Kit and method for detecting mycoplasma pollution in CHO cultured cells
A technology for culturing cells and mycoplasma, which is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms, which can solve the problems of wasting reagents, cumbersome, and increasing the complexity of detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] 1) Primer pair A and primer pair B
[0048] where primer pair A
[0049] Upstream primer GF: 5'- CAAAGGCACAGTCAAGGCTGA -3';
[0050] Downstream primer GR: 5'- TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTAGATT -3'.
[0051] Primer pair B
[0052] Upstream primer MF: 5'- ACACCATGGGAGCTGGTAAT -3';
[0053] Downstream primer MR: 5'- GTTCATCGACTTTCAGACCCAAGGCAT -3'.
[0054] The base sequences of primer pair A and primer pair B are references: Eldering JA, Felten C, Veilleux CA, Potts BJ. Development of a PCR method for mycoplasma testing of Chinese hamster ovary cell cultures used in the manufacture of recombinant therapeutic proteins, Biologicals , 2004, 32(4):183-193.
[0055] Primer pair B is a primer pair for specifically amplifying the conserved region of mycoplasma 16s rRNA, which can cover a variety of mycoplasma in one detection, and can cover the common types of mycoplasma infection in CHO cultured cells. The types of mycoplasma that this kit can detect include M. fermentans, M. hyorh...
Embodiment 2
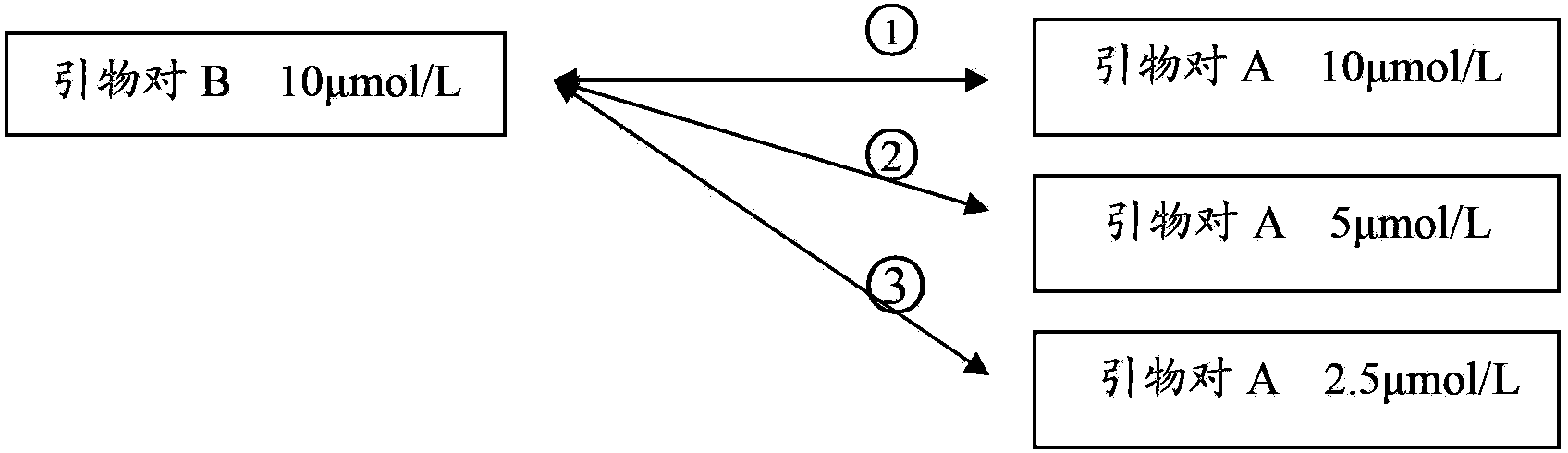
[0060] 1) In order to make the thickness of the corresponding amplification bands of the positive control in the detection appropriate, and the detection of mycoplasma contamination bands will not cause corresponding amplification bands due to insufficient primer concentration, adjust the PCR amplification reaction system For the concentration ratio of primer pair A and primer pair B, three combinations are set, see attached figure 1 , respectively ①②③.
