Method of embryonic stem cell differentiation into neurons by in vitro induction
An embryonic stem cell and neuron technology, applied in the field of in vitro induction of embryonic stem cells to differentiate into neurons and induced differentiated cells, can solve the problems of small amount of neuronal cells, difficulty, lack of clear data on the amount of use and induction time, etc. Induction rate, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
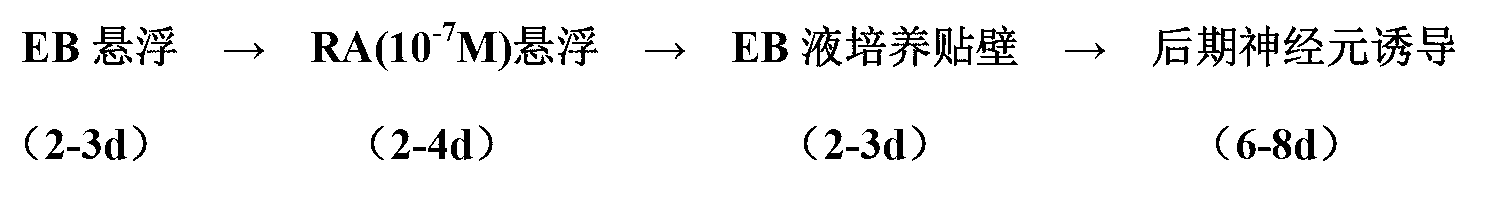
[0029] Separation of ES and MEF: use the differential adherence method, inoculate in a cell culture dish coated with 0.1% gelatin, incubate at 37°C for 45 minutes, collect the supernatant and centrifuge, repeat 1-3 times, and perform ES Separated from MEFs.
[0030] EB formation: add EB formation solution to resuspend cells, inoculate 2-3×10 6 Cells in 10cm bacterial culture dish, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured for 4 days, the medium was changed every 2 days.
[0031] Induction of RA neurons: preparation of neural induction solution: preparation of RA for induction: 1-5×10 -7 M was induced for 4 days, and the medium was changed every 2 days.
[0032] Adhesive culture of nerve-induced EBs: use PLL-coated culture plates, inoculate EBs on the coated culture plates, add appropriate amount of EB-forming solution, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured for 2 days.
[0033] Late neuron induction: 2 days later, use EB formation medium and neuron culture medium for culture, and change half of the medium ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Separation of ES and MEF: use the differential attachment method, inoculate in a cell culture dish coated with 0.1% gelatin, incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes, and repeat twice to separate ES and MEF.
[0036] EB formation: add EB formation solution to resuspend cells, inoculate 2-3×10 6 Cells in 10cm bacterial culture dish, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured for 4 days, the medium was changed every 2 days.
[0037] Induction of RA neurons: preparation of neural induction solution: preparation of RA for induction: 4×10 -7 M was induced for 4 days, and the medium was changed every 2 days. All the other steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Separation of ES and MEF: using the differential adherence method, inoculate in a cell culture dish coated with 0.1% gelatin, incubate at 37°C for 45 minutes, collect the supernatant and centrifuge, and repeat once to separate ES and MEF .
[0040] EB formation: add EB formation solution to resuspend cells, inoculate 2-3×10 6 Cells in 10cm bacterial culture dish, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured for 3 days, the medium was changed every 2 days.
[0041] Induction of RA neurons: preparation of neural induction solution: preparation of RA for induction: 5×10 -7 M was induced for 4 days, and the medium was changed every 2 days.
[0042] Adhesive culture of nerve-induced EBs: use PLL-coated culture plates, inoculate EBs on the coated culture plates, add appropriate amount of EB-forming solution, 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured for 2 days.
[0043] Late neuron induction: After 2 days, use EB formation medium and neuron culture medium for culture, and change half of the medium every day for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com