dissolve, heated at 70°C and stirred at a stirring speed of 500r / min, reacted for 1h, cooled to 50°C, and set aside;
[0046] (2) Measure 140 parts by weight of liquid paraffin into the emulsifier at the bottom of the tank, add 0.5 parts by weight of Tween20 and 0.3 parts by weight of Tween60, heat at 60°C and stir for 2 hours at a stirring speed of 500r / min to completely dissolve it;
[0047] (3) Add the starch solution obtained in step (1) dropwise to the system of step (2), disperse for 2 minutes at a stirring speed of 10000r / min, so that the starch droplets are evenly dispersed in the oil phase, and add 0.8 parts by weight of Co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com