Proteins that interact with Clostridium difficile cytotoxin b
A Clostridium difficile and cytotoxin technology, applied in the field of protein engineering, can solve the problem of unclear host receptor protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
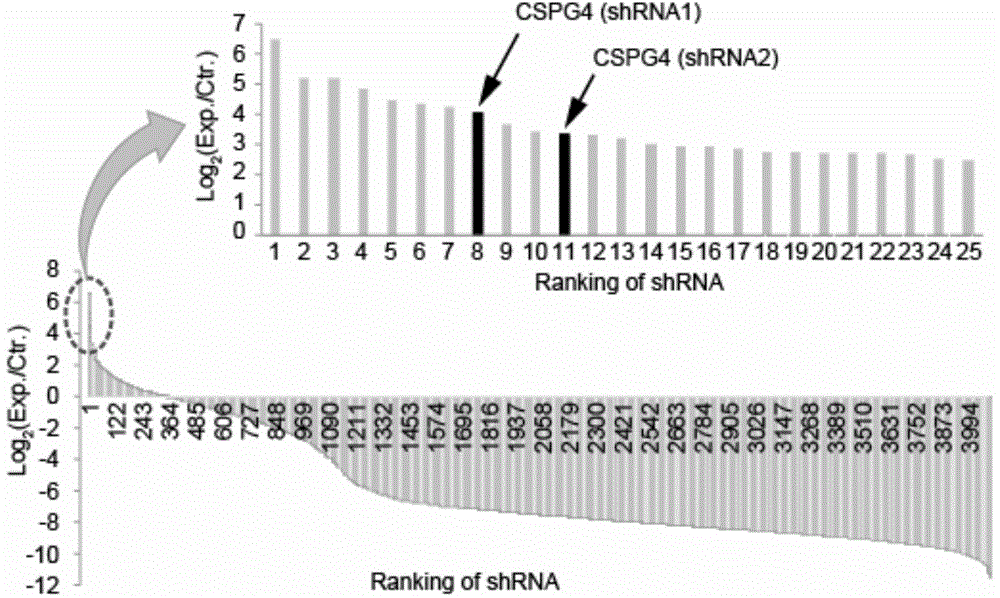
[0029] Example 1 Whole genome shRNA library screening
[0030] The shRNA library was purchased from Open-biosystem, with a total of 65,000 shRNAs targeting 20,000 human genes. The library was constructed in HeLa cells by lentiviral system. Cultured 2×10 using medium containing 70pg / mL TcdB 6 After 8 hours, the cells infected by TcdB were removed with a pipette and replaced with normal medium for 3 days. After repeating the operation 6 times, HeLa cells resistant to TcdB were collected ( figure 1 ), using primers (5'-ACGTCGAGGTGCCCGAAGGA-3' and 5'-TACATCTGTGGCTTCACTA-3') for PCR amplification, and further confirmed by deep sequencing that the shRNA against CSPG4 can inhibit the toxicity of TcdB ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 CSPG4 gene knockout
[0032] The sequence of TALENs against the CSPG4 gene is as follows: 5'-TCCAGCCCCCGGCCT-3'(TALEN L ), 5'-CTGGCCAACATAGTC-3'(TALENR ). The target sequence used in the CRISPR system for the CSPG4 gene is: 5'-TTGGCCAGACTTGCATCCG-3', and the gRNA sequence is: 5'-GTTTTAGGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAGGCTAGTCCGTTATCAACTTGAAAAAGTGGCACCGAGTCGGTGCTTTTTTT-3'.
[0033] After transfecting TALENs or CRISPR system plasmids into cells, single clones were selected, and CSPG4 gene knockout cells were determined by Western Blot. After obtaining the CSPG4 gene knockout cell line, compare wild-type HeLa cells and CSPG4 overexpression HeLa cells, use TcdB to treat, and pass the cell shape ( image 3 ) and cell death ( Figure 4 ) and other phenotypes to evaluate the toxicity of TcdB.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 The expression level of CSPG4 directly affects the binding of TcdB to the cell surface
[0035] After synchronous culture of the above CSPG4 knockout HeLa cells and CSPG4 overexpression HeLa cells obtained by lentivirus infection, they were cultured at 4°C for one hour with a medium containing 10 μg / mL TcdB. It was further washed 5 times with PBS to wash away TcdB not bound to the cell surface. After the cells were lysed, the relationship between the expression level of CSPG4 and the amount of TcdB bound to the cell surface was determined by Western Blot. At the same time, after culturing at 37°C for half an hour with a medium containing 10 μg / mL TcdB, use FractionPREP TM The Cell Fraction Kit was used to separate the cell membrane structure, and the relationship between the expression level of CSPG4 and the amount of TcdB in the cell membrane was determined by Western Blot ( Figure 5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com