Electrode, electrically heated catalytic converter using same and process for producing electrically heated catalytic converter
一种催化剂装置、制造方法的技术,应用在电极领域,能够解决电极龟裂、剥离等问题,达到电阻值抑制的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
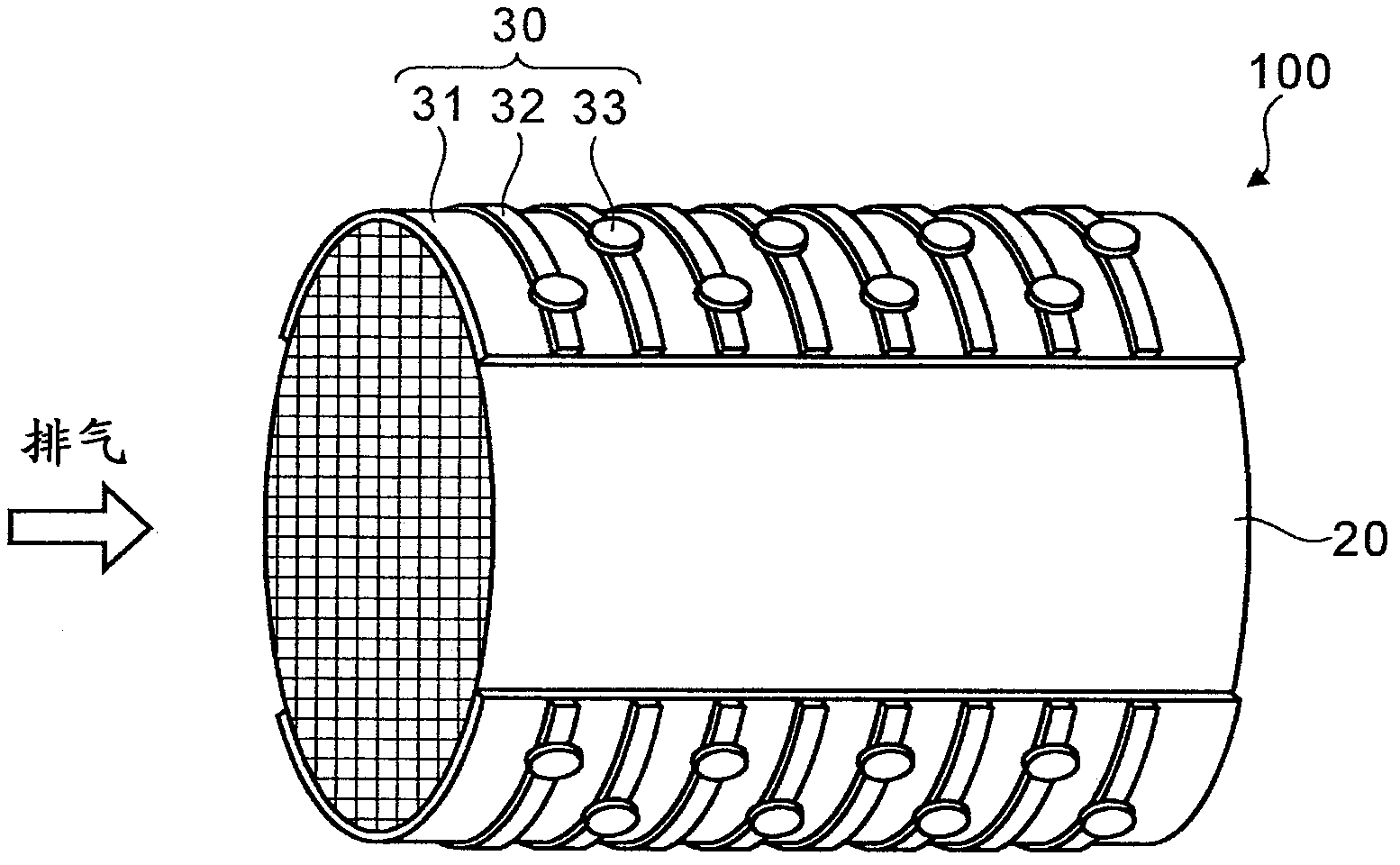
[0070] First refer to figure 1 , figure 2 The electrically heated catalyst device according to this embodiment will be described. figure 1 It is a perspective view of the electrically heated catalyst device 100 according to the first embodiment. The electrically heated catalyst device 100 is installed, for example, in an exhaust port of an automobile, and is used to purify exhaust gas discharged from the engine. like figure 1 As shown, the electrothermal catalyst device 100 includes a carrier 20 and an electrode 30 .
[0071] The carrier 20 is a porous member for supporting a catalyst such as platinum or palladium. In addition, the carrier 20 itself is made of conductive ceramics, specifically SiC (silicon carbide), for example, since it is heated by energization. like figure 1 As shown, the carrier 20 is cylindrical in shape and has a honeycomb structure inside. As indicated by the arrow, the exhaust gas passes through the inside of the carrier 20 along the axial dire...
