Protection and action mechanisms of combination of gastrodin and rhynchophylla to vascular endothelial cells
A technique for endothelial cells and rhynchophylline, which is applied in the field of cell biology and can solve the problems of complex composition, synthesis limitation, eNOS inactivation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
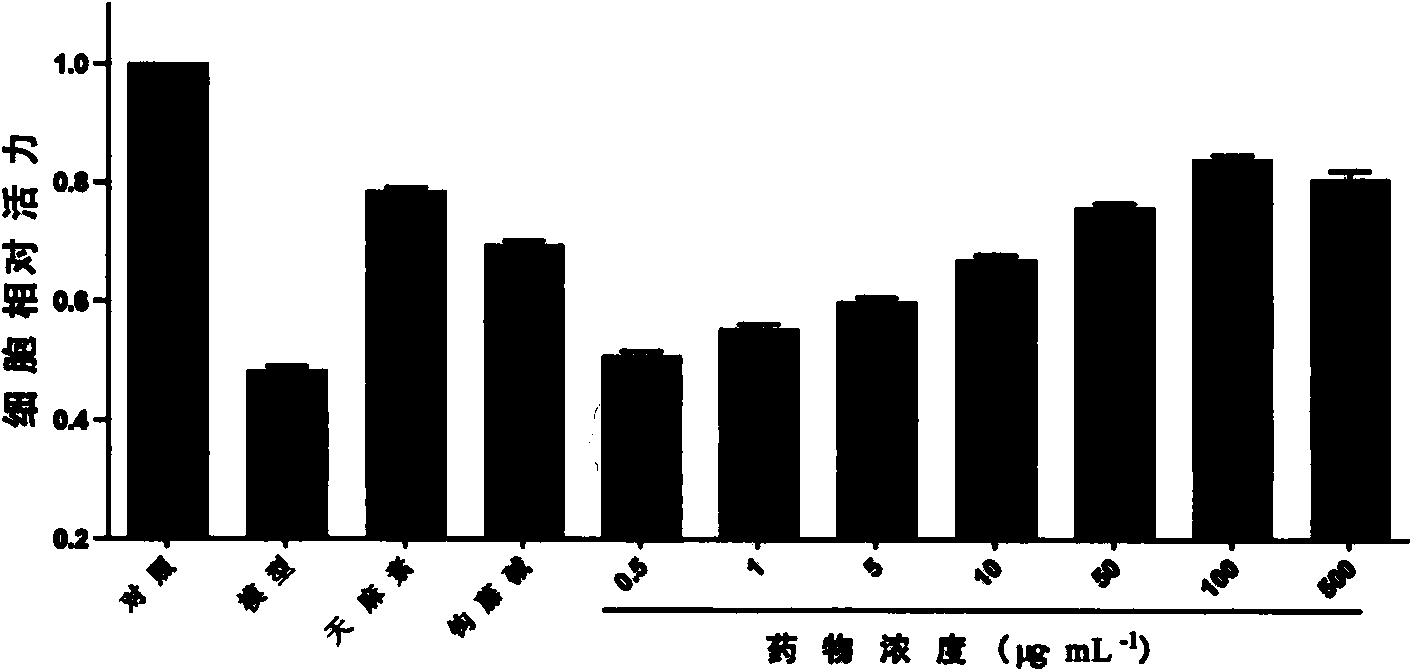
[0027] Embodiment 1 The effect of gastrodin rhynchophylline compatibility on the viability of ECV-304 cells
[0028] Grouping: (1) control group: add 10% DMEM medium; (2) model group: 1000μmol L -1Hcy; (3) Gastrodin group: 100 μg·mL -1 (4) Rhynchophylline group: 100 μg·mL -1 (5) Experimental group: add 10% DMEM medium containing different concentrations of gastrodin rhynchophylline (0.1-10):1 compatibility; (6) Zeroing group: add cell-free medium. Each group has 6 replicate wells.
[0029] Detection of cell viability: (1) EVC-304 cells in logarithmic phase were collected, and after the cells were 80-90% full, 100 μL of drug solutions of different concentrations were added to the experimental group. Add 100 μL of culture medium to the control group and the zeroing group. The final volume of each well is 100 μL. (2) 5%CO 2 , respectively incubated at 37°C for 12, 24, 36, and 48 hours, and observed under an inverted microscope. 16 μL of MTT solution was added to each well,...
