Method for separating heterotrophic ammonia-oxidizing microorganism from oligotrophic aquatic sediment
A technology for ammonia oxidizing microorganisms and nutrient-poor water bodies, which is applied in the field of environmental protection and can solve problems such as underestimation of microbial functions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
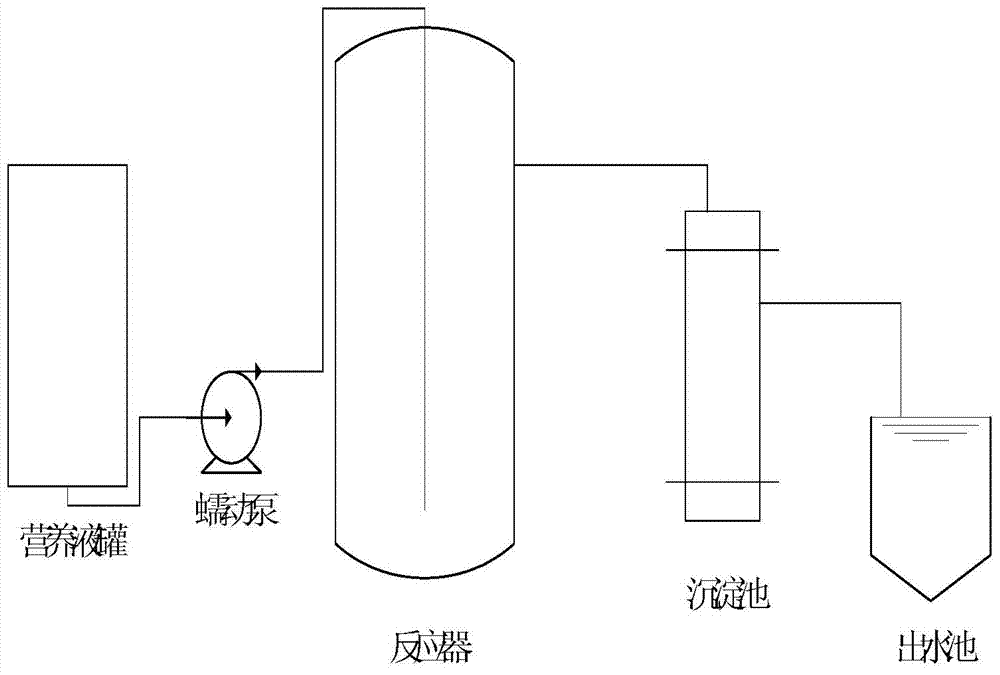
[0024] (1) Take 100g of sediment on the surface (5-10cm) of the bottom sediment of Xinfeng River in Heyuan, after conventional isolation, removal of sand and sedimentation, pre-aerate for 5 minutes, and put it into the sequence batch according to the mass ratio of mud to water at 1:1 In the first stage of the reactor, M0 liquid medium was added for enrichment, and the reactor was cultivated for 2 weeks. The residence time of the reactor in the first stage was 3-4 days. Enrichment of ammonia oxidizing microorganisms; 2. Screening of non-oligotrophic ammonia oxidizing microorganisms, the structure of the domestication device (sequencing batch reactor) is as follows figure 1 As shown, the culture temperature is 25°C, adjusted with sodium bicarbonate to maintain the pH between 6-7, without aeration, observe the clarification of the medium in the first stage of cultivation, and transfer to the second stage of cultivation after the sediment is flocculent. Gradually replace the M1 li...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Take 300g of the bottom sediment surface (4-8cm) of the Dongjiang section of Heyuan, after conventional isolation and sedimentation, pre-aerate for 5 minutes, and put it into the sequencing batch reactor according to the mass ratio of mud to water at 1:1 for enrichment Set, add M0 liquid medium in the first stage of the reactor, and cultivate for 4 weeks. The residence time of the reactor in the first stage is 3 days. The culture medium was observed to be clarified in the first stage, and the sediment was flocculent and transferred to the second stage for cultivation. Then gradually replace the M1 liquid medium for batch culture. Cultivate for 6 weeks, the residence time of the second stage is 5-7 days, the culture temperature is 20°C, the pH is adjusted to be between 7-8 with sodium bicarbonate, no aeration is required, and the pre-culture solution containing domesticated flora is obtained through cultivation.
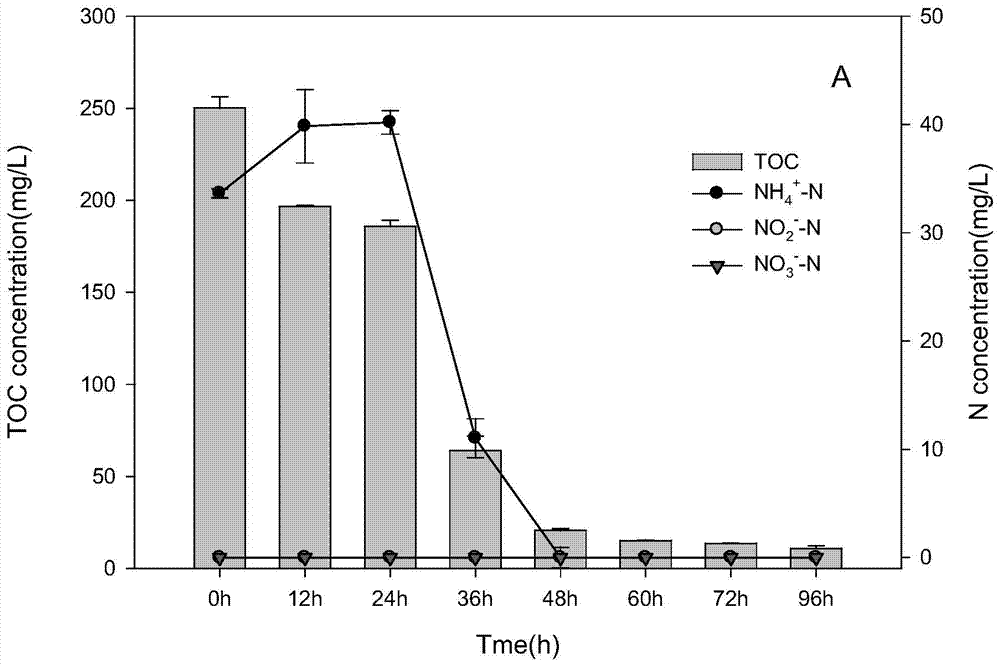
[0036] (2) Take 20ml of the bacteria solution from t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com