Element refinement methods and systems in arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) based finite element analysis
A finite element, time-based technology, applied in the direction of computer, CAD technology, CAD numerical modeling, etc. for distributed networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
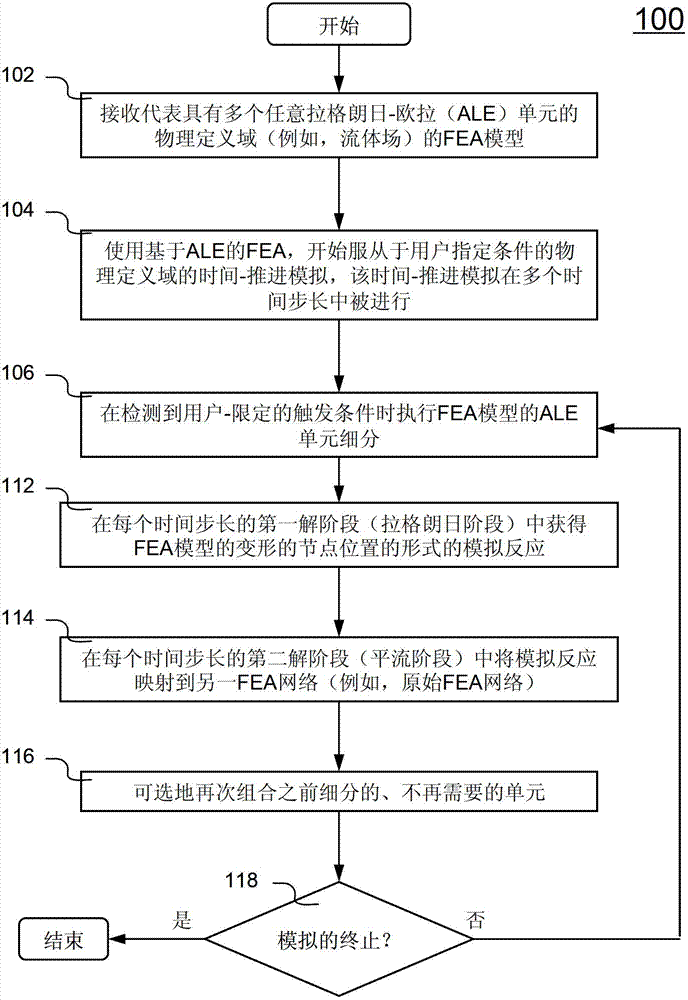
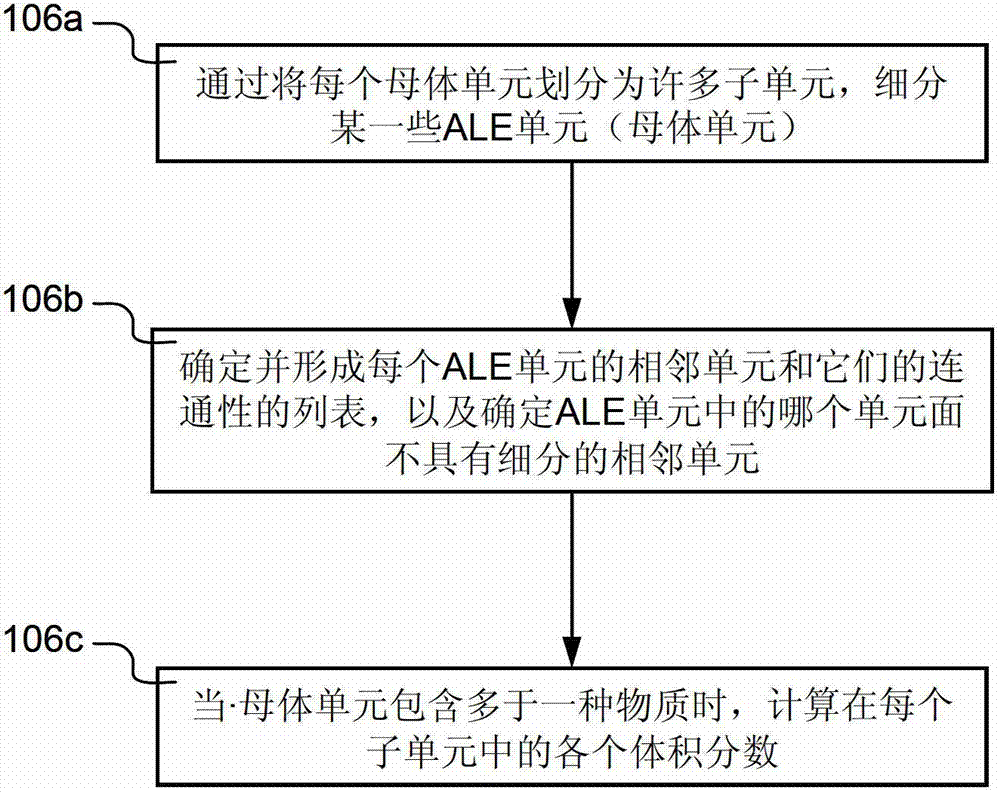
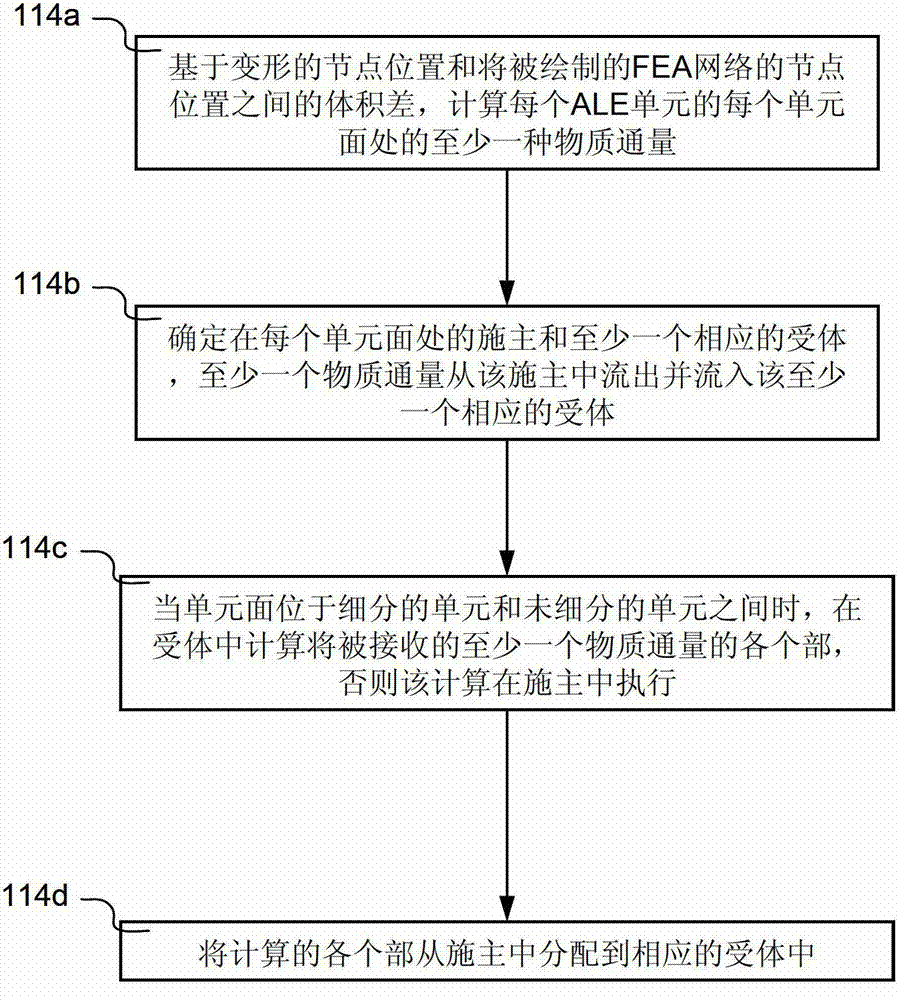
[0020] Figure 1A Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian ( ALE) flow chart of the schematic process 100 of the unit. Process 100 is implemented in software and is preferably understood in conjunction with the other figures herein.
[0021] Process 100 begins at step 102 by receiving a finite element analysis (FEA) model representing a physical domain (eg, air, ocean, etc.) having a plurality of ALE elements. Next, in step 104 , time-marching simulations are performed for obtaining simulated physical phenomena (eg, aerodynamics, hydrodynamics) of the physically defined domain subject to user-specified conditions using ALE-based FEA. The user-specified conditions include but are not limited to: initial conditions, boundary conditions, load conditions, and the like. The time-marching simulation is performed over multiple time steps (sometimes called solution cycles). Typically, in a time-marching simulation, the initial simulated response is obtained at time zero (t=0). Subsequent sim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com