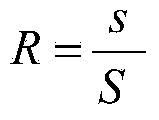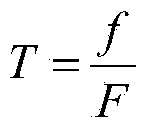Complex supply network robust performance analyzing method based on topological structure
A topology and analysis method technology, applied in data processing applications, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as lack of in-depth analysis of structures, failure to consider the diversity of node roles, and ignore the locality of node selection ranges to achieve accurate The effect of robust performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Random failure within the enterprise: When a node in the supply chain has a severe random failure and causes the node to fail completely, the node can be considered to be removed from the network. Similar to scale-free networks, supply chains exhibit strong robustness to internal random failures. When 20% of the nodes are deleted, the supply chain model can still have high robust performance, R≈0.75, T≈0.5. With the increase of the number of deleted nodes, R and T show a gradually decreasing trend, and the number of deleted nodes has an approximately linear relationship with R and T. This situation occurs due to the existence of a large number of nodes with little connectivity in the supply chain. The deletion of these nodes has little impact on the connectivity of the network and the efficiency of the network. That is, the heterogeneity of the supply network connections leads to its strong robustness against internal random failures.
Embodiment 2
[0060] External random faults of the enterprise: The heterogeneity of connections between supply chain nodes not only leads to its high robustness to internal random faults, but also makes it more resistant to external random faults. When 80% of the connection edges are deleted, its robustness index can still have a high value, R≈0.85, T≈0.3. Compared with internal random faults, the reason why the supply chain shows higher robustness to external random faults is that there are certain redundant connections in the supply chain, and deleting these connections will not lead to less robust performance of the network. big change. However, R and T also have certain differences in external random faults, and the random deletion of connection edges has a greater impact on T. This is because although the random deletion of connection edges in the network has less impact on the connectivity of the network, it leads to a greater change in the efficiency of the network. The supply chai...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Artificial attacks on internal nodes: against attacks on internal nodes, the supply chain shows great vulnerability. Due to the heterogeneity of supply chain node connections. Making a very small number of nodes with high connectivity has an extremely important impact on network connectivity and network efficiency. When these nodes fail due to artificial attacks, the robustness of the supply chain drops sharply. When 15% of the nodes with high connectivity in the supply chain are deleted, the connectivity and efficiency of the supply chain drop to zero, R≈0, T≈0. This also explains from one aspect why in the actual supply chain, a few core enterprises play an irreplaceable role in the normal operation of the entire supply network. A human-made attack on a core enterprise can easily paralyze the entire supply chain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com