Biochemical novel technology capable of realizing solar energy utilization
A biochemical, new process technology, applied in biosynthesis, waste fuel, energy input, etc., can solve the problems of increasing engineering complexity, increasing system operating costs, and difficulty in automatic control, reducing operational complexity, enhancing Engineering feasibility, effect of reducing fixed investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
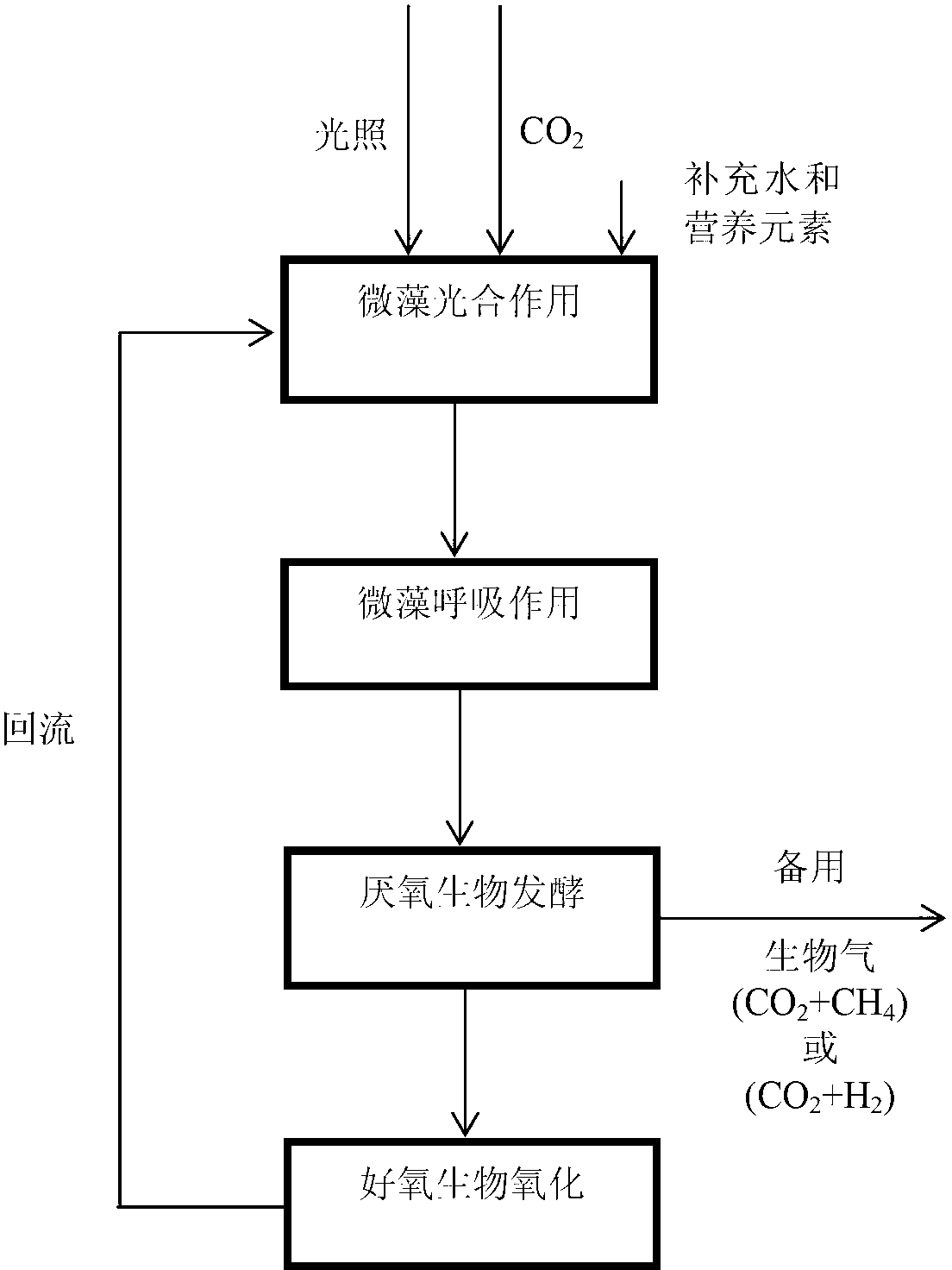
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, the equipment adopted in the present embodiment comprises independently arranged photobioreactor 1, respiratory deaerator 2, anaerobic fermenter 3 and aerobic bioreactor 4, wherein in photobioreactor 1 there are make-up water and Nutrient elements (i.e. elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur), respiratory deaerator 2 is a light-proof container, and the content of anaerobic microorganisms in anaerobic fermenter 3 is 60kgVSS / m 3 , the content of aerobic microorganisms in aerobic bioreactor 4 is 15kgVSS / m 3 .
