Method for treating gas containing nitrogen oxides (NOx), using composition comprising zirconium, cerium and niobium as catalyst
A nitrogen oxide, cerium oxide technology, applied in catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalyst, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, etc., to achieve the effect of stabilizing the specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
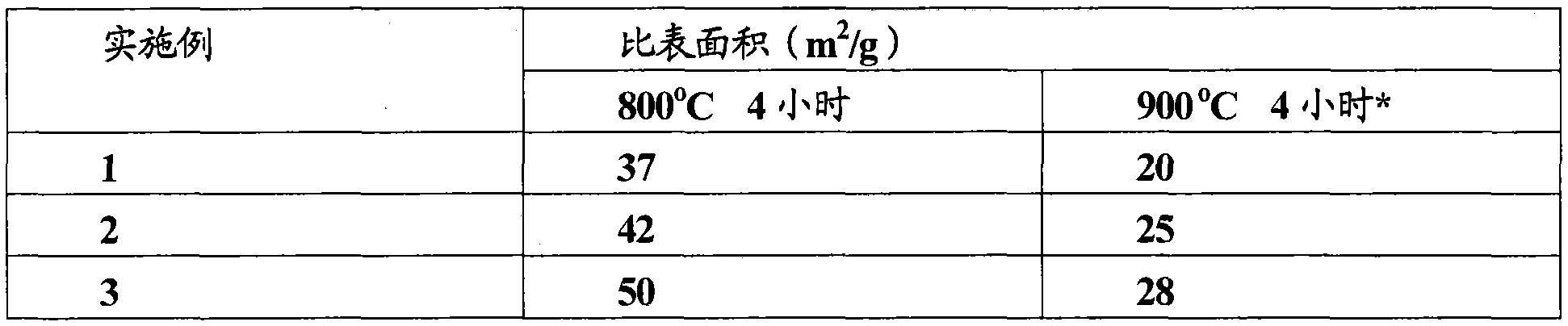
[0075] This example relates to the preparation of compositions based on oxides of cerium, zirconium and niobium with corresponding mass proportions of 18%, 72% and 10%.
[0076] Ammonium niobium(V) oxalate solution was prepared by thermally dissolving 192 g of ammonium niobium(V) oxalate in 300 g of deionized water. This solution was kept at 50°C. The concentration of this solution is Nb 2 o 5 Expressed as 14.2%. Then the mixed oxide powder of cerium and zirconium (mass composition CeO 2 / ZrO 2 20%-80%, the specific surface area after calcination at 800°C for 4 hours is 62m 2 / g) impregnated with this solution until the pore volume is saturated.
[0077] The impregnated powder was then calcined at 800°C for 4 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0079] This example relates to the preparation of compositions based on oxides of cerium, zirconium and niobium with corresponding mass proportions of 19%, 74% and 7%.
[0080] Ammonium niobium(V) oxalate solution was prepared by thermally dissolving 134 g of ammonium niobium(V) oxalate in 300 g of deionized water. This solution was kept at 50°C. The concentration of this solution is Nb 2 o 5 Expressed as 9.9%. The same mixed oxide powder of cerium and zirconium as in Example 1 was then impregnated with this solution. The impregnated powder was then calcined at 800°C for 4 hours.
Embodiment 4
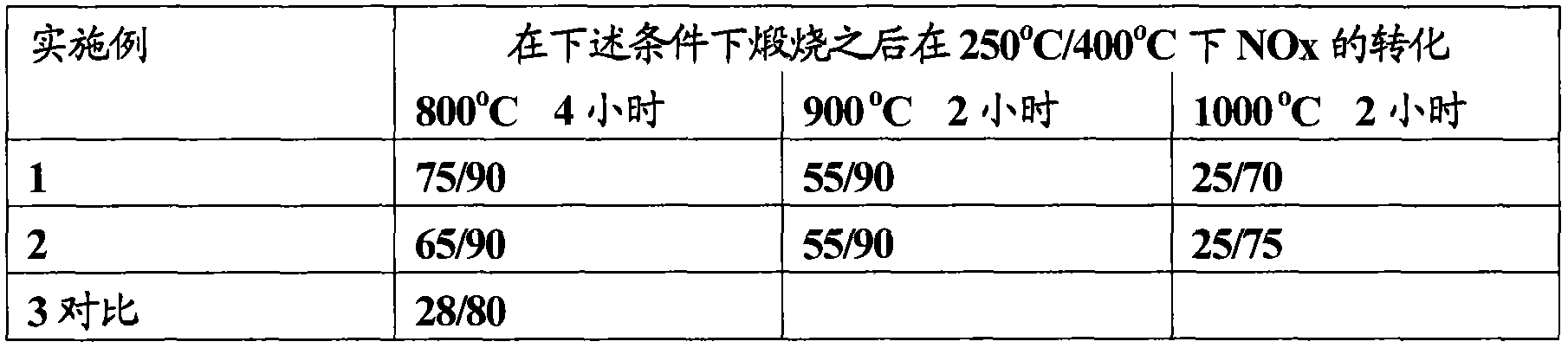
[0090] This example describes the catalytic performance of the compositions of the above examples in SCR catalysis. These properties were evaluated under the following conditions.
[0091] In the first series of measurements, the composition used was the composition obtained directly from the synthesis described in the preceding examples, ie a composition that had been calcined at 800° C. for 4 hours.
[0092] In the second series of measurements, the composition used was that of the preceding examples, but after an additional calcination in both cases at 900° C. and 1000° C. for 2 hours.
[0093] The compositions were then evaluated by catalytic tests. In this test, a synthesis gas mixture (Table 2) representative of the catalytic process was passed (30 L / h) through the composition (90 mg).
[0094] Table 2
[0095]Composition of a representative mixture
[0096] NH 3
500vpm
NO
500vpm
O 2
13vol%
h 2 o
5vol%
N 2
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com