Anti-nerve growth factor antibodies and methods of preparing and using the same
一种抗体、供体的技术,应用在抗生长因子免疫球蛋白、化学仪器和方法、神经系统疾病等方向,能够解决抗原结合亲和性与亲合力降低等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0234] Example 1 - Production of Antibodies
[0235] Complete antibody sequences were generated by combining the equinized light chain variable domain sequences and heavy chain variable domain sequences of SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 with a C-terminal equine constant heavy chain or constant light chain, respectively . The equinized αD11 VH domain was combined with two different equine heavy chain constant domains, HC2 (IgG2) and HC6 (IgG6); and the equinized αD11 VL domain was combined with the equine kappa light chain constant domain. The sequences of the full-length mature antibody chains are shown in SEQ ID No: 4 (light chain with kappa constant domain) and SEQ ID No: 6 (heavy chain with HC2 constant domain).
Embodiment 2
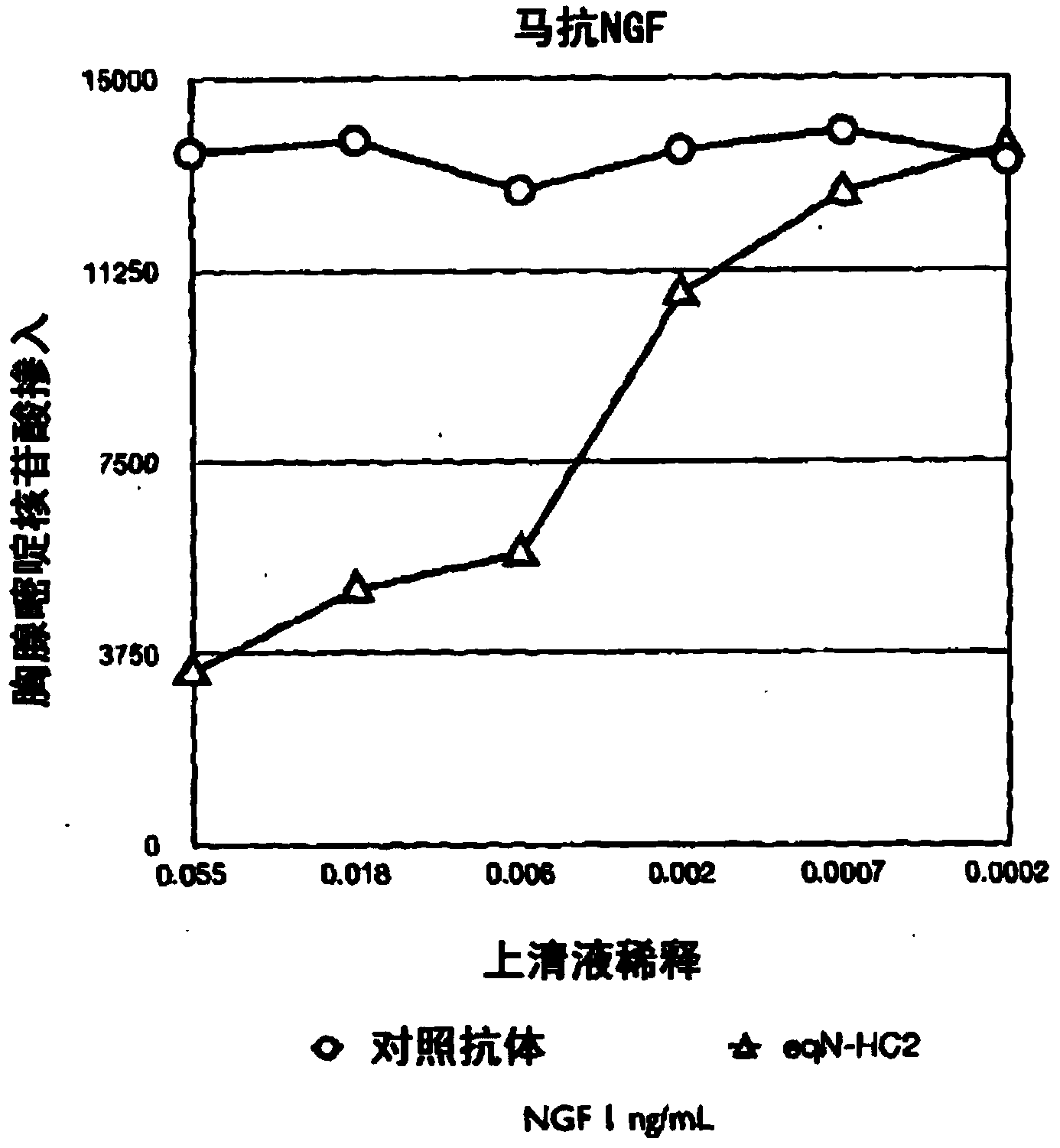
