Magnetic resonance imaging K space movement artifact correction parallel acquisition reconstruction method
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and motion artifacts, which is applied in the directions of magnetic resonance measurement, magnetic variable measurement, and magnetic variable measurement to achieve the effect of improving acquisition speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
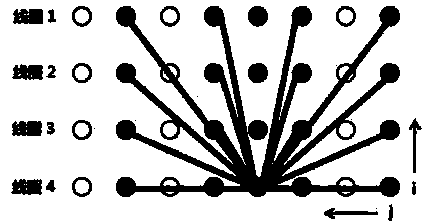
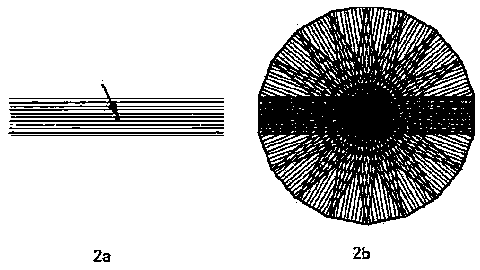
[0049] Put the human tissue (object) that needs MRI into the MRI system, collect the K-space in multiple leaves to obtain the leaf-shaped K-space data subset (such as image 3 shown), each subset of K-space data is obtained in an under-sampling manner, thereby speeding up data acquisition, where, image 3 It is a single leaf collection method, the solid line represents the collected data, and the dotted line represents the undersampled data (the part that needs to be filled by calculation). Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the collection and reconstruction grouping of this scheme, Figure 4 In , two boxes with solid lines are one group (thick solid line plus thin solid line), and two boxes with dashed lines are another group. The area surrounded by solid lines represents a leaf-shaped subset of K-space data. In the scheme presented in this paper, the coil merge coefficient computer data padding process occurs within the group.
[0050] For the convenience of illustration, it ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] If the two blades do not meet the vertical relationship, the blade calculated as the coefficient will be transformed into the grid point under the Cartesian coordinate system of the target blade as follows: Figure 7 situation shown.
[0058] Figure 7 a is the relationship between the two blades, Figure 7 b is an illustration considering the gray dotted leaf alone. In this case, since the gray leaf points still have continuous distribution points in the x direction, use Image 6 The window shown in a, extract this part of data, and calculate the combination coefficient.
[0059] In order to make the relationship of the inter-calibration data leaves as vertical as possible, after the first leaf is collected, the phase encoding and frequency encoding gradients are exchanged, and the other leaf (such as image 3 b First collect the solid thin line, then collect the solid thick line, one group is completed; then collect the virtual thin line, then the virtual thick li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com