In Vitro Countercurrent Regeneration of Ion Exchange Resin
An ion exchange resin, countercurrent regeneration technology, applied in ion exchange regeneration, ion exchange, ion exchange water/sewage treatment and other directions, can solve the problems of continuous water production, low water saving rate, high consumption of regeneration liquid, and achieve energy saving. Consumption and time, improve utilization, ensure the effect of water quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
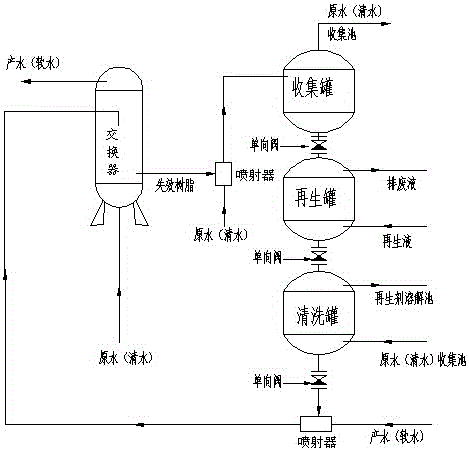
[0035] The extracorporeal countercurrent regeneration process of ion exchange resin is characterized in that: carry out according to the following steps:
[0036] A While producing soft water, continuously discharge the invalid resin from the lower part of the ion exchanger;
[0037] B. The expired resin is transported into the collection tank by spraying, the delivery liquid is discharged from the upper part of the collection tank, and the expired resin is discharged from the bottom of the collection tank and enters the regeneration tank;
[0038] C. Feed the regeneration liquid into the lower part of the regeneration tank, and the invalid resin is regenerated in countercurrent, and the regenerated resin is discharged from the bottom of the regeneration tank and enters the cleaning tank;
[0039] D Water is fed from the bottom of the cleaning tank, and the residual regeneration liquid on the regenerated resin is reversely cleaned. The cleaned regenerated resin is discharged f...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The extracorporeal countercurrent regeneration process of ion exchange resin is characterized in that: carry out according to the following steps:
[0042] A While producing soft water, continuously discharge the invalid resin from the lower part of the ion exchanger;
[0043] B. The expired resin is transported into the collection tank by spraying, the delivery liquid is discharged from the upper part of the collection tank, and the expired resin is discharged from the bottom of the collection tank and enters the regeneration tank;
[0044] C. Feed the regeneration liquid into the lower part of the regeneration tank, and the invalid resin is regenerated in countercurrent, and the regenerated resin is discharged from the bottom of the regeneration tank and enters the cleaning tank;
[0045] D Water is fed from the bottom of the cleaning tank, and the residual regeneration liquid on the regenerated resin is reversely cleaned. The cleaned regenerated resin is discharged f...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The extracorporeal countercurrent regeneration process of ion exchange resin is characterized in that: carry out according to the following steps:
[0051] A While producing soft water, continuously discharge the invalid resin from the lower part of the ion exchanger;
[0052] B. The expired resin is transported into the collection tank by spraying, the delivery liquid is discharged from the upper part of the collection tank, and the expired resin is discharged from the bottom of the collection tank and enters the regeneration tank;
[0053] C. Feed the regeneration liquid into the lower part of the regeneration tank, and the invalid resin is regenerated in countercurrent, and the regenerated resin is discharged from the bottom of the regeneration tank and enters the cleaning tank;
[0054] D Water is fed from the bottom of the cleaning tank, and the residual regeneration liquid on the regenerated resin is reversely cleaned. The cleaned regenerated resin is discharged f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com