Shape sensing devices for real-time mechanical function assessment of an internal organ
An organ and mechanical technology, applied in the field of interventional procedures with minimally invasive real-time functional organ assessment, can solve problems such as difficulties in motion and function estimation, low signal-to-noise ratio, and limited field of view.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
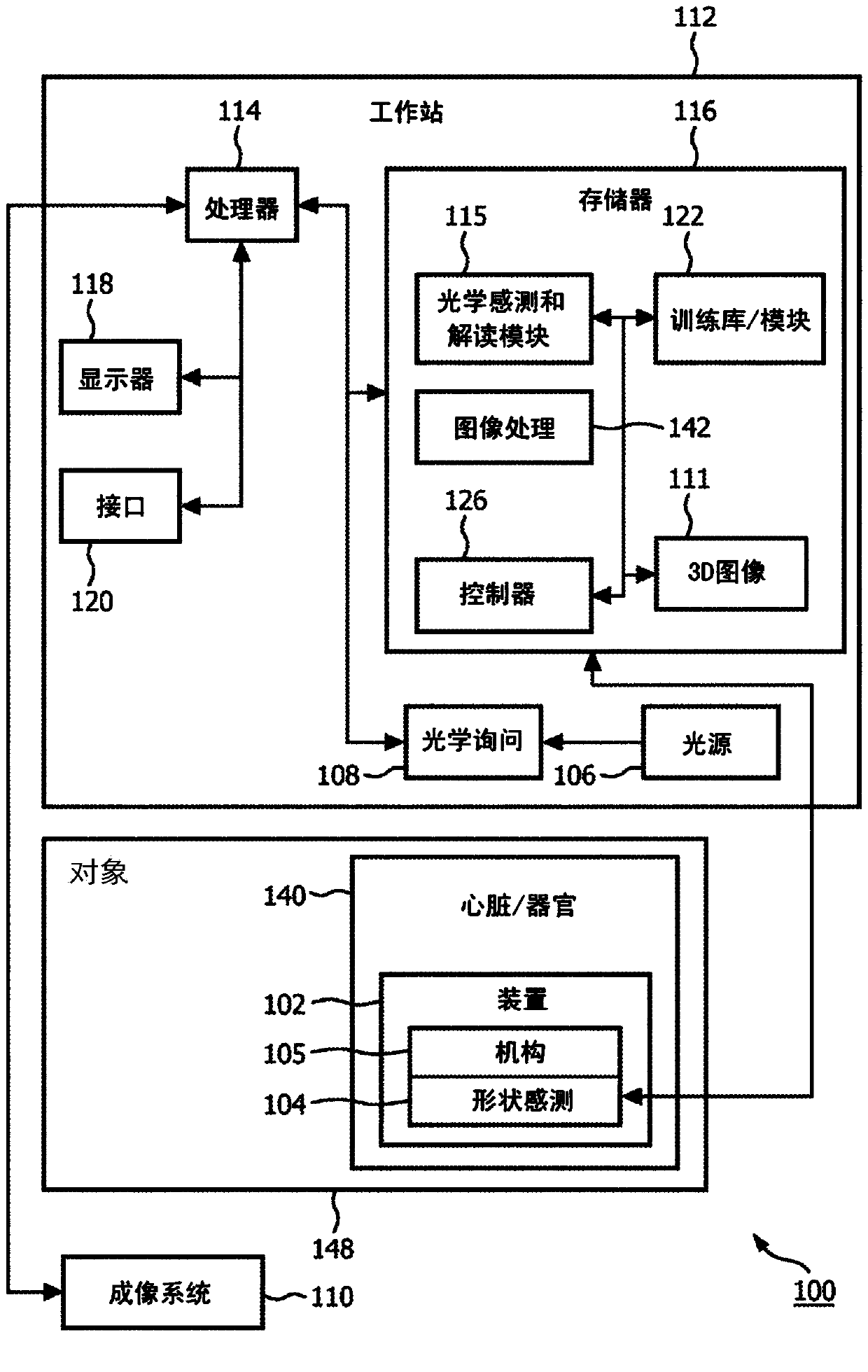
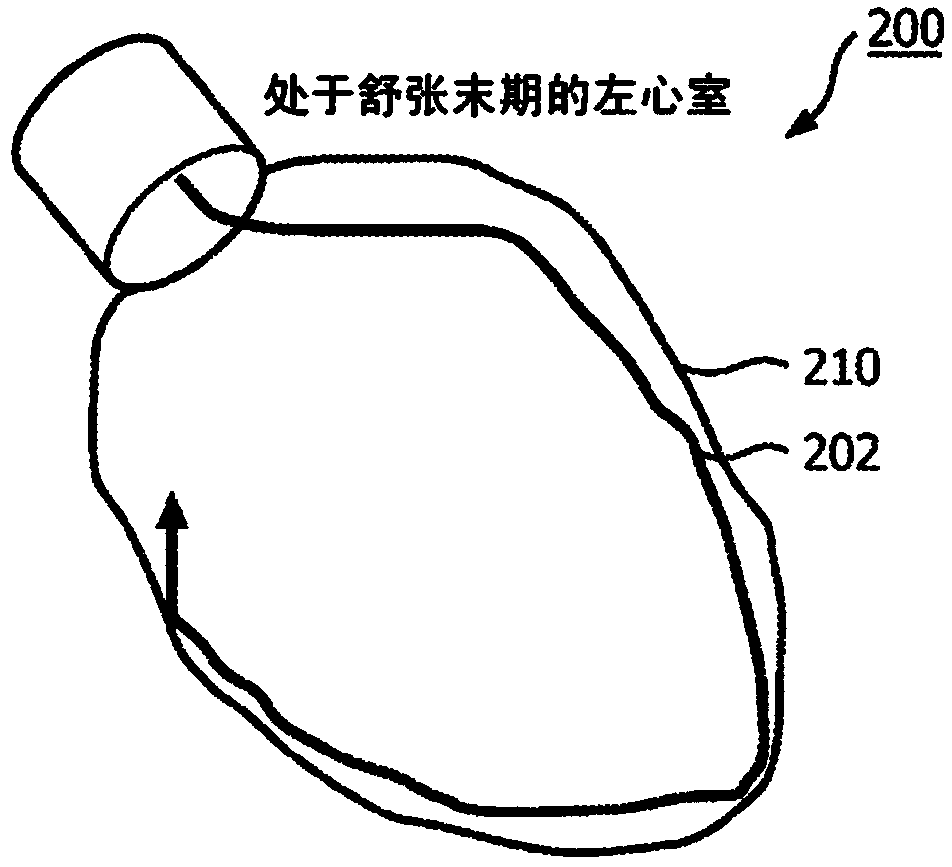
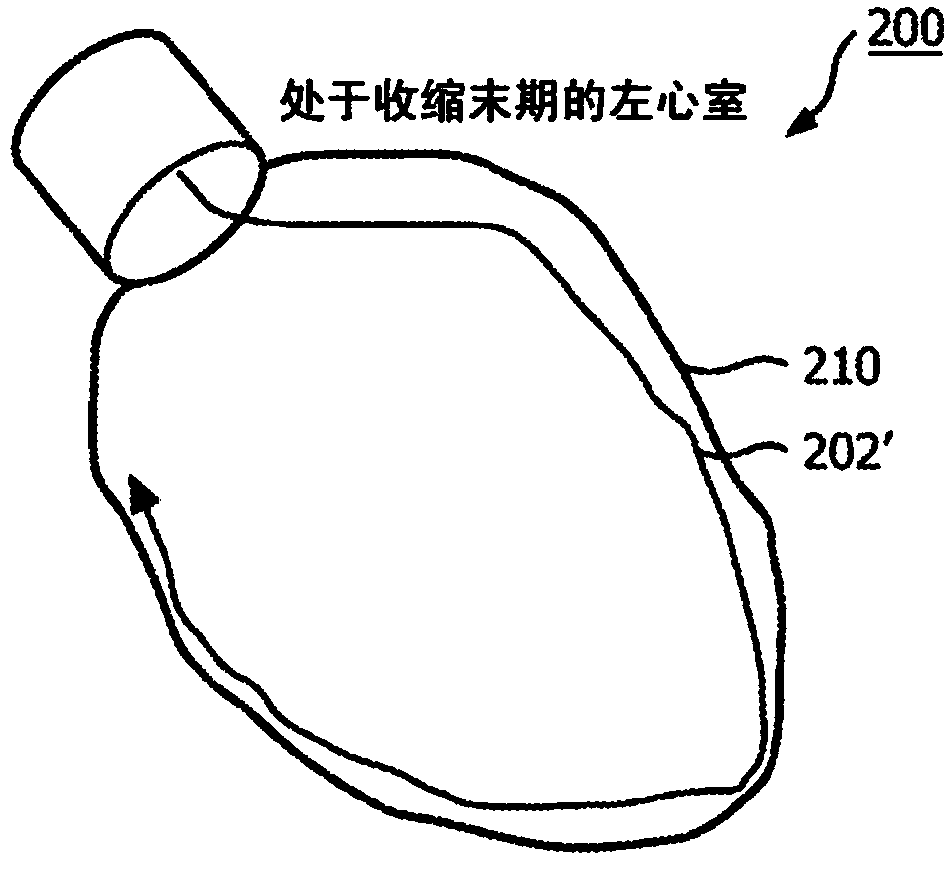
[0015] According to the present principles, continuous spatial and temporal measurement of boundaries allows real-time mechanical function assessment of the heart and verification of the success of cardiac interventional procedures such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). In one embodiment, optical shape sensing enabled flexible devices (eg, catheters, guidewires, leads, etc.) are included to perform continuous real-time motion and function assessment of the heart or other organs. In accordance with present principles, embodiments can provide information such as, by direct interrogation of motion providing mechanical asynchrony or other phenomena, by indirect estimates of myocardial viability and cardiac output derived from motion characteristics measured during an interventional procedure. In addition to discrete optical sensors, the present principles provide spatially and temporally continuous sensing of distribution parameters along known three-dimensional (3D) path...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com