[0047] The above-mentioned equipment is used to realize the new biochemical process of solar energy utilization, which specifically includes the following steps (such as figure 2 shown):
[0048] Step 1: Total 10000m in sunlight receiving area 2 And in the photobioreactor 1 with a thickness of 0.2m, the microalgae in the water can synthesize inorganic carbon dioxide, water and nutrient elements into their own organic matter...
Embodiment 2
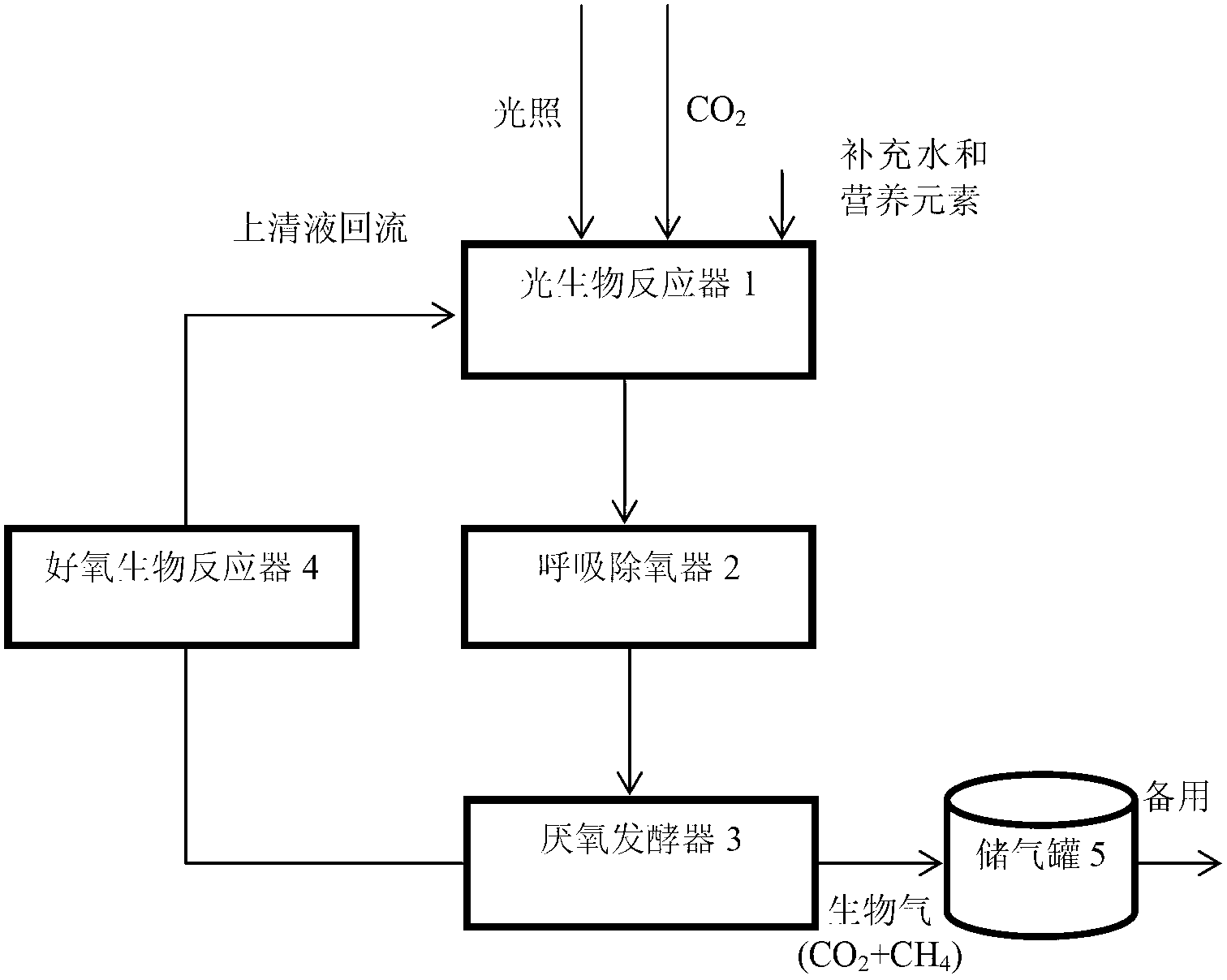
[0054] Such as image 3 As shown, in the equipment used in this embodiment, the photobioreactor and the aerobic bioreactor are coupled together as an aerobic coupled photobioreactor 1', and also includes a respiratory deaerator 2 and an anaerobic fermenter 3, Among them, there are aerobic microorganisms in the aerobic coupled photobioreactor 1', as well as supplementary water and nutrients (i.e. elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur), and the content of aerobic microorganisms is 8kgVSS / m 3 , the respiratory deaerator 2 is a light-proof container, and the anaerobic microorganism content in the anaerobic fermenter 3 is 45kgVSS / m 3 .
[0055] The above-mentioned device is used to realize the new biochemical process of solar energy utilization, which specifically includes the following steps (such as image 3 shown):
[0056] Step 1: Total 1000m in sunlight receiving area 2 And in the aerobic coupled photobioreactor 1' with a thickness of 0.2m, the microalgae in the...
