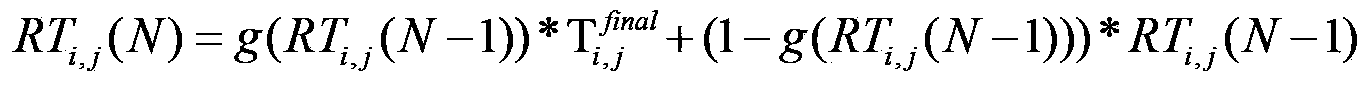Recognition relay network trust management device and method based on dynamic evolution
A dynamic evolution, cognitive relay technology, applied in the field of cognitive relay network trust management, can solve the problems of node selfishness and cooperative misjudgment, lack of engineering feasibility, cognitive decision deviation, etc., to suppress false information. and collusive behavior, stable optimization strategy solution, and the effect of promoting direction evolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in more detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
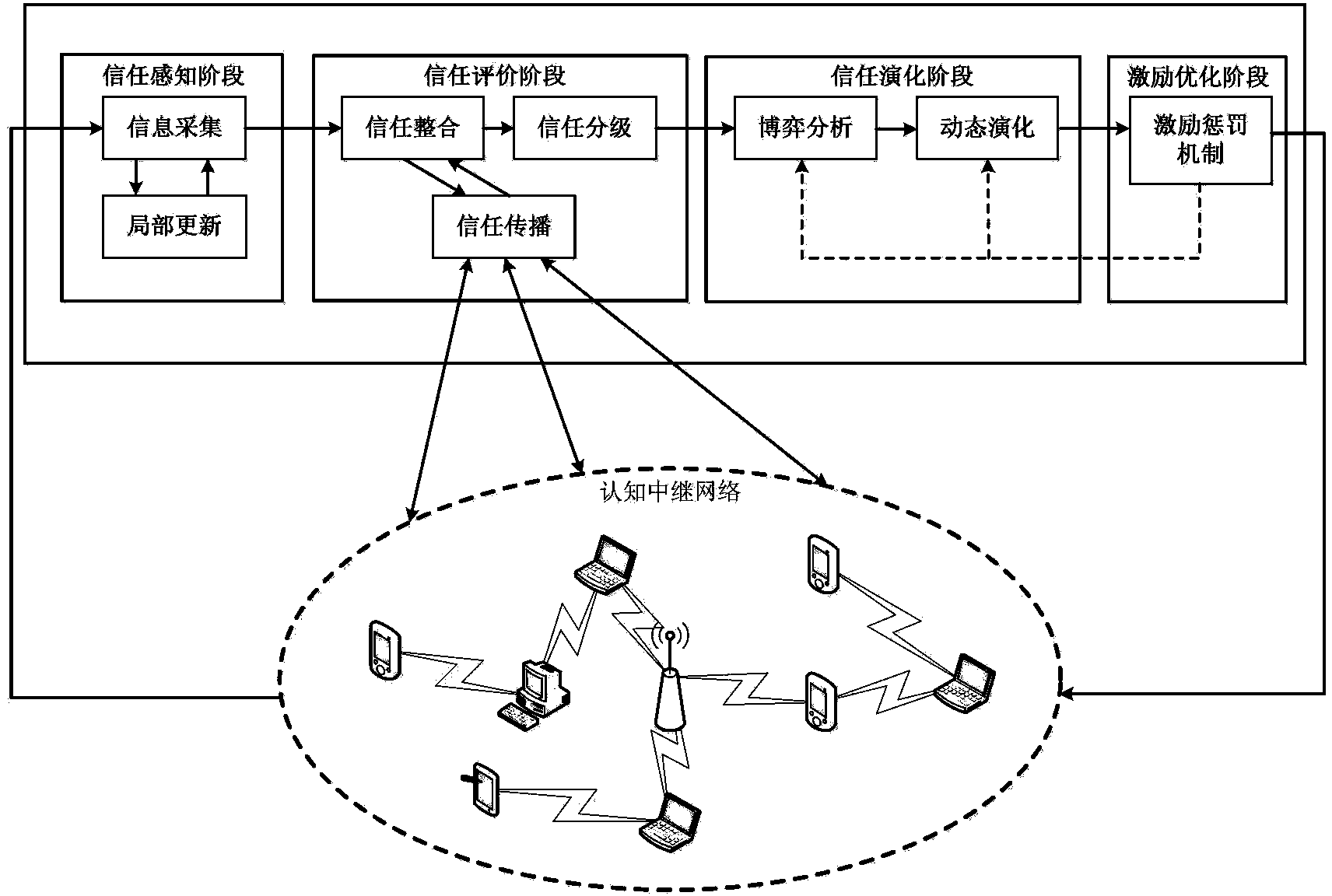
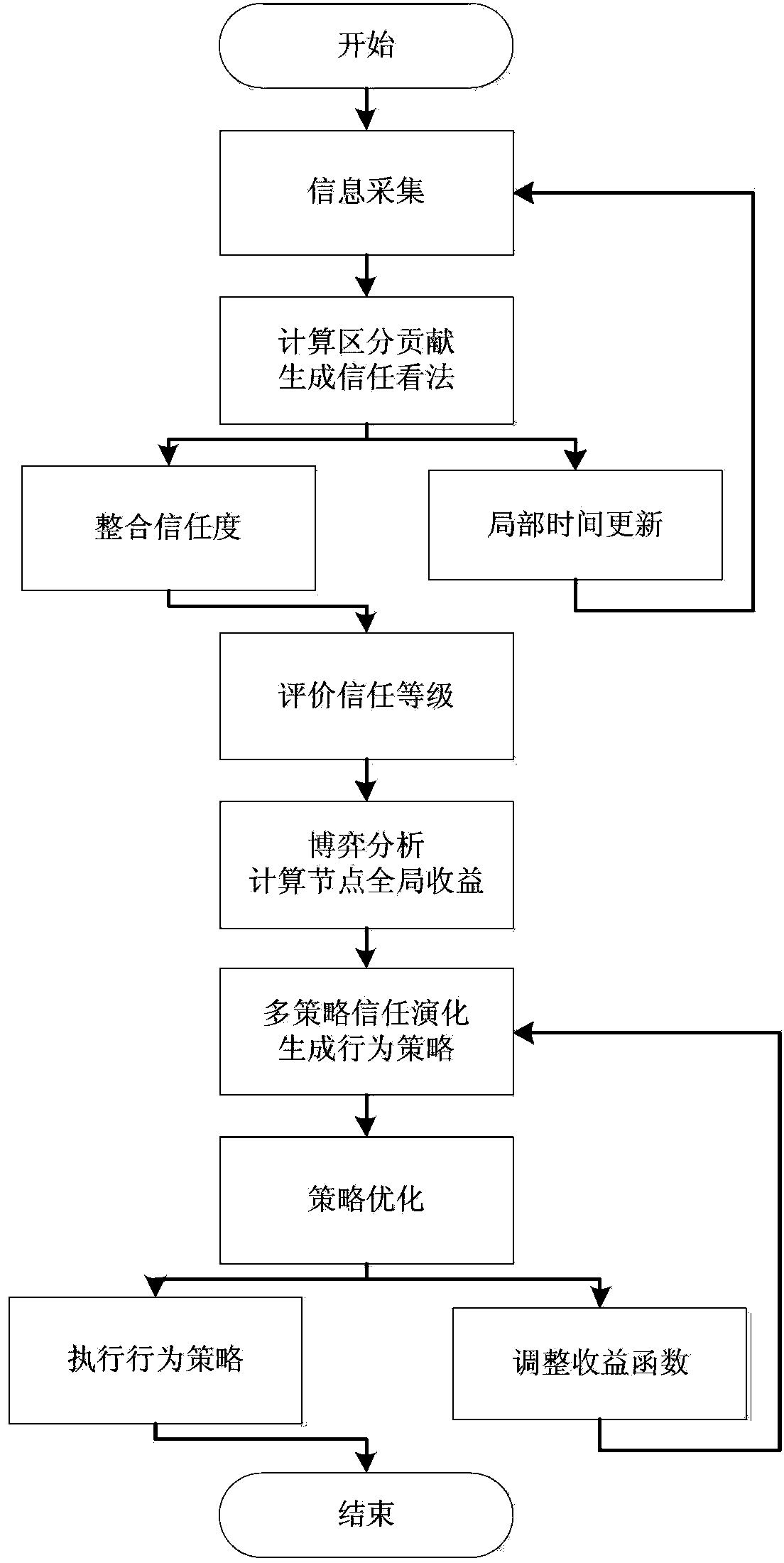
[0025] exist figure 1 The stage process of a cognitive relay network trust management method based on dynamic evolution is described in the present invention, which mainly includes four stages: trust perception stage, trust evaluation stage, trust evolution stage, and incentive optimization stage. Each stage connected sequentially and executed cyclically.
[0026] The trust perception stage is the entrance of the system, including information collection sub-stage and partial update sub-stage. The information collection sub-stage is responsible for collecting network environment information such as spectrum resources, bandwidth, and communication delay, as well as node service behavior information such as node transaction history, active service and passive service frequency, etc. The information is fused and processed, which is characterized as the distinguishing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com