Phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe and application thereof in detection of nuclease
A technology of oligonucleotides and fluorescent probes, which is applied in the field of sulfurated (sulfonylated) modified oligonucleotide fluorescent probes, which can solve the problem of increasing design costs and workload, and losing the advantages of fluorescent nucleic acid probe detection etc. to achieve good fluorescence recovery effect, improved fluorescence quenching efficiency, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1
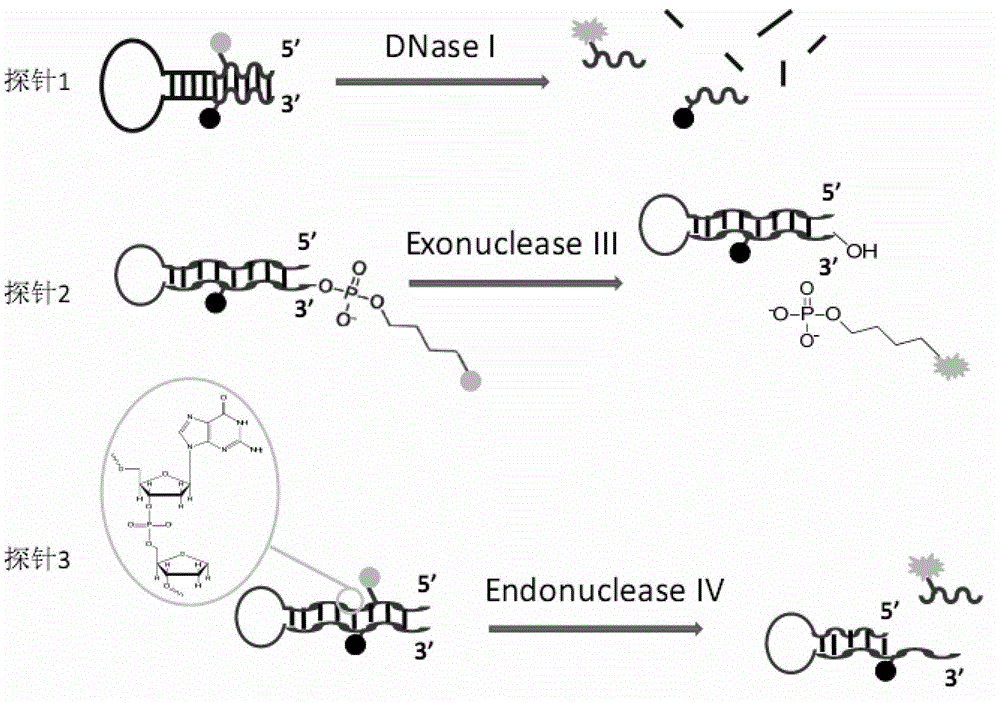
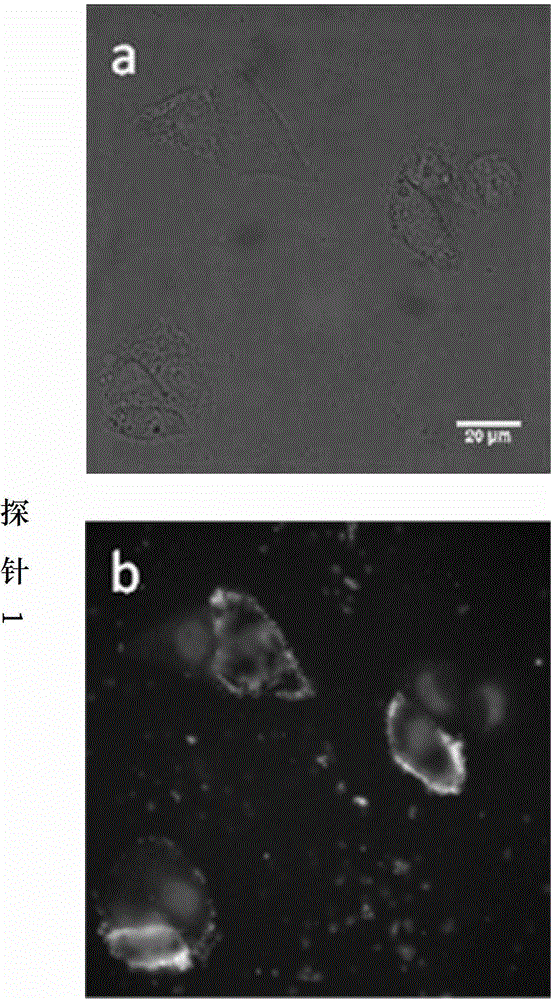
[0036] In this example, thio-modified oligonucleotide fluorescent probe 1 was used to detect the activity of the non-restrictive endonuclease DNase I and compared with the signals generated by other enzymes.
