Organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme transformed through mutation and encoding gene thereof
A technology of organophosphorus pesticides and coding genes, which is applied in the field of organophosphorus pesticides degrading enzymes, can solve the problems of no achievements and achieve the effects of great application value, high degradation efficiency, and not easy to inactivate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Expression of the organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme of the present invention in E. coli (1) PCR amplification: PCR amplification of the present invention with upstream primer 5'-ATTCATATGGCCGCACCGCAGGTG-3' and downstream primer 5'-TAACTCGAGCTTGGGGTTGACGACCG-3' The organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene.
[0026] PCR (50μL system) reaction conditions: 50ng of the organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene of the present invention (SEQ ID No.1) as a template, 0.3μM each of the upstream primer and downstream primer, 200μM each of dNTPs, 5U Taq DNA polymerase, 5μL PCR buffer Solution, 30 cycles, denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 55°C for 1 min, extension at 72°C for 1 min, and the last cycle for extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0027] The composition of PCR buffer is: 100mM Tris-HCl pH8.3, 500mM KCl and 15mM MgCl 2 , The solvent is deionized water.
[0028] (2) Expression vector construction: The above...
Embodiment 2
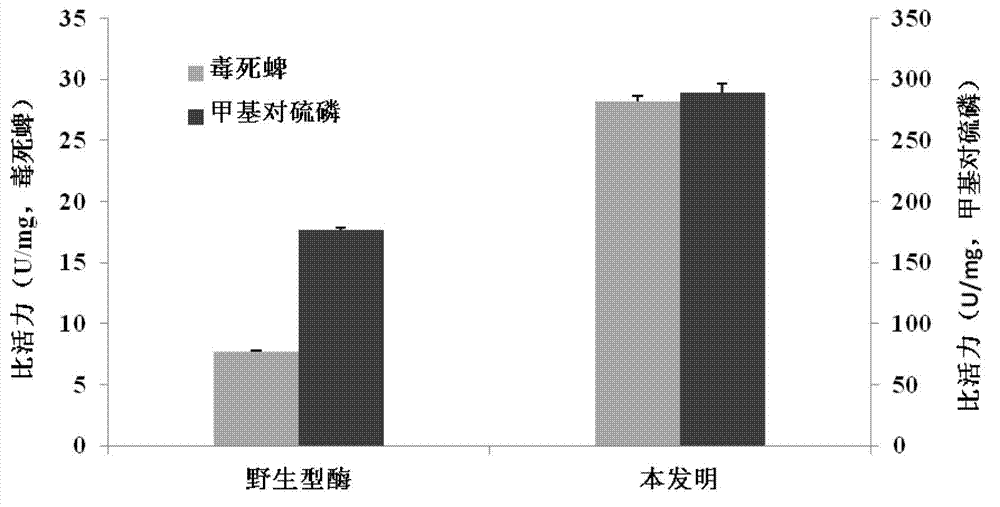
[0074] Example 2: Determination of the degradation specific activity of the organophosphorus pesticide of the present invention
[0075] Using methyl parathion and chlorpyrifos as substrates, respectively, the specific activities of the organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme and the wild-type enzyme of the present invention are measured.
[0076] The production method of the wild-type enzyme is as follows: the organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene mpd (GenBank accession number: JQ686087) is used as a PCR template, and the other operation steps are completely performed in accordance with the method of Example 1.
