Acinetobacter baumannii, and screening method and application thereof in degradation of azo dye Congo red
A technology of Acinetobacter baumannii and azo dyes, applied in the field of environmental engineering and bioengineering, can solve the problems of large differences in the structure of azo reductase, the inability of general microorganisms, and the difficulty of growth and reproduction, etc., to enrich the decolorization mechanism of dyes , good tolerance and removal effect, not easy to change the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
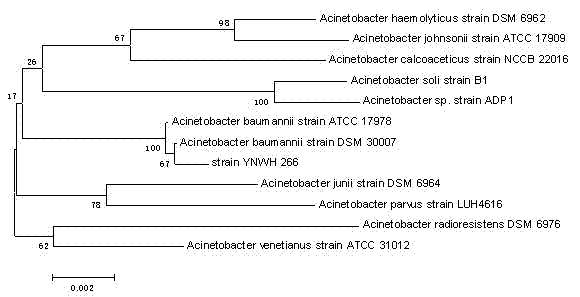
[0033] Embodiment 1 Acinetobacter baumannii ( Acinetobacter baumannii ) Screening of YNWH 226
[0034] S1. Take 10mL of wastewater from the aerobic tank of a printing and dyeing wastewater treatment plant in Dongguan City in 100mL of LB medium, and cultivate it at 30°C and 150rpm for 16 hours to obtain the initial culture solution;
[0035] S2. Take out 10 mL of the primary culture solution described in S1 and put it in 100 mL of inorganic salt medium containing 1 g / L Congo red, and cultivate it for two days at 30° C. and 150 rpm to obtain the culture solution;
[0036] S3. Take out 10 mL of the culture solution described in S2 and put it in a fresh inorganic salt medium containing 1 g / L Congo red, cultivate it for two days at 30° C. at 150 rpm, and repeat S63 3 times to obtain the final culture solution;
[0037] S4. Take 10 mL of the final culture solution described in S3 and properly dilute it, then evenly spread it on a solid inorganic salt medium plate containing 1 g / L...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 Acinetobacter baumannii ( Acinetobacter baumannii ) Application of YNWH 226 in degrading Congo red
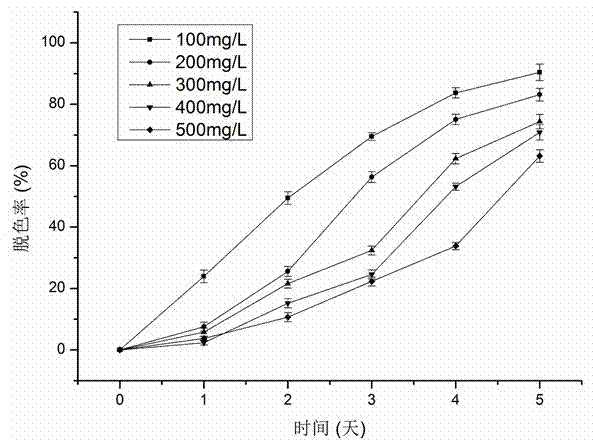
[0045] 1. The strain YNWH 226 was cultured in LB medium for 16 hours (late logarithmic growth stage), and 5 mL was inoculated until the concentrations of the azo dye Congo red were 0.1 g / L, 0.2 g / L, 0.3 g / L, and 0.4 g / L, respectively. L, 0.5g / L 200mL inorganic salt medium, cultured at 30°C, 150rpm, pH7.0 for 5 days. During this period, 5 mL of the culture solution was taken every 24 hours, centrifuged for 2 minutes under the action of 700 g centrifugal force, and the supernatant was taken.
[0046]2. Measure the absorbance of the supernatant obtained in step 1 at 490nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Puyi TU-1901), and calculate the degradation rate of the dye with the dye culture solution without adding bacteria as a control.
[0047] The results are attached figure 1 Shown: the degradation rate of strain YNWH 226 to 100mg / L Congo red is 90.37%, t...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3 Acinetobacter baumannii ( Acinetobacter baumannii ) Application of YNWH 226 in degrading Congo red
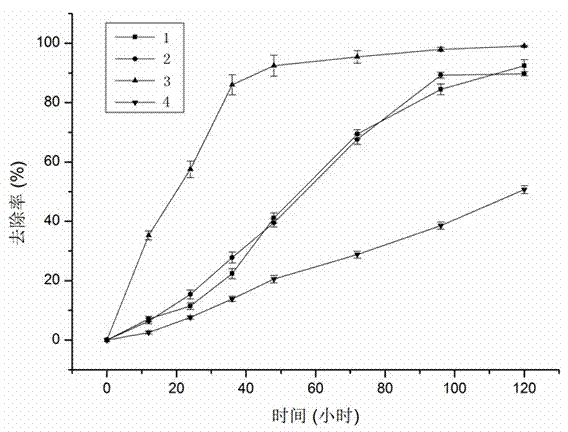
[0050] Cultivate strain YNWH 226 in LB medium for 16 hours (late logarithmic growth period), take 10 mL of ice bath for 30 min, centrifuge at 4°C and 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, and wash the bacteria with sterile water Twice, and then inoculated into 200mL inorganic salt medium containing the azo dye Congo red at a concentration of 0.1g / L, and cultured for 5 days according to the conditions in Table 1. During this period, 5 mL of culture solution was taken every 12 hours, centrifuged for 2 minutes under the action of 700 g centrifugal force, and the supernatant was taken. The obtained supernatant was measured at 490nm by a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Puyi TU-1901), and the degradation rate of the dye was calculated using the culture solution without bacteria and dye as a control. The result is as figure 2 shown. The statistical resu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com