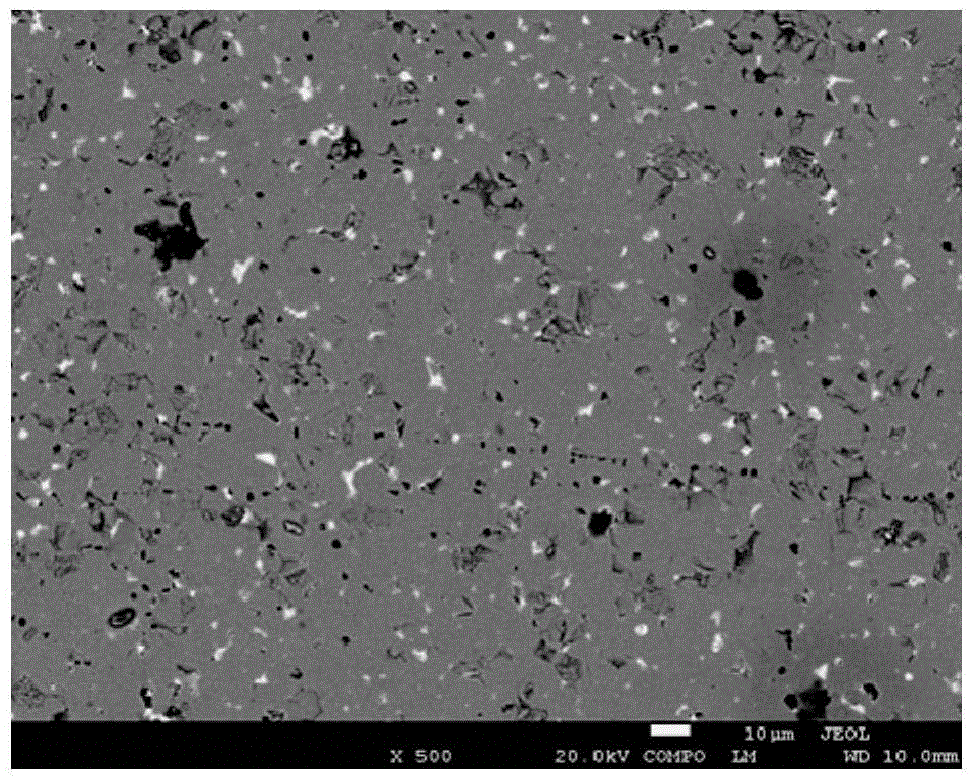
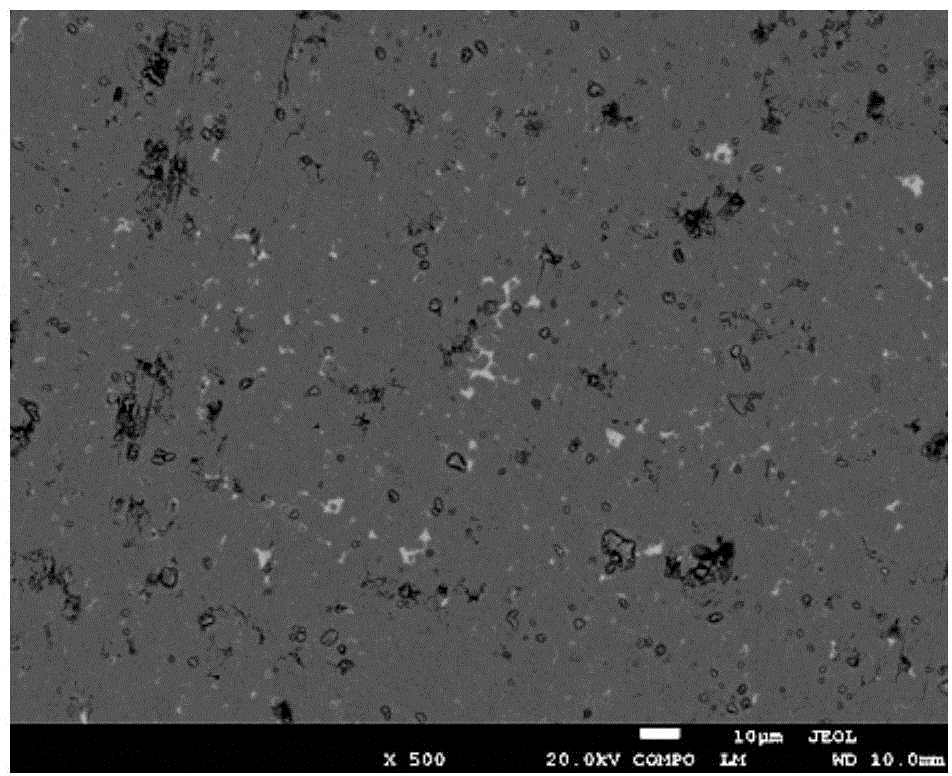
Heat treatment process for sintered nd-fe-b
A neodymium iron boron and heat treatment technology is applied in the field of heat treatment of metal materials, and can solve the problems of poor thermal stability, low coercivity and magnetic energy product, and poor magnetic properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Cut the N48 sintered NdFeB magnets produced by a magnet factory that have undergone primary tempering (tempering temperature is 900 ° C, time 2 hours) into cuboids of 20mm*20mm*12mm, and put them in a vacuum hot-press furnace. Raise the temperature in a vacuum hot pressing furnace with a heating rate of 10°C / min and a vacuum of 5×10 -3 Pa, when the temperature reaches 750°C, pressurize to 40MPa, and the pressure is loaded on the magnet for an instant, and the temperature is maintained for 1h. Cool to room temperature under this vacuum after completion. Then carry out three-stage tempering, the temperature is 550 ℃, the vacuum degree is 5×10 -3 Pa, the heating rate is 10°C / min, the holding time is 1h, the sample is cooled to room temperature under the vacuum degree, and the sample is taken out.
[0032] Table 1. Performance analysis before and after treatment
[0033]
Embodiment 2
[0035] Cut the N48 sintered NdFeB magnets produced by a magnet factory that have undergone primary tempering (tempering temperature is 900 ° C, time 2 hours) into cuboids of 20mm*20mm*12mm, and put them in a vacuum hot-press furnace. Raise the temperature in a vacuum hot pressing furnace with a heating rate of 10°C / min and a vacuum of 5×10 -3 Pa, when the temperature reaches 650°C, pressurize 20MPa, the pressure is loaded on the magnet for an instant, and keep the pressure for 1h. Cool to room temperature under this vacuum after completion. Then carry out three-stage tempering, the temperature is 550 ℃, the vacuum degree is 5×10 -3 Pa, the heating rate is 10°C / min, keep warm for 1h, cool the sample to room temperature under the vacuum degree, and take out the sample.
[0036] Table 2. Performance analysis before and after treatment
[0037]
[0038] As can be seen from Table 1 and Table 2, the magnet obtained after heat treatment using the method of the present invention...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com