[0061] 2) Extract the DNA of CHO cultured cells confirmed to be contaminated by mycoplasma and the DNA of CHO cultured cells determined not to be contaminated by mycoplasma. 5 centrifuge at 6,000 rpm for 5 minutes; fully suspend the precipitate with PBS buffer, and centrifuge at 6,000 rpm for 5 minutes; discard the supernatant, add 50 μL TE buffer to fully suspend the precipitate, and bathe in boiling water for 5 minutes; centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and take 4 μL of each supernatant and add it to the PCR system ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Extract the DNA of 14 groups of different culture batches of CHO cells to be tested in the logarithmic growth phase. For the method, see step 2 of Example 2), add 4 μL of the extracted DNA reaction template to the PCR reaction amplification system described in Example 2 In the process, add the nucleic acid-free water to another PCR reaction amplification system , as a negative control. Perform PCR amplification. For the reaction conditions of the amplification reaction, see Step 3 of Example 2), and then perform agarose gel electrophoresis.
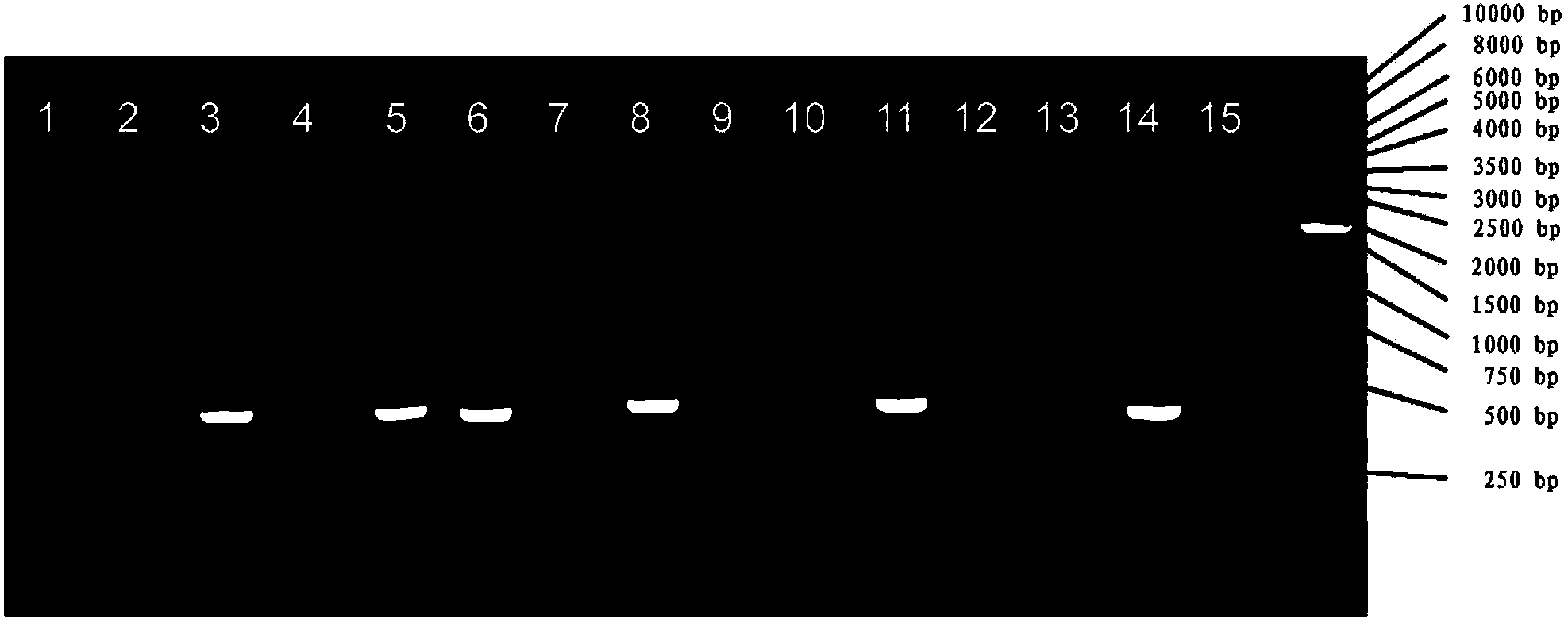
[0068] The test results are attached image 3 . Swimming lane 1 is a negative control, and no amplification product appears; swimming lanes 2-15 are the tested samples, corresponding to the 1st-14th batch of samples tested in turn. It can be seen from the figure that the 150bp primer pair A has corresponding amplification products, which shows that the PCR system is working normally, and the PCR system is not polluted, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com