Cloud detection method by using MODIS remote sensing thermal infrared data
A cloud detection and thermal infrared technology, applied in the field of cloud detection, can solve the problem of not being able to detect very stably
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the preferred embodiments described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
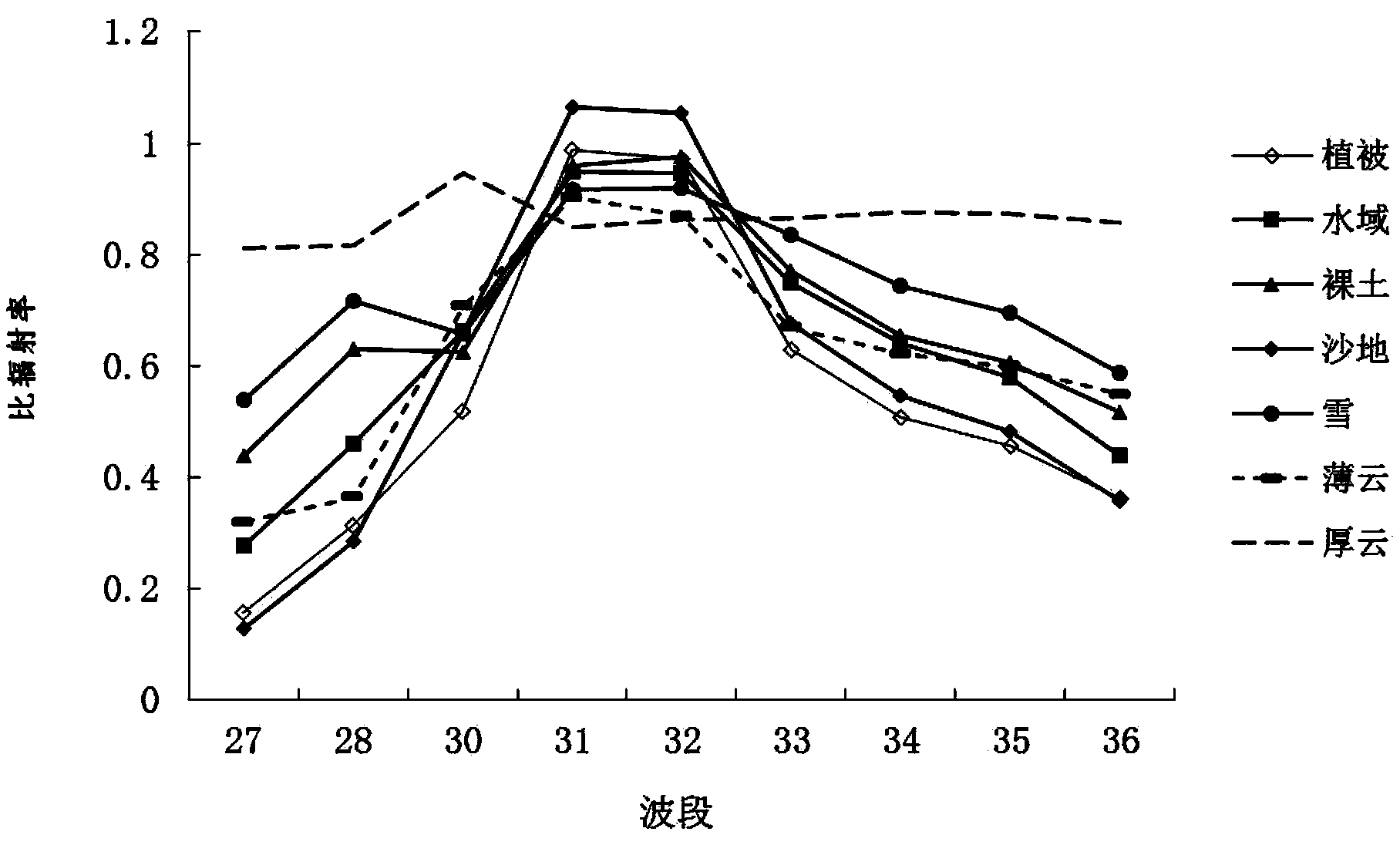
[0028] The invention provides a method for cloud detection by using the difference in specific emissivity between clouds and underlying objects such as vegetation, bare soil, snow, sand and water in the long-wave radiation band of MODIS data.
[0029] 1. Theoretical Basis
[0030] According to the mutual effect of earth radiation and solar radiation, the earth radiation received by the sensor can be divided into three sections, namely short-wave radiation (0.3-2.5 μm), mid-infrared radiation (2.5-6 μm), and long-wave radiation (above 6 μm). The short-wave radiation is mainly reflected by the earth's surface to sunlight, and the heat radiation of the earth itself is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com