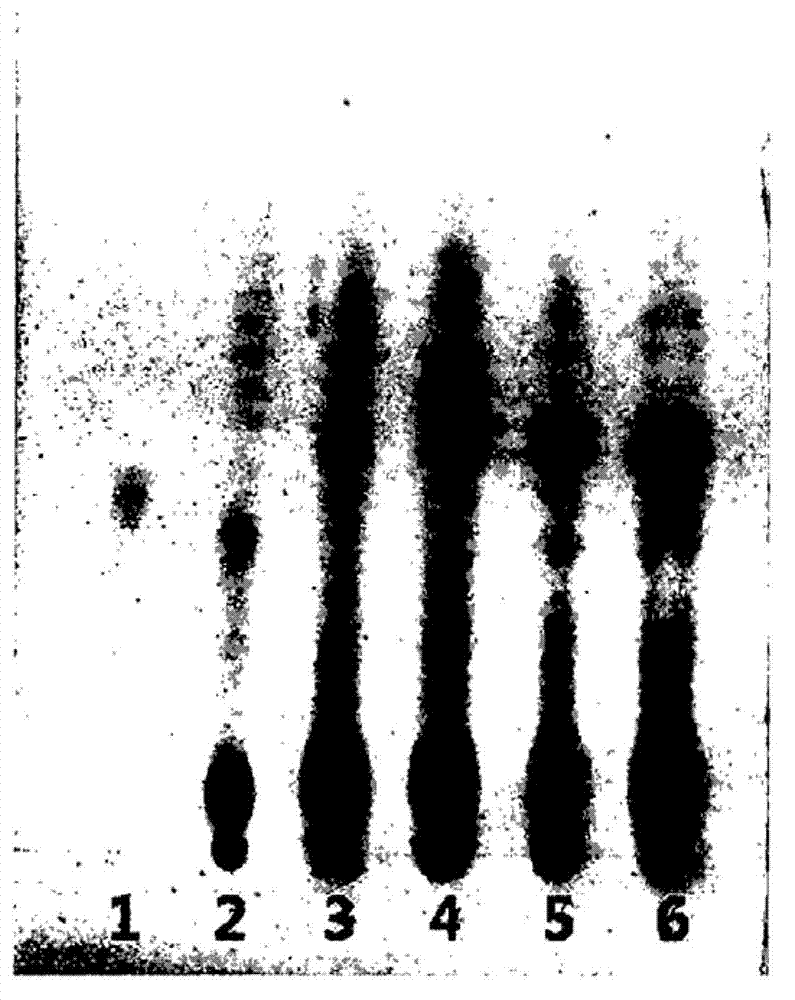Polypeptide associated with the synthesis of 1-deoxynojirimycin, and a use therefor
A technology of deoxynojirimycin and polynucleotides, which is applied to polypeptides related to the synthesis of 1-deoxynojirimycin and its application fields, and can solve problems such as genes that are not isolated from polypeptides.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0057] The present invention will be described in more detail below. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
[0058] The following examples are provided to illustrate preferred embodiments of the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
Embodiment 1
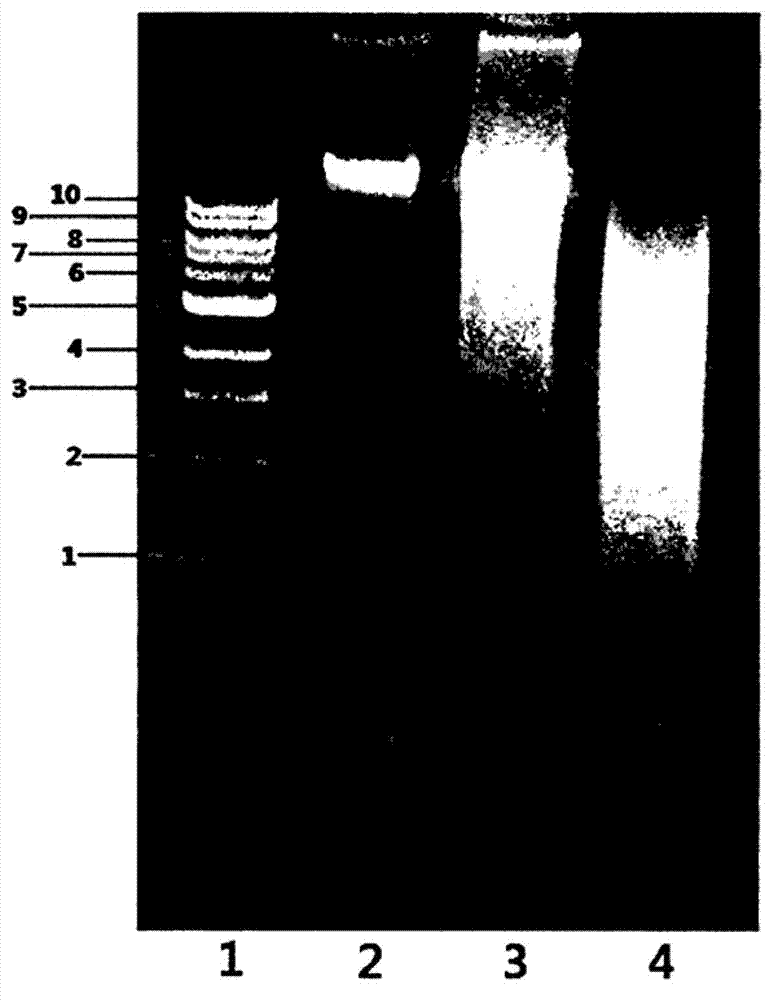
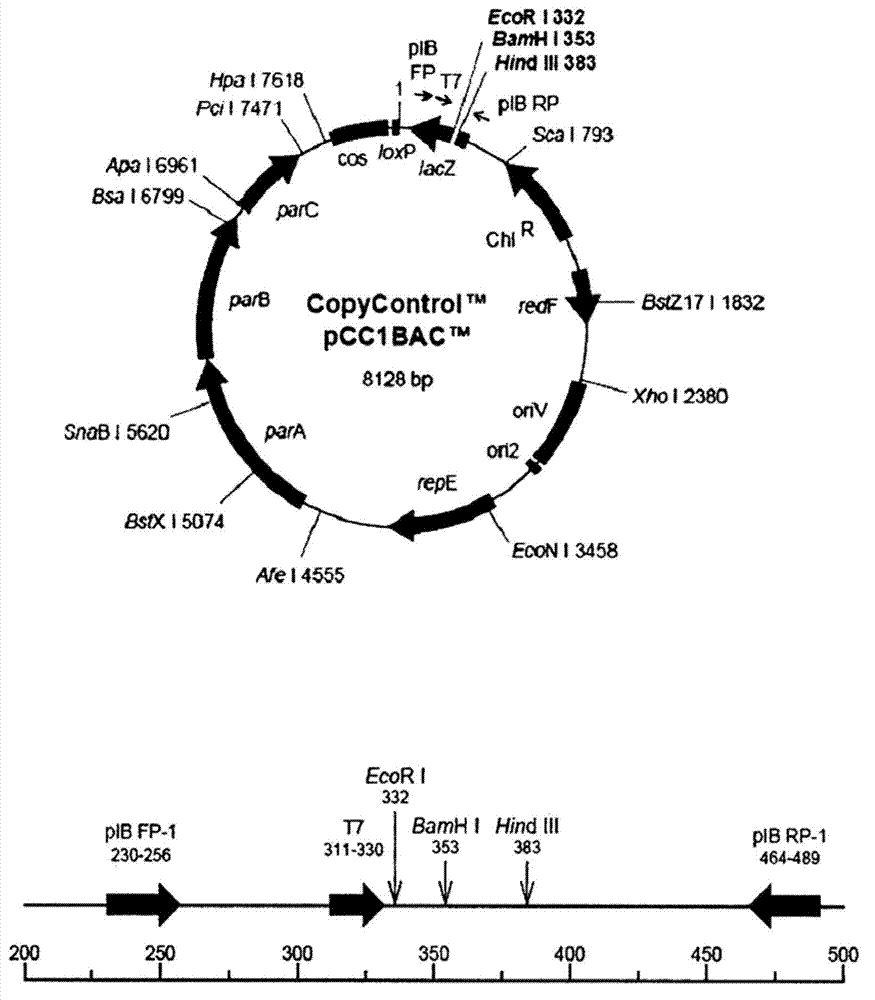
[0059] Example 1 Construction of a library using the genome of Bacillus subtilis MORI3K-85 producing 1-deoxynojirimycin
[0060] Strain culture
[0061] The improved Bacillus subtilis MORI3K-85 strain with improved α-glucosidase inhibitory activity was obtained from the isolated and identified Bacillus subtilis MORI (preservation number KCCM-10450) from Korean traditional food and irradiated with gamma rays. Specifically, the MORI strain was cultivated in Difco TMYM [Becton Dickinson and Company (BD), American BD Company] liquid medium, 180rpm shaking culture at 37°C for one day, and then irradiated with γ-rays (Soya GreenTec, South Korea) at a dose of 3kGy or 5kGy. The γ-ray-irradiated culture solution was spread on a YM agar plate and incubated at 37°C for 18 hours. Then, the formed colonies were transferred to fresh YM agar plates for incubation. Again, the colonies grown on the plate were inoculated into YM liquid medium, and cultured with shaking at 180 rpm at 37° C...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2 is screened by measuring inhibition of α-glucosidase activity
[0075] In order to select clones capable of producing 1-deoxynojirimycin from the white colonies, a method of measuring the activity of inhibiting α-glucosidase was used. The culture prepared in of Example 1 was heated at 100° C. for 10 minutes, and centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 10 minutes. To 5 μL of the supernatant were added 75 μL of 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), 50 μL of 12 mM p-nitrophenyl-α-glucopyranoside as a substrate, and 20 μL of crude enzyme solution. In order to prepare the crude enzyme solution, 0.8 g of rat small intestine acetone powder (Sigma, USA) was weighed and extracted in 100 mL of 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer for 1 hr. The resulting solution was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, and the resulting supernatant was used as a crude enzyme solution.
[0076] The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 35 min, and the enzyme reaction was terminated with 50 μL o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com