Method for recovery of elemental cobalt from lithium cobaltate by microbial fuel cell (MFC) self-driven microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) coupled system
A technology of microbial electrolysis cell and fuel cell, which is applied in the direction of fuel cell, battery recycling, waste collector recycling, etc., and can solve the problem of inputting large energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
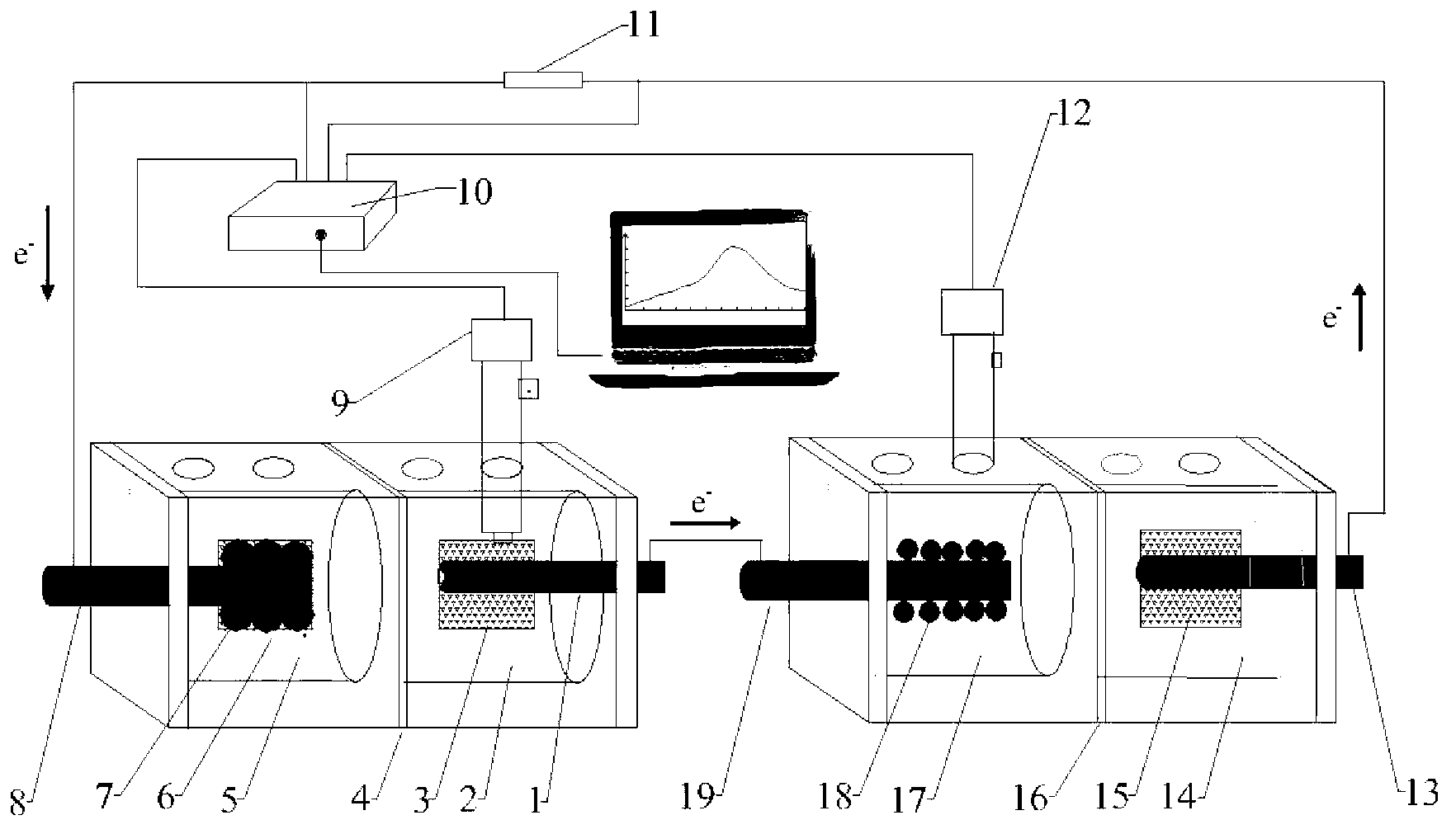
[0024] Step 1: Build MFCs and MECs, such as figure 1 Shown: MFCs anode compartment 2 and cathode compartment 5, MECs anode compartment 14 and cathode compartment 17 are made of plexiglass, the volume of the solution in the anode compartment of MFCs and MECs is 15 mL, the volume of solution in the cathode compartment of MFCs and MECs is 25 mL, Separated by an ion exchange membrane (CMI-7000) 4 or 16, a 10Ω small resistor 11 is connected in series between MFCs and MECs, so as to collect and calculate the current in the circuit.
[0025] Step 2: MFCs anode electrode (carbon rod and carbon felt) and cathode electrode (carbon rod and carbon felt) are placed in MFCs anode chamber 2 and cathode chamber 5 respectively, MECs anode electrode (carbon rod and carbon felt) and cathode Electrodes (carbon rods) are placed in the anode chamber 14 and cathode chamber 17 of the MECs. The apparent size of the carbon rod (Beijing Sanye Carbon Material Co., Ltd.) is 0.8cm×3.5cm, the carbon felt (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com