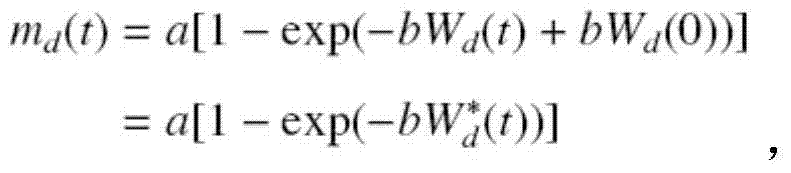FDE and FCE considered software reliability growth model establishing method based on ISQ
A technology for growing models and establishing methods, applied in the field of software fault detection and fault correction, which can solve the problem of not considering the impact of fault detection workload and fault correction workload on software reliability, reducing the practical significance of the model and the reliability of the results. and other issues to achieve the effect of improving the credibility of the results and improving the practical significance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0010] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Describe this specific embodiment, the establishment method of the software reliability growth model based on ISQ considering FDE and FCE described in this specific embodiment, the software reliability growth model based on ISQ includes the mean value function model of the fault detection process and the fault The mean function model of the correction process, the establishment method comprises the following steps:
[0011] Step 1, establish a differential equation according to the condition of the ISQ-FDEFCE software reliability growth model to be established, and obtain the mean value function model of the fault detection process of the ISQ-FDEFCE software reliability growth model by this differential equation;
[0012] Step 2. According to the probability that the software fault is completely corrected, the fault correction time and the mean value function model of the fault detection process of the ISQ-FDEFCE soft...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0014] Embodiment two, the difference between this embodiment and the establishment method of the ISQ-based software reliability growth model considering FDE and FCE described in embodiment one is that the ISQ-FDEFCE software to be established described in step one The conditions of the reliability growth model are:
[0015] The software fault detection process follows an NHPP,
[0016] The failure of the software system at any time is caused by the residual fault in the software;
[0017] The number of detected software faults in the time interval (t,t+Δt] is proportional to the number of remaining faults in the software system and the workload of fault detection;
[0018] Software failures are independent of each other;
[0019] The software fault correction process cannot be ignored, and the number of corrected faults lags behind the total number of detected faults;
[0020] Each fault that causes the failure of the software system will be corrected eventually. The softw...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0023] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the method for establishing the ISQ-based software reliability growth model considering FDE and FCE described in Embodiment 2 is that the ISQ-FDEFCE described in step 1 is based on the ISQ-FDEFCE to be established. The differential equation established by the conditions of the software reliability growth model is:
[0024] dm d ( t ) dt = bw d ( t ) [ a - m d ( t ) ] ,
[0025] Among them, m d (t) is the expected value of the number of faults detected by the software until time t, w d (t) is the instantaneous fault detection workload at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com