[0037] Specific steps are as follows:
[0038] 1. The fluorescent signal of the thio-modified oligonucleotide fluorescent probe 1 is in a quenched state at the beginning, and it is mixed with different concentrations of DNase I and placed in a suitable solution condition to form a reaction system. The phosphodiester bond of the non-sulfonylated part of the probe is hydrolyzed into small fragments under the catalysis of DNase I, resulting in the separation of the fluorescent group and the quencher group, and the release of the fluorescent signal, which is detected by a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument. As the reaction progresses, the number of probes hydrolyzed increases, and the fluorescence signal increases rapidly until the reaction balances...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2
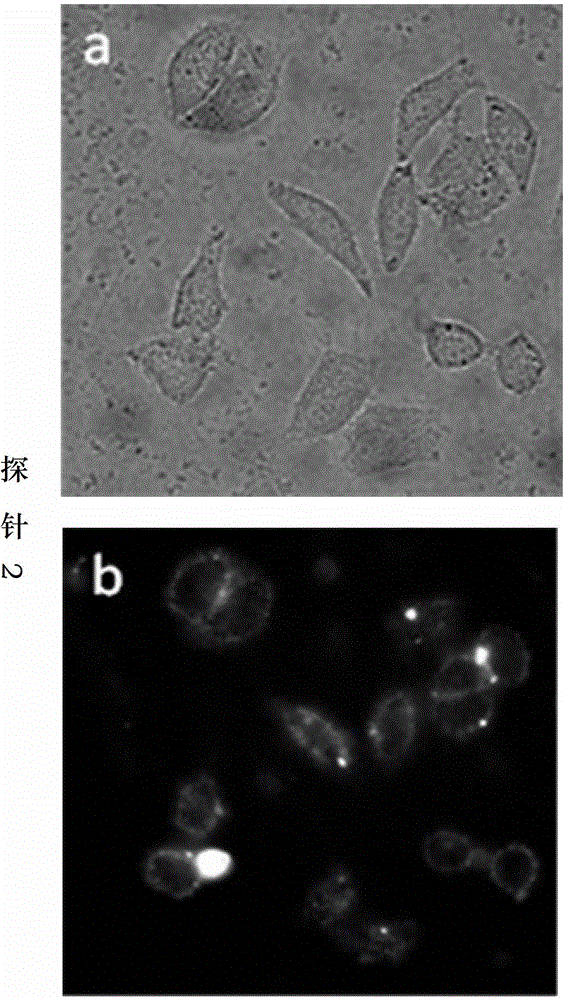
[0052] In this example, the activity of the non-restrictive endonuclease Exonuclease III was detected using the thio-modified oligonucleotide fluorescent probe 2 and compared with the signals generated by other enzymes.
[0053] Specific steps are as follows:
[0054] 1. The fluorescent signal of the thio-modified oligonucleotide fluorescent probe 2 is in a quenched state at the beginning, and it is mixed with different concentrations of Exonuclease III and placed in a suitable solution condition to form a reaction system. The phosphodiester bond of the probe 3' connected to the fluorescent group is hydrolyzed under the catalysis of Exonuclease III, causing the fluorescent group to leave the probe, separate from the quencher group, and the fluorescent signal is released, which is detected by a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument. As the reaction progresses, the number of probes hydrolyzed increases, and the fluorescence signal increases rapidly until th...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3
[0069] In this example, the activity of the apurinic / apyrimidinic site endonuclease Endonuclease IV was detected using the fluorescent probe 3 of the thio-modified oligonucleotide and compared with the signals generated by other enzymes.
[0070] Specific steps are as follows:
[0071] 1. The fluorescent signal of the thio-modified oligonucleotide fluorescent probe 3 is in a quenched state at the beginning, and it is mixed with different concentrations of Endonuclease IV and placed in a suitable solution condition to form a reaction system. The phosphodiester bond at the 5' of the AP site of the probe is hydrolyzed under catalysis, the small fragment oligonucleotide with the fluorescent group leaves the probe, the fluorescent group is separated from the quencher group, and the fluorescent signal is released. Real-time fluorescent PCR instrument for detection. As the reaction progresses, the number of probes hydrolyzed increases, and the fluorescence signa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com