Low-common-mode-noise grid-connected inverter circuit and reactive power control method
An inverter circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of converting irreversible DC power input to AC power output, control/regulation systems, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve large switching noise and current ripple amplitude, harmonics, etc. Wave distortion, common mode noise interference, large change in common mode voltage amplitude, etc., to achieve the effect of suppressing common mode current, reducing EMI, and strong overload capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
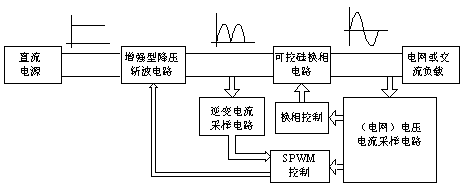
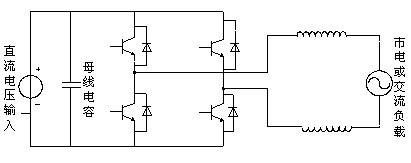
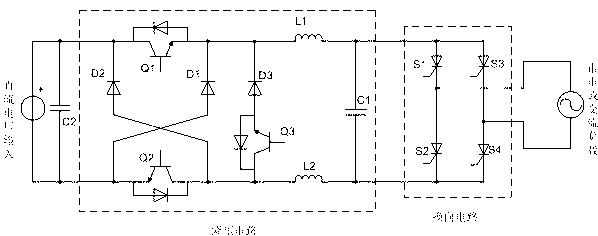
[0034] Such as figure 1 , image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, the DC / AC grid-connected inverter circuit includes enhanced step-down chopper circuit, thyristor commutation circuit, inverter current sampling circuit, voltage and current detection circuit, thyristor commutation control circuit and SPWM control circuit .
[0035] The enhanced step-down chopper circuit includes power switch Q1 (MOSFET or IGBT), power switch Q2 (MOSFET or IGBT), power switch Q3 (MOSFET or IGBT), diode D1, diode D2, diode D3, inductor L1, inductor L2, capacitor C1 and low frequency switch Q3, the drain (or collector) of power switch Q1 is connected to the anode of DC power supply and the cathode of diode D2, and its source (or emitter) is connected to one end of inductor L1, the cathode of diode D1 and the cathode of diode D3 The cathode is connected; the drain (or collector) of the power switch tube Q2 is connected to the anode of the diode D2, one end of the inductor L2 is connected to the source (o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com