Embodiment 3
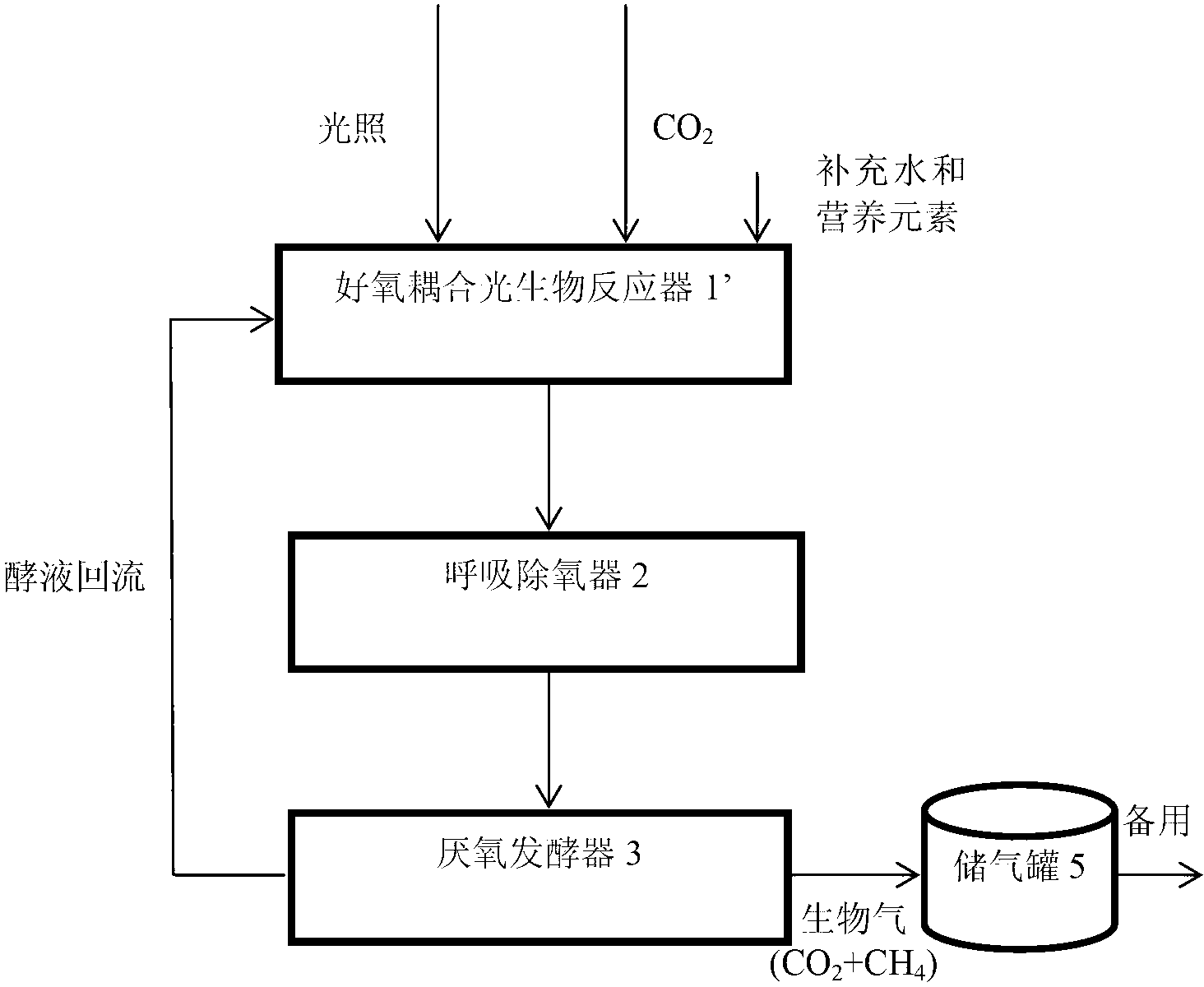
[0061] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the equipment used in this embodiment, the photobioreactor, respiratory deaerator and aerobic bioreactor are coupled together to form a multifunctional photobioreactor 1'', which also includes an anaerobic fermenter 3, wherein There are aerobic microorganisms in the multifunctional photobioreactor 1'', as well as supplementary water and nutrients (i.e. elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur), and the content of aerobic microorganisms is 4kgVSS / m 3 , the content of anaerobic microorganisms in anaerobic fermenter 3 is 30kgVSS / m 3 .
[0062] Above-mentioned device is used for realizing the biochemical new technique of solar energy utilization, and this technique comprises the following steps (as Figure 4 shown):
[0063] Step 1: Total 100m in sunlight receiving area 2 And in the multifunctional photobioreactor 1'' with a thickness of 0.1m, the microalgae in the water can synthesize inorganic carbon dioxide, water and nutrients ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com