Peptide nucleic acid probe set for fluorescence in-situ hybridization detection of enterococcus faecalis and/or other enterococcocci, reagent kit, using method and applications
A fluorescence in situ hybridization, Enterococcus faecalis technology, applied in the detection field of clinically relevant microorganisms, can solve the problems of easy misjudgment, cumbersome steps, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieves increased penetration, high sensitivity, and high sensitivity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
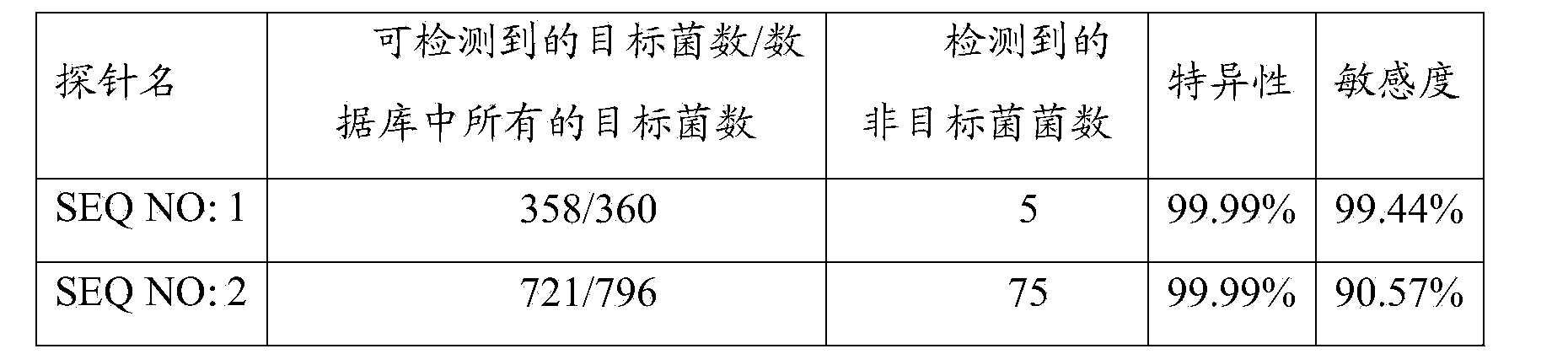
[0108] Example 1, PNA-FISH sensitivity verification
[0109] PNA probe:
[0110] Alexa488-O-TTA TCC CCC TCT GAT GGG (SEQ NO: 1)
[0111] Alexa546-O-TAC TGA TCG GCA GCT (SEQ NO: 2)
[0112] Sensitivity validation of different subspecies of Enterococcus faecalis and other enterococci.
[0113] The experimental procedure is described below.
[0114] bacterial strain
[0115] The bacterial strains were clinical isolates and reference strains obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). One drop of each strain culture was added to a glass slide and left to dry at 55°C.
[0116] fixed
[0117] To prevent loss during 16S rRNA hybridization, samples were immersed in 4% paraformaldehyde (wt / vol) and 50% ethanol (vol / vol) solutions for 10 minutes each.
[0118] hybridize
[0119] In this step, a drop containing 10% (wt / vol) dextran sulfate, 10mM NaCl, 50% (v / v) formamide, 0.1% (wt / vol) sodium pyrophosphate, 0.2% (wt / vol) A hybridization solution of polyvinylpyrrol...
