Functional group modified phase-change heat-storing ionic liquid
A functional group modification, ionic liquid technology, applied in heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of low heat storage density and low heat storage density of alkyl chain ionic liquids, and achieve thermal stability. high sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
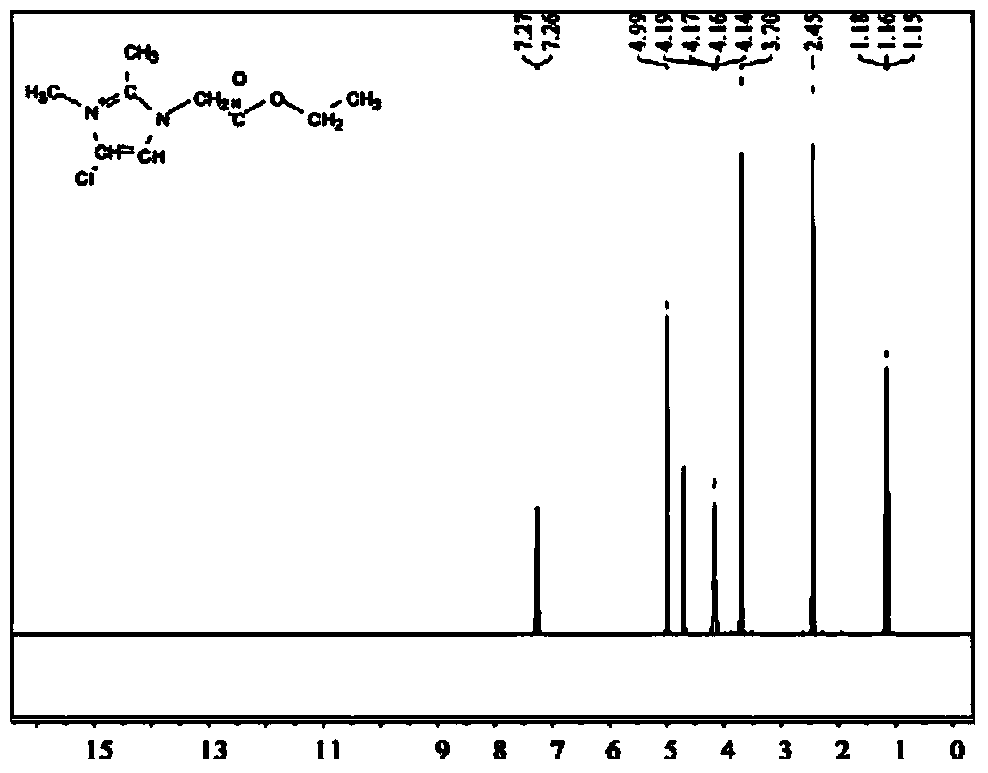
[0026] Add 1,2-dimethylimidazole and ethyl chloroacetate (molar ratio 1:1.2) into a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer and a thermometer. The upper part of the flask was refluxed with a condenser tube and nitrogen gas was passed into the three-necked flask through a nitrogen conduit for protection. The raw material was reacted at 70°C for 48 hours to obtain a pale yellow viscous liquid. Distilled under reduced pressure at 50°C, and then washed repeatedly with a small amount of ethyl acetate to remove residual reactants. Dry under vacuum at 70°C to remove the residual ethyl acetate from the previous step to obtain a white powdery solid 1,2-dimethyl-3-carboxyimidazole chloride, which forms a phase transition at a phase transition temperature of 161°C The heat is 105.02J / g ( Figure 15 ) of the ionic liquid, the upper limit of its use temperature is 204°C ( Figure 8 ).
Embodiment 2
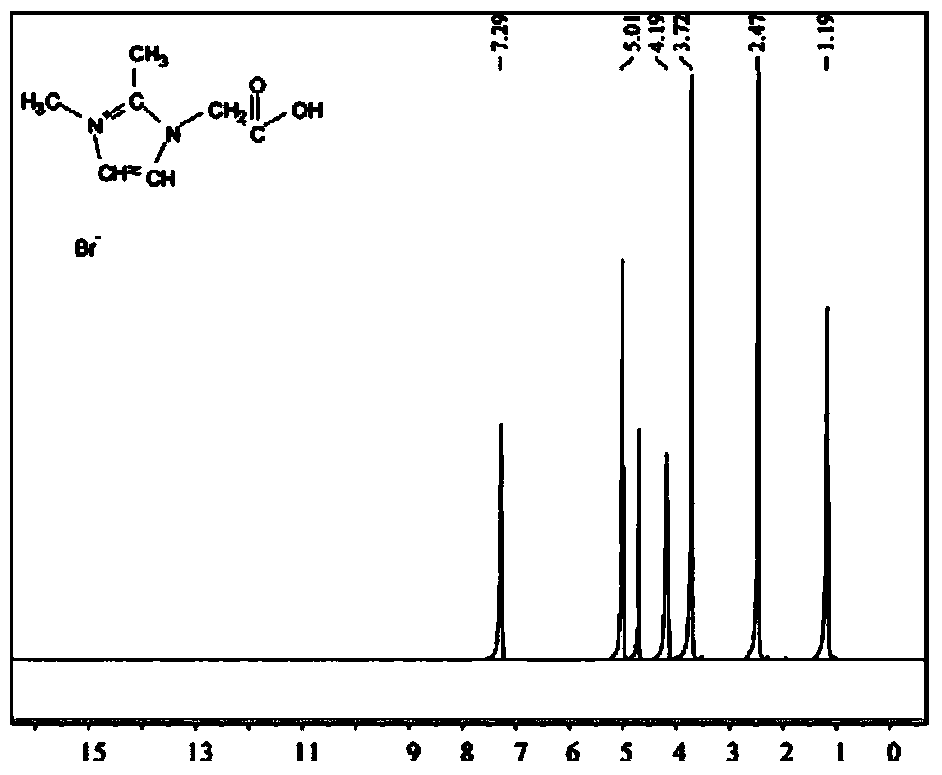
[0028] Add 1,2-dimethylimidazole and bromoacetic acid (molar ratio 1:1.2) and solvent ethyl acetate into a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer and a thermometer. The upper part of the flask was refluxed with a condenser tube and nitrogen