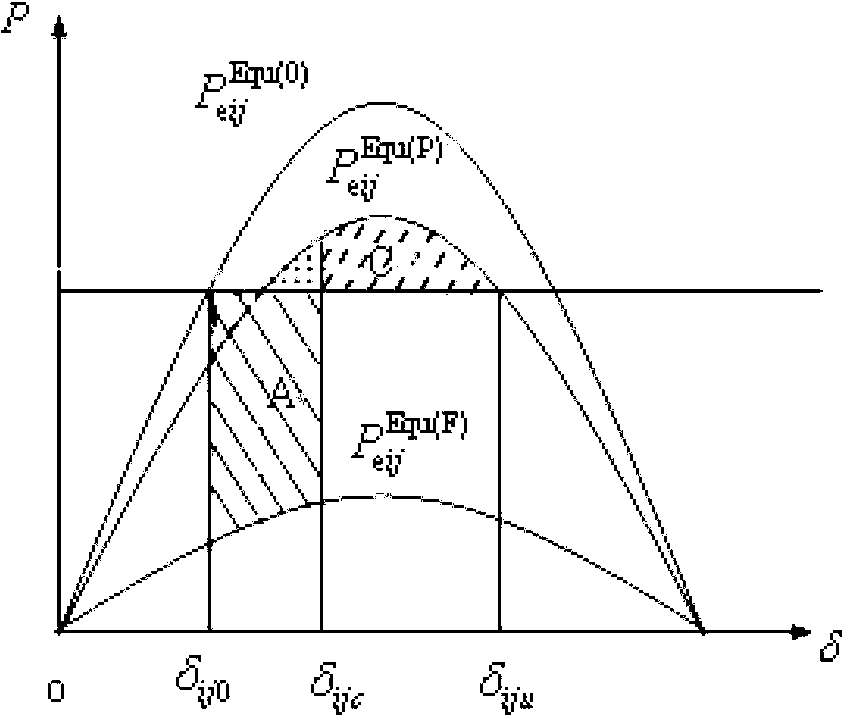
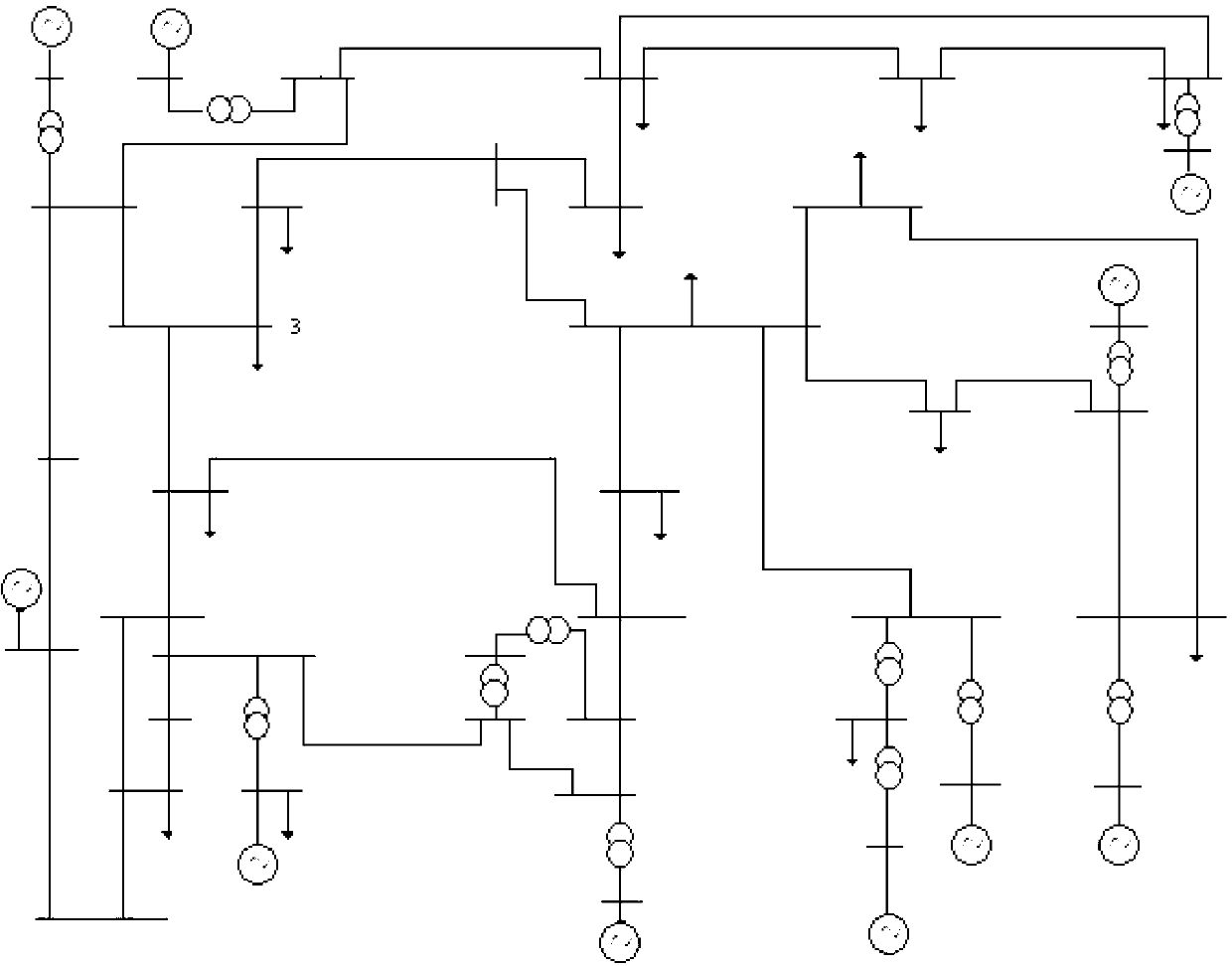
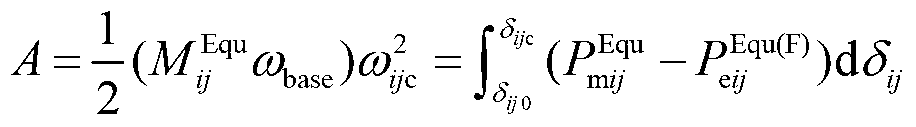Method for calculating failure critical clearing time based on critical unit pair
A technology of critical cut-off time and calculation method, applied in the direction of AC network circuits, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of inability to adapt to online analysis, long calculation time of time domain simulation methods, etc., to reduce the data processing process and calculation speed. Fast, visible results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The specific implementation steps of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with examples. This implementation is carried out in the New England 10-machine 39-node system. The wiring diagram of the system is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0016] Step 1: Obtain the expected accident set under the current power grid operation state from the power dispatching department, and extract a fault from the expected accident set. Assuming that the acquired fault is a three-phase-to-ground short circuit at node 3, t clmax =0.27 seconds to remove the fault.
[0017] Step: 2: Select the critical unit pair
[0018] The method of selecting the critical unit pair is as follows:
[0019] If Ωcr is recorded as the critical cluster set and Ωnon-cr is the remaining cluster set, then for any i∈Ωcr, j∈Ωnon-cr, the pair (i, j) is called a “critical unit pair”. The critical unit pair selection steps are as follows:
[0020] (1) Transient numerical simulation of the sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com