Embodiment 1)
[0110] By a gas atomization method, substrate particles having a particle diameter of 10 to 50 μm (average particle diameter of 30 μm) formed of a Ni-50% by mass Cr alloy constituting the metal substrate were produced.
[0111] On the other hand, dispersed phase particles comprising bentonite having a particle diameter of 10 to 50 μm (average particle diameter of 30 μm) constituting the dispersed phase were produced by a spray drying method. The particles were sintered at a temperature of 1050° C. in a hydrogen atmosphere.
[0112] Next, the matrix particles and the dispersed phase particles were composited by kneading and granulation using a polymeric binder as a medium, and sintered at a temperature of 1050°C in a hydrogen atmosphere to produce particles for spraying.
[0113] Next, the aforementioned particles for spraying were plasma sprayed onto the surface of the carrier 20 made of SiC to form a base layer 31 with a thickness of 150 μm.
[0114]Next, a metal foil 32 wit...
Embodiment 2)
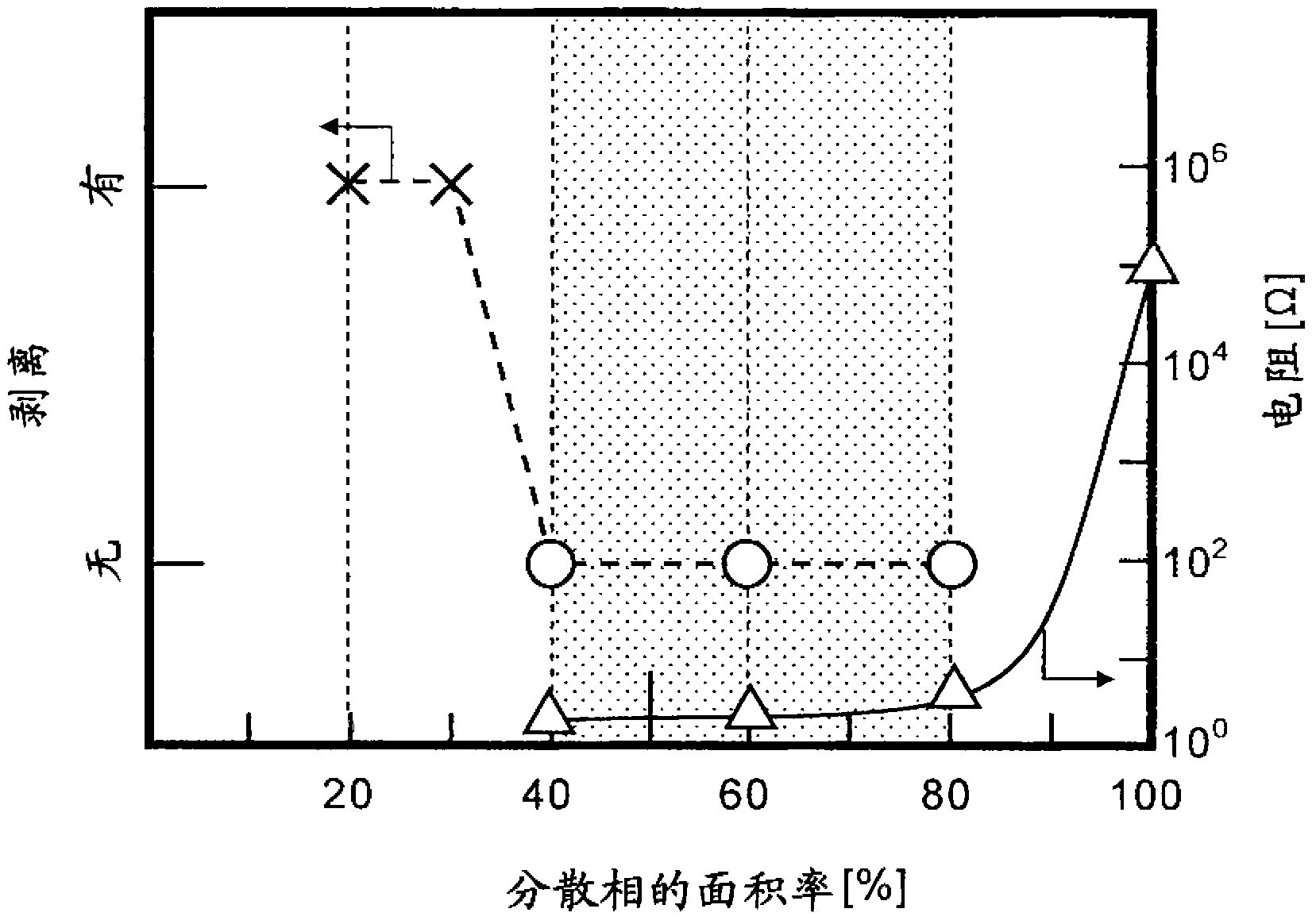
[0118] A fusion coating was formed in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the area ratio of the dispersed phase was 60%. As a result, the resistance after thermal cycling was 2.8Ω, which is very good.
[0119] here Figure 16 This is a photograph of the cross-sectional structure of the fusion coating according to Example 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com