[0237] Example 2 - Determination of Antibody Binding to Murine NGF and Horse NGF
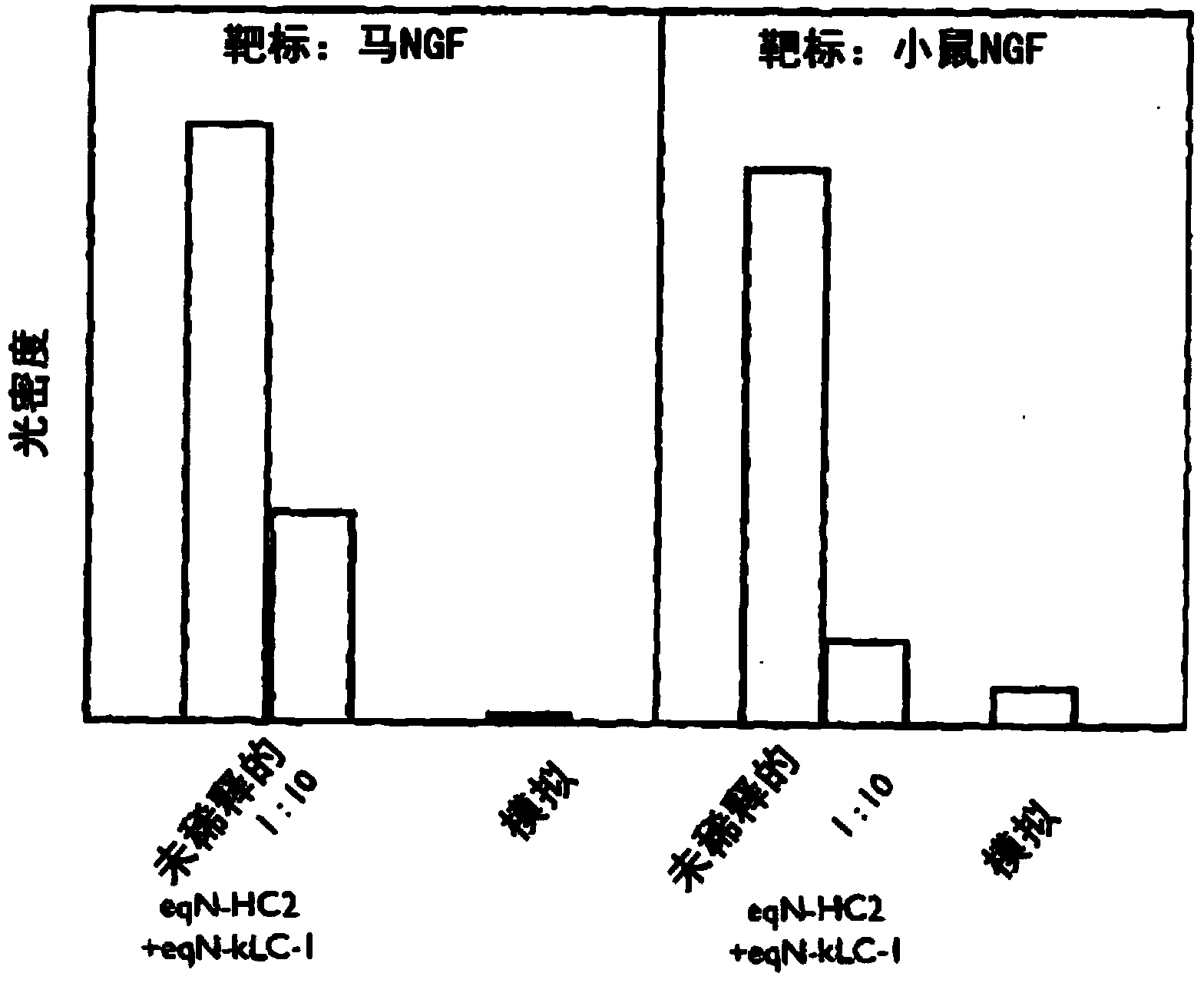
[0238] The equinized heavy chain cDNA and light chain cDNA were transfected into CHO cells, and the supernatant was collected and reacted with equine NGF or mouse NGF in ELISA format. After incubation and washing steps, bound horse antibodies were detected by the reactivity of a goat-anti-horse IgG-specific polyclonal antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and visualized using TMB. The optical density of the resulting product was measured at 450 nm and compared with the supernatant from mock blank vector transfection ( figure 1 Denoted as "Mock (Mock)" in the optical density) for comparison.
[0239] figure 1 The graph in the figure shows the result. Binding of HC2 (HC2 constant domain) equinized antibody (designated eqN-HC2+eqN-kLC-1 ) to mouse NGF is shown. In the second part of the graph, the binding of the eqN-HC2+eqN-kLC-1 antibody comprising the eqN-KlC-1 light chain and...