gas was passed into the three-necked flask through a nitrogen conduit for protection. The raw material was reacted at 70°C for 48 hours to obtain a pale yellow viscous liquid. Vacuum filtration at 80°C for 2 hours, followed by repeated washing with a small amount of methyl ether to obtain a white powder. After vacuum drying at 70°C to remove the residual methyl ether, a white snowflake-like solid 1,2-dimethyl-3-carboxyimidazole bromide was obtained, and a phase change heat of 57.92J was formed at a phase transition temperature of 148°C / g( Figure 16 ) of the ionic liquid, its use temperature limit is 305 ℃ ( Figure 9 ).
Embodiment 3
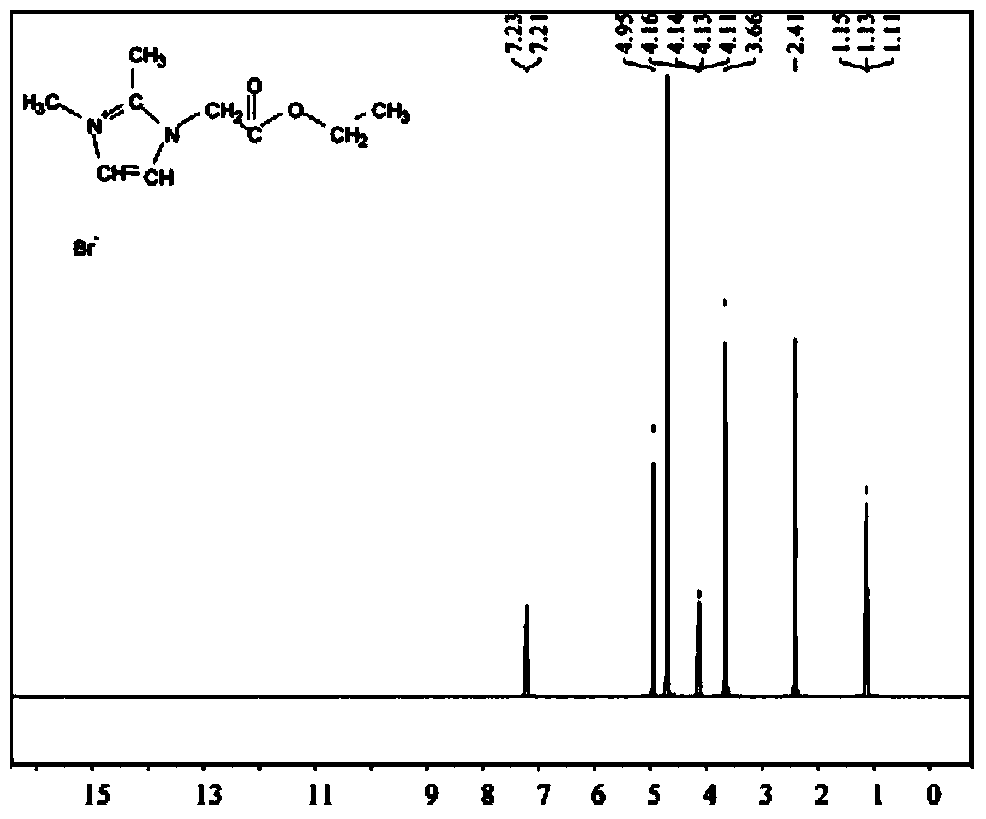
[0030] Add 1,2-dimethylimidazole and ethyl bromoacetate (molar ratio 1:1.2) into a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer and a thermometer. The upper part of the flask was refluxed with a condenser tube and nitrogen gas was passed into the three-necked flask through a nitrogen conduit for protection. The raw material was reacted at 70°C for 48 hours to obtain a pale yellow viscous liquid. Distilled under reduced pressure at 50°C, and then washed repeatedly with a small amount of ethyl acetate to remove residual reactants. Dry under vacuum at 70°C to remove the residual ethyl acetate from the previous step to obtain a white powdery solid 1,2-dimethyl-3-ester imidazole bromide, which forms a phase at a phase transition temperature of 150°C Heat up to 92.95J / g ( Figure 17 ) of the ionic liquid, the upper limit of its use temperature is 238°C ( Figure 10 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com