Methods for Determining Cancer Incidence or Risk of Cancer Incidence
A cancer, risk technology, used in disease diagnosis, material excitation analysis, nanotechnology for sensing, etc., can solve problems such as low detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
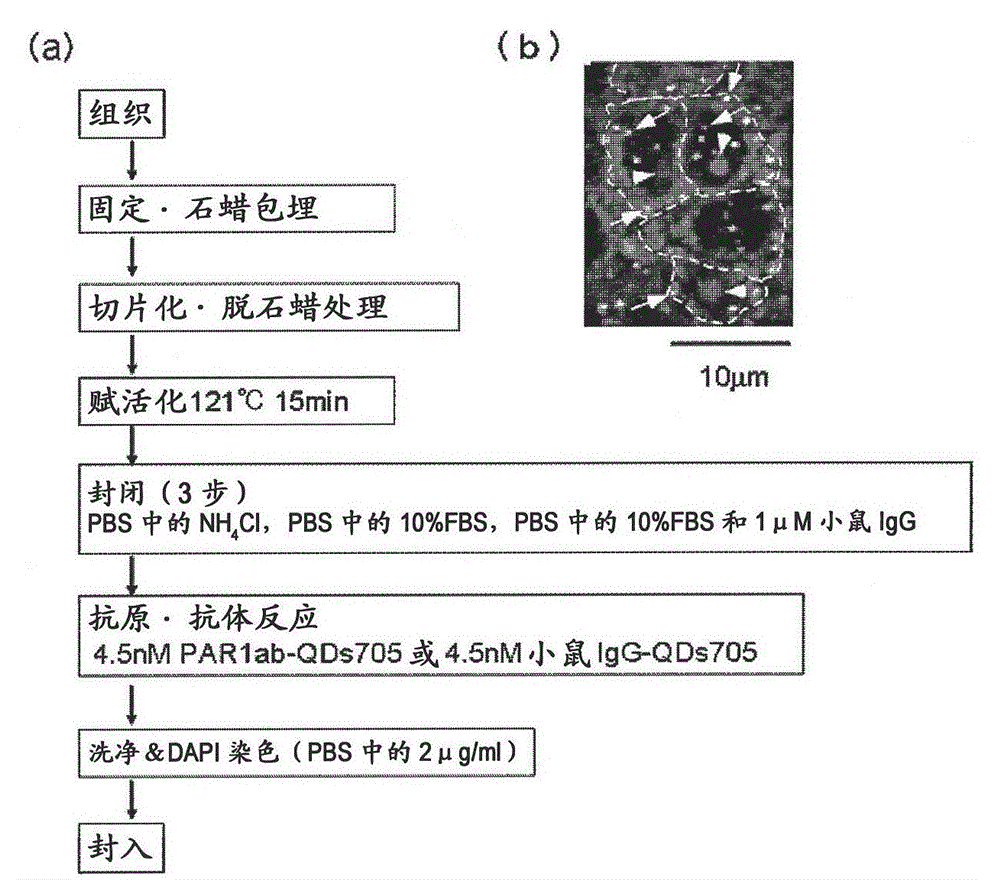
[0087] Preparation method of immunostained tissue sample
[0088] In order to distinguish the difference from HercepTest (breast cancer tissue detected by HER2 antibody), all HercepTest-negative tissue samples were used as human breast cancer pathological tissue. On the other hand, there are cancer cases unrelated to the three main factors (ER, PgR, HER2) related to the proliferation of breast cancer. It is generally believed that the "triple negative" breast cancer has a poor prognosis and is difficult to treat. Here, "triple negative" breast cancer tissue samples are also discussed. Specifically, 4 test samples of breast cancer tissues from recurrent patients (relapse within about 1 year and death within 4 years) (one of the test samples was triple negative [because 20-25% of recurrent patients are "triple negative", so random Add the "triple negative" label to 1 of the 4 test samples]), "triple negative" breast cancer tissue from recurrent patients (recurrence within 4 yea...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Problems with fluorescent immunohistostaining
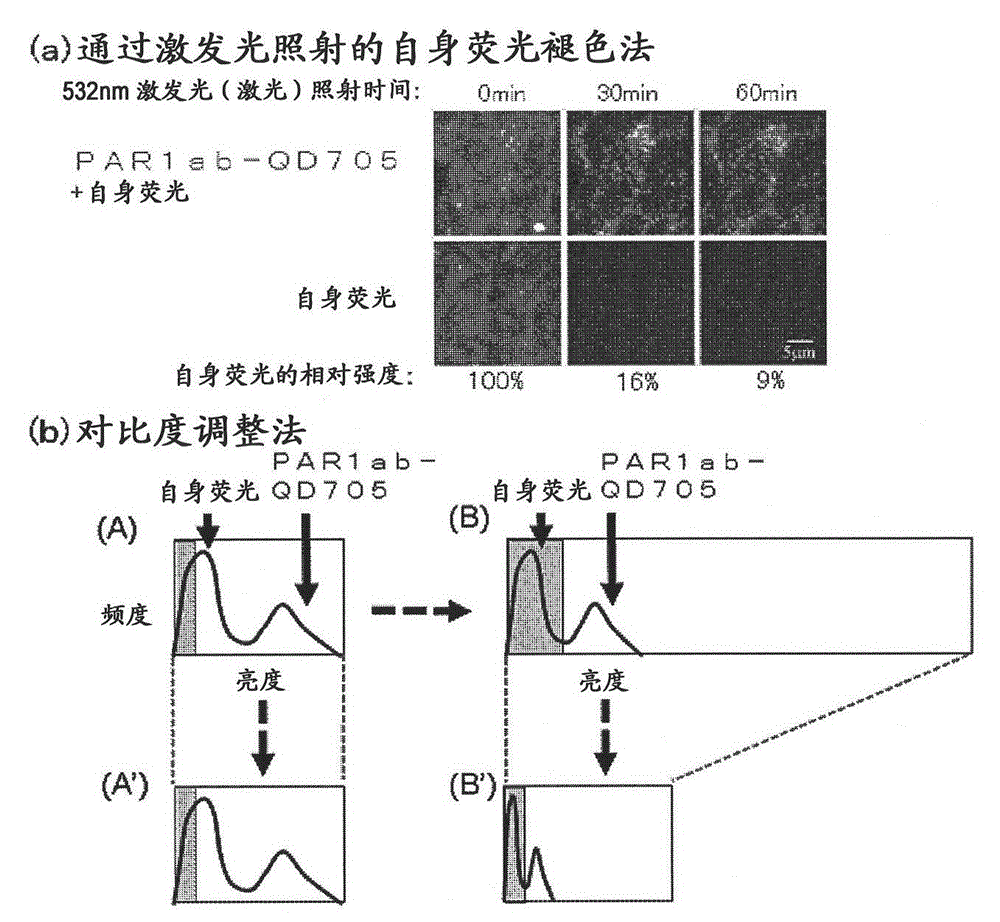
[0091] For the immunostained tissue sample prepared in Example 1 above, a combination of a confocal unit (manufactured by Yokogawa Electric Corporation), a fluorescence microscope (manufactured by Olympus Corporation), and an electron multiplier CCD (EM-CCD) imaging device (Andor (manufactured by the