Embodiment 2
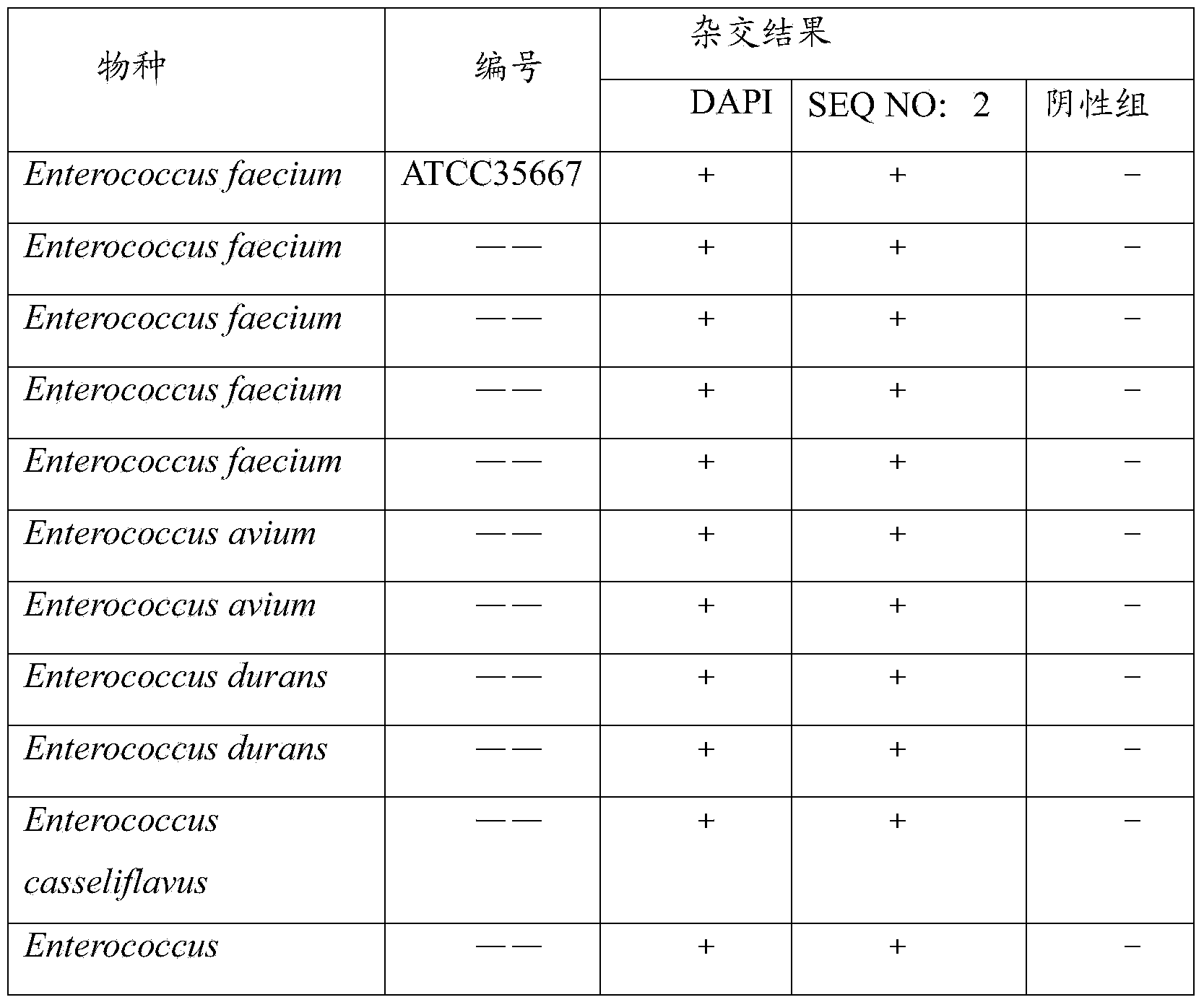
[0135] Example 2 PNA-FISH specific verification
[0136] Select Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium and other pathogenic bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii and other common pathogenic bacteria, the test procedure And method is described with embodiment 1.
[0137] The results showed that only the positive control (DAPI) could bind to all bacteria, while the probes SEQ NO: 1 and 2 could only bind to the target strain (Table 5). Consistent with the expected results, SEQ NO: 1 and 2 have good specificity.
[0138] Table 5 PNA probe specificity verification
[0139] species
[0140] Note: ——is isolated from hospitals, food, and the environment, without the description of the strain number.
Embodiment 3
[0141] Embodiment 3 drug susceptibility test
[0142] Select the quality control strain of Enterococcus number and different drug-sensitive Enterococcus faecalis and other Enterococcus bacterial strains isolated in hospital, food, environment to carry out drug susceptibility test, test procedure and method are as described in Example 1, each test At the same time, the K-B method was used as a positive control. The results are shown in Table 6.
[0143] The results show that the present invention can better detect the drug sensitivity of the target strain.
[0144] 1 Table 6 Enterococcus drug susceptibility test
[0145]
[0146] Note: A: fluorescence ratio method; B: K-B method; S: sensitive; I: intermediate; R: resistant
[0147] 2 The present invention uses PNA probe combined with in situ fluorescence hybridization (FISH) technology, compared with traditional biochemical identification, it does not need to extract DNA from bacteria, does not need cell membrane permeabi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com