[0077] With methyl parathion as the substrate, the specific activity determination method is as follows:
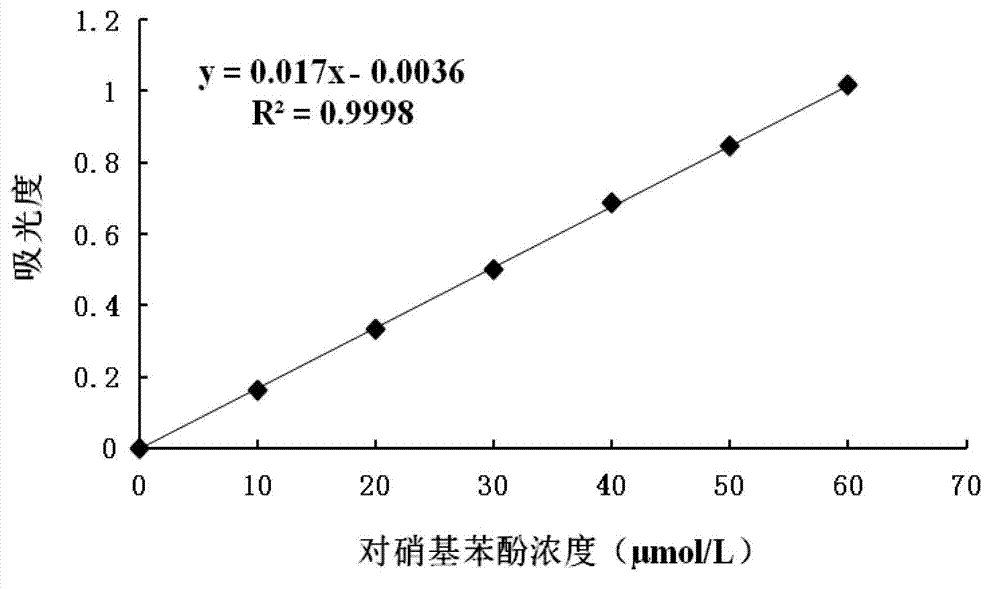
[0078] (1) Preparation of p-nitrophenol standard solution: use 20μM Tris-HCl (pH8.0) buffer as a solvent to prepare p-nitrophenol with concentrations of 10μM, 20μM, 30μM, 40μM, 50μM, 60μM. Phenol standard solution.
[0079] (2) Drawing the standard curve o...
Embodiment 3
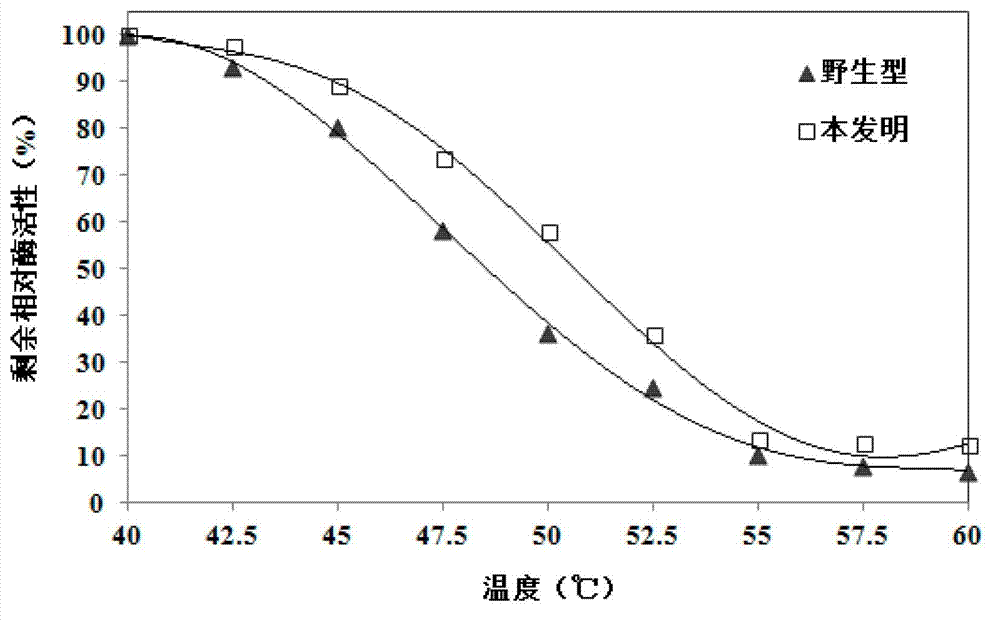
[0108] Example 3: Determination of the thermal stability of the organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme of the present invention
[0109] The purified organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme and wild-type enzyme of the present invention with a concentration of 100 μg / ml obtained in Example 1 were heated at 40°C, 42.5°C, 45°C, 47.5°C, 50°C, 52.5°C, 55°C, respectively After heat treatment at 57.5°C and 60°C for 10 minutes, immediately place it on ice and keep for 30 minutes. Use chlorpyrifos as a substrate to determine enzyme activity and analyze thermal stability.
[0110] The production method of the wild-type enzyme is as follows: the organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene mpd (GenBank accession number: JQ686087) is used as a PCR template, and the other operation steps are completely carried out in accordance with the method of Example 1.
[0111] The determination method of enzyme activity is as follows:
[0112] (1) Preparation of chlorpyrifos standard solution: u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com