Strain for producing alginate lyase and use thereof
A technology of alginate lysing enzyme and bacterial strain, which is applied in the field of marine biology, can solve the problems of poor hydrolysis effect of alginate, achieve remarkable fermentation effect, reduce production cost, and simple ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Screening and Identification of Example 1 Bacterial Strains
[0035] 1. Screening of enzyme-producing strains
[0036] The present invention uses the ground sea urchin intestinal tract to screen the production strain of alginate lyase, dilutes the ground sample of sea urchin intestinal tract, and then cultures it in the screening medium with sodium alginate as the only carbon source. The strains surviving in the base were used for the fermentative production of alginate lyase, and the strains were identified and stored frozen in glycerol tubes. Specific steps are as follows:
[0037] Dilute the ground sea urchin intestine samples in multiple ratios, spread them on the selection medium with sodium alginate as the only carbon source, and culture them at 25°C to 30°C for 1 to 7 days. Select the ones that can grow under these conditions Colonies, the obtained fermentation strains were selected and the one with the highest enzyme activity was identified as Halomonas sp. by...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Experimental determination of the optimum living conditions for fermenting alginate lyase on the bacterial strain SH-19 obtained by screening:
[0059] 1) The selection and determination experiment of the carbon source in the fermentation medium:
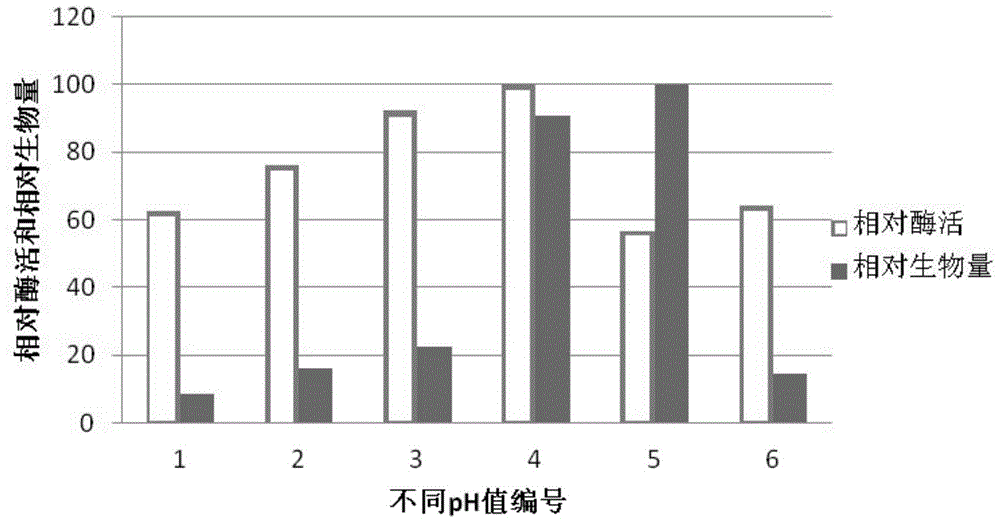
[0060] First, five experimental groups were set up, in which, except for the carbon source, the fermentation medium was fermented under the conditions that the nitrogen source was ammonium sulfate, the pH value was 6.5, the mass percent concentration of NaCl was 3%, and the temperature was 30°C. The carbon source is respectively glucose, sucrose, starch, sodium alginate or xylose with a concentration of 0.5% by mass.
[0061] After the above-mentioned five experimental groups were fermented and cultured, the enzyme activity of the fermentation liquid of each experimental group was measured respectively, and the influence of different carbon sources on the enzyme production was tested. Such as figure 2 As shown, t...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The method for producing alginate lyase by the bacterial strain producing alginate lyase described in embodiment 3 comprises the following steps:
[0071] 1) Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate the screened strain SH-19 on the seed medium, ferment at 26-30°C for 24-48 hours to reach the logarithmic growth phase, stop the fermentation, and obtain the seed liquid;
[0072] 2) Large-scale propagation of bacterial strains: after the seed liquid is inoculated in a primary fermentation medium, the primary fermentation medium is continuously fermented for 36 to 60 hours at a pH of 4.5 to 9.5 and a temperature of 26 to 30°C, Thereby, described bacterial strain carries out mass propagation, provides condition for later stage alginate lyase;
[0073] 3) Inducing a large amount of alginate lyase to synthesize: after the large-scale propagation of the bacterial strain SH-19, add sodium alginate and 1-3% sodium alginate and 1-3% chloride to the primary fermentation medium Sodium ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com