A Metallographic Corrosion Method for Revealing Grain Boundary of Austenitic Stainless Steel
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and metallographic corrosion, which is applied in the field of heat treatment, can solve the problems of affecting grain size rating, inconvenient metallographic structure analysis, and inability to distinguish grains, etc., to achieve easy grain size rating, simple assembly, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
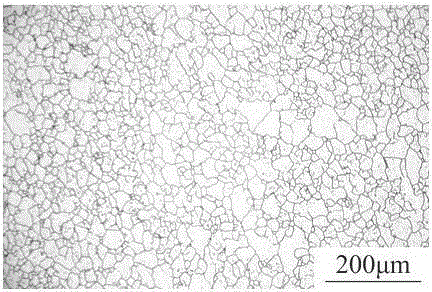
[0034] First add 1g of sodium chloride to 30ml of distilled water, then add 0.1g of potassium thiocyanate to the sodium chloride solution, and finally add 70ml of nitric acid with a concentration of 65% to the above-mentioned prepared solution slowly, and stir uniform. The 304 austenitic stainless steel that has been heat-treated at 1150°C for 120 minutes is processed into a sample to be corroded. After polishing and cleaning, it is connected to a DC stabilized voltage power supply. The sample is connected to the positive electrode, the titanium plate is connected to the negative electrode, the voltage is 3.0V, the time is 60s, the power is cut off, the sample is removed, rinsed with distilled water, then washed with alcohol and dried, and the grain size is observed with a metallographic microscope. figure 1 shown. The grain boundaries are clear, the grains are uniform, and the grain twins are less or not obvious, which is conducive to the evaluation of grain size.
Embodiment 2
[0036] First add 3g of sodium chloride into 50ml of distilled water, then add 0.5g of potassium thiocyanate into the sodium chloride solution, and finally add 50ml of nitric acid with a concentration of 65% into the above-mentioned prepared solution slowly, and stir uniform. The 316LN austenitic stainless steel that has been heat-treated at 1100°C for 30 minutes is processed into a sample to be corroded. After polishing and cleaning, it is connected to a DC stabilized voltage power supply. The sample is connected to the positive electrode, the titanium plate is connected to the negative electrode, the voltage is 0.5V, the time is 240s, the power is cut off, the sample is removed, rinsed with distilled water, then washed with alcohol and dried, and the grain size is observed with a metallographic microscope. figure 2 shown. The grain boundaries are clear, both large grains and small grains are corroded, and grain twins are not obvious, which is conducive to the evaluation of ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] First add 2g of sodium chloride into 40ml of distilled water, then add 0.3g of potassium thiocyanate into the sodium chloride solution, and finally add 60ml of nitric acid with a concentration of 65% into the above-mentioned prepared solution slowly, and stir uniform. The 316LN austenitic stainless steel that has been heat-treated at 1050°C for 10 minutes is processed into a sample to be corroded. After polishing and cleaning, it is connected to a DC stabilized voltage power supply. The sample is connected to the positive electrode, the titanium plate is connected to the negative electrode, the voltage is 1.5V, the time is 100s, the power is cut off, the sample is removed, rinsed with distilled water, then washed with alcohol and dried, and the grain size is observed with a metallographic microscope. image 3 shown. The grain boundaries are clear, the grains are fine and uniform, and the grains have no twins, which is conducive to the evaluation of grain size.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com