Embodiment 3
[0240] Example 3 - Purification of equinized antibodies
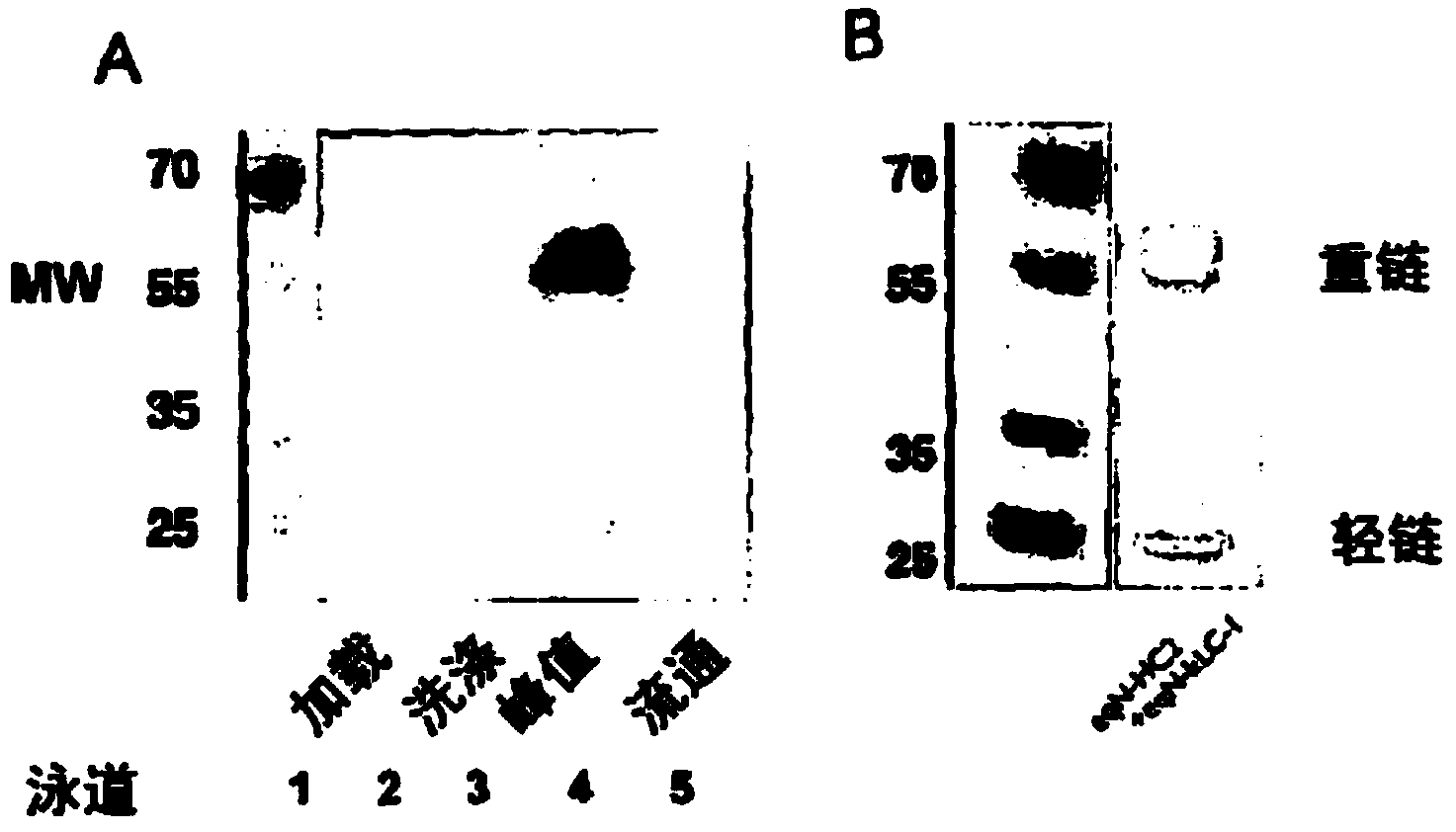
[0241] The supernatant obtained from Example 2 was purified using a protein A column, separated by SDS-PAGE, and tested for reactivity with anti-equine IgG polyclonal antibody HRP. SDS-PAGE gels were also stained with Coomassie blue to detect heavy and light chains. Anti-horse IgG polyclonal antibody preparations primarily recognize horse heavy chains. The results are shown in figure 2 A and B.
[0242] Results show purification of horse anti-NGF with type 2 heavy chain by protein A as shown by western blot formed with anti-horse polyclonal antibody HRP. Peak fractions were analyzed by Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE. Degradation of the heavy and light chains was evident using SDS-PAGE. Coomassie blue stained gel ( figure 2 B) Shows the presence of heavy and light chains as well as intact antibody (MW 70).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com