company) was irradiated with excitation light at 488 nm, and then a fluorescence image (fluorescence still image) of quantum dot fluorescent particles (detected by PAR1ab-QD705) was obtained using a bandpass filter of 695 to 740 nm. figure 1 (b) shows an example of a fluorescence still image of a tissue sample of a patient with recurrent breast cancer. Autofluorescence is so strong that quantum dot fluorescent particles (detected by PAR1ab-QD705) cannot be detected at first glance. Actually, when comparing the fluorescence brightness of autofluorescence and quantum dot fluorescent particles (detected by PAR1-antibody), only a...
Embodiment 3
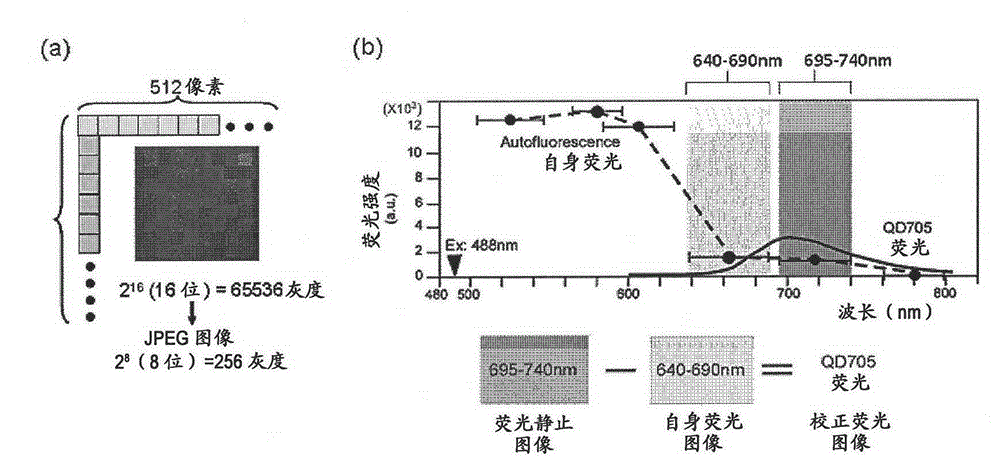
[0094] Creation of corrected fluorescence images with autofluorescence removed
[0095] Fluorescence still images with zero (0) fluorescence intensity of autofluorescence as background are required. In this way, the total fluorescence in the fluorescence still image can be calculated as the fluorescence derived from the quantum dot fluorescent particles. The contrast adjustment method of the above-mentioned embodiment 2 is a division method of fluorescence intensity, and zero (0) cannot be obtained by division, so it must be an image processing method using a subtraction method that can obtain zero (0). Thus, as an image processing method for removing autofluorescence in a fluorescent still image, the method described below is considered. First, the breast cancer tissue sample immunostained with quantum dot fluorescent particles is irradiated with excitation light (laser) with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm, and a fluorescence image of quantum dot fluorescent particles is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com