Hydrocracking method for catalytic cracking diesel
A catalytic cracking diesel and hydrocracking technology, applied in the field of hydrocarbon oil cracking, can solve the problems of little change in diesel density, limited improvement of cetane number, low octane number of naphtha fractions, etc. Alkane number, improvement of hydrocarbon composition, effect of high cetane number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
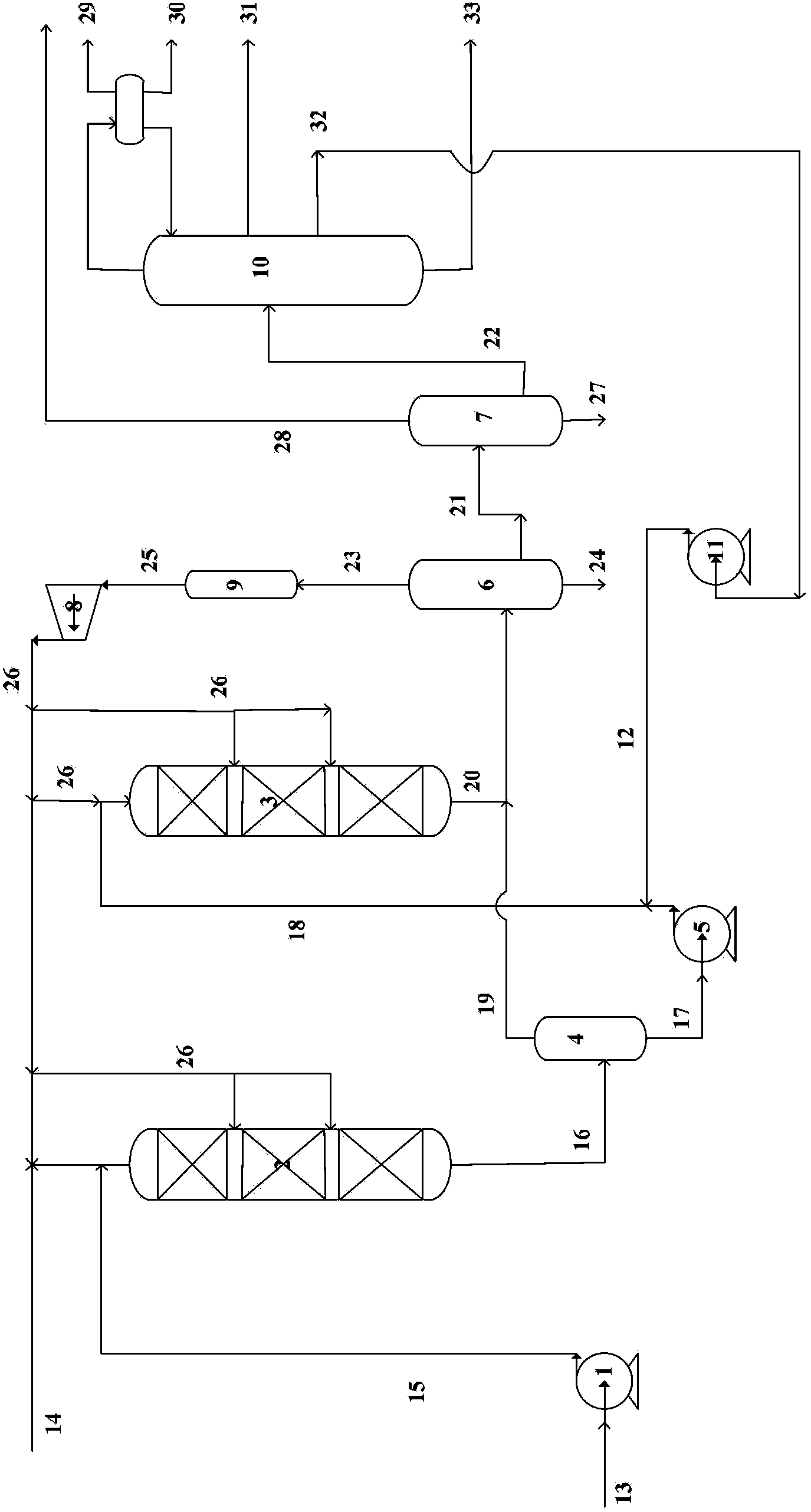
[0050] The raw material oil F enters the first reaction zone together with hydrogen, and reacts with the hydrofining catalyst A, and the reaction effluent from the first reaction zone enters the middle high-pressure stripping tower, and hydrogen sulfide and NH are removed by stripping 3 Finally, the liquid product is mixed with the refractory fraction from the fractionation part, and then enters the second reaction zone to contact and react with the hydrocracking catalyst D. The effluent after the reaction is cooled, separated and fractionated to obtain light naphtha fraction, gasoline fraction, recycle fraction and diesel fraction. The refined fraction is a narrow fraction at 200°C to 240°C, in which the total aromatic content of the refined fraction is 75.6% by mass, and the content of single-ring aromatics is 71% by mass. This part of the narrow fraction is all smelted back to the inlet of the second reaction zone. The reaction conditions are shown in Table 2, and the prod...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The raw material oil G enters the first reaction zone together with hydrogen, and contacts and reacts with the hydrotreating catalyst B, and the reaction effluent from the first reaction zone enters the second reaction zone to contact and react with the hydrocracking catalyst D without any intermediate separation. The effluent after the reaction is cooled, separated and fractionated to obtain light naphtha fraction, gasoline fraction, recycle fraction and diesel fraction. Among them, the refractory fraction is a narrow fraction at 200°C to 250°C, in which the total aromatics content of the refractory fraction is 82 mass%, and the single-ring aromatics content is 77 mass%, and this part of the narrow fraction is returned to the entrance of the second reaction zone, and the The effluent from one reaction zone is mixed and then passed to the second reaction zone. The reaction conditions are shown in Table 2, and the product properties are shown in Table 3.
[0054] It can...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The raw material oil G enters the first reaction zone together with hydrogen, and contacts and reacts with the hydrotreating catalyst C, and the reaction effluent from the first reaction zone enters the second reaction zone to contact and react with the hydrocracking catalyst D without any intermediate separation. The effluent after the reaction is cooled, separated and fractionated to obtain light naphtha fraction, gasoline fraction, recycle fraction and diesel fraction. Among them, the refined fraction is a narrow fraction at 200°C to 260°C, wherein the total aromatic content of the refined fraction is 78% by mass, and the content of single-ring aromatics is 72% by mass. And this part of the narrow fraction is returned to the inlet of the second reaction zone, mixed with the effluent of the first reaction zone, and then enters the second reaction zone. The reaction conditions are shown in Table 2, and the product properties are shown in Table 3.
[0057] It can be se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com