Embodiment 2
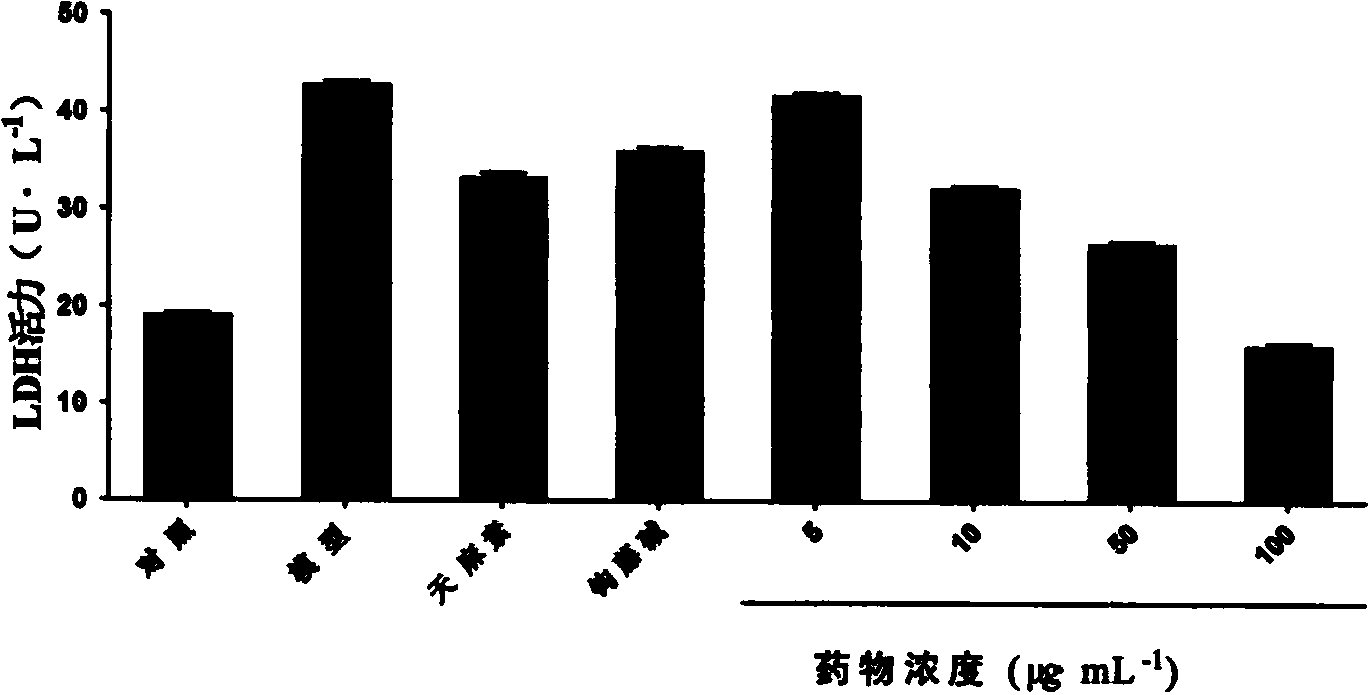
[0031] Example 2 Determination of the protective effect of gastrodin and rhynchophylline compatibility on the ECV-304 cell model of HCY damage
[0032] According to the drug concentration and grouping determined in Example 1, 4 replicate wells were set up for each group. Measure various biochemical indexes according to lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) kit, malondialdehyde (MDA) kit, NO kit instruction method, test result is as follows Figure 2 ~ Figure 4 shown. According to the results, compared with the model group, the compatibility of gastrodin and rhynchophylline can reduce the release of MDA and LDH, and can increase the release of NO in vascular endothelial cells, and the protection effect on ECV-304 cells is more significant than that of the single component with the same concentration. Example 3 Effect of gastrodin and rhynchophylline compatibility on the expression of CAV-1 protein in ECV-304 cells
Embodiment 3
[0033] The total protein in the cells was extracted, and the target band was analyzed by the Western Blot detection gel image processing system. Analysis results such as Figure 5 , Figure 6 shown. Compared with the control group, the model group can increase the expression of CAV-1 in cells. In the experimental group, low concentration of drugs (5 μg·mL -1 and 10μg·mL -1 ) can inhibit the expression of CAV-1 in Hcy-damaged cells, and high-concentration drugs (50 μg·mL -1 and 100μg·mL -1 ) had no significant inhibitory effect on the expression of CAV-1 in injured cells. The results indicated that the combination of gastrodin and rhynchophylline has the characteristics of irreversible recovery for the protection of Hcy-induced vascular endothelial cell injury, and the mechanism of action is through the CAV-1 / eNOS / NO signaling pathway, so as to achieve the effect of lowering blood pressure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com