A conductive agent suitable for lithium iron phosphate material and preparation method thereof
A technology of lithium ferrous phosphate and conductive agent, which is applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, battery electrodes, etc., and can solve the problems of large residual capacity of electrodes, low utilization rate of active materials, and insufficient discharge depth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
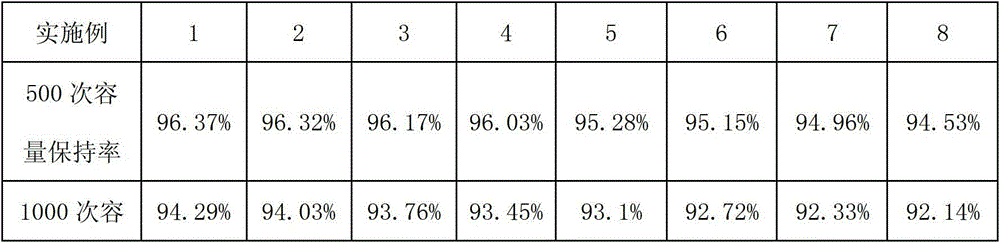
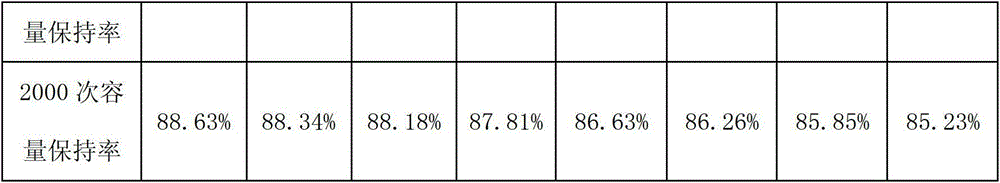
[0021] Embodiment 1: A conductive agent suitable for lithium ferrous phosphate material in this example, the mass ratio of carbon nanotubes, conductive carbon black, and conductive graphite is 1:25:1.
[0022] A preparation method for a conductive agent suitable for lithium iron phosphate materials, the steps are: under the condition of a constant temperature of 25 ° C, 1 g of conductive carbon black is added to 20 ml of ethanol solution, and then 1 g of cobalt nitrate, 1 g of nickel nitrate, and 1 g of zinc nitrate are added. Wherein, the whole process was carried out under the condition of stirring and ultrasonic for 12h. After 12 hours, it was heated to become a rheological phase, and put into a high-temperature furnace for heating. During the heating process, argon gas was always passed through, and the heating temperature was maintained at 1500°C for 3 hours. Cooled to room temperature, washed with 10mol / L hydrochloric acid for 12h, suction filtered, and dried for 12 hour...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: A suitable conductive agent for lithium ferrous phosphate material in this example, the mass ratio of carbon nanotubes, conductive carbon black, and conductive graphite is 1:30:1.
[0030] A preparation method for a conductive agent suitable for lithium iron phosphate materials, the steps are: under the condition of a constant temperature of 25 ° C, 1 g of conductive carbon black is added to 20 ml of ethanol solution, and then 1 g of cobalt nitrate, 1 g of nickel nitrate, and 1 g of zinc nitrate are added. Wherein, the whole process was carried out under the condition of stirring and ultrasonic for 12h. After 12 hours, it was heated to become a rheological phase, and put into a high-temperature furnace for heating. During the heating process, argon gas was always passed through, and the heating temperature was maintained at 1500°C for 3 hours. Cooled to room temperature, washed with 10mol / L hydrochloric acid for 12h, suction filtered, and dried for 12 hour...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: A conductive agent suitable for lithium ferrous phosphate material in this example, the mass ratio of carbon nanotubes, conductive carbon black, and conductive graphite is 1:35:1.
[0033] A preparation method for a conductive agent suitable for lithium iron phosphate materials, the steps are: under the condition of a constant temperature of 25 ° C, 1 g of conductive carbon black is added to 20 ml of ethanol solution, and then 1 g of cobalt nitrate, 1 g of nickel nitrate, and 1 g of zinc nitrate are added. Wherein, the whole process was carried out under the condition of stirring and ultrasonic for 12h. After 12 hours, it was heated to become a rheological phase, and put into a high-temperature furnace for heating. During the heating process, argon gas was always passed through, and the heating temperature was maintained at 1500°C for 3 hours. Cooled to room temperature, washed with 10mol / L hydrochloric acid for 12h, suction filtered, and dried for 12 hour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com