Method for directional induction of differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
A stem cell differentiation and mesenchymal stem cell technology, applied in the field of directional induction of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, can solve problems such as cell separation difficulties, identification or application obstacles, and achieve the effect of improving induction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1. Growth and migration of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycarbonate membranes with different pore sizes
[0033] 1. Group processing
[0034] 1. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells were treated with a mesenchymal stem cell medium containing 10 mg / L mitomycin C for 3 hours, and then the cells were washed with the mesenchymal stem cell medium and suspended.
[0035] 2. Group processing:
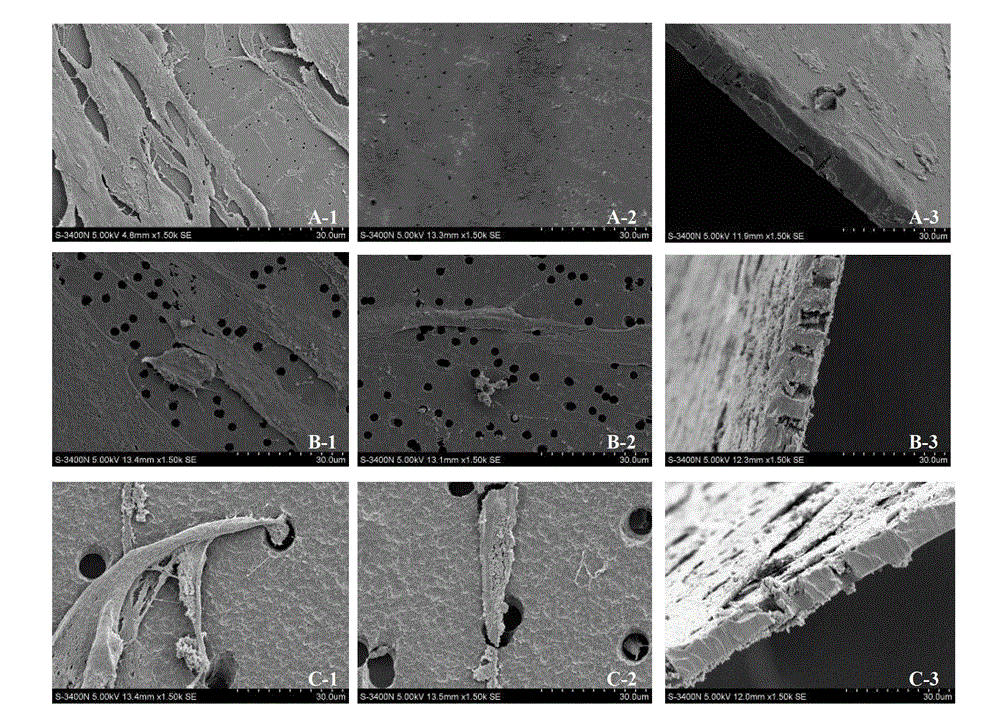
[0036] The first group: 6 Transwell chambers (polycarbonate membrane at the bottom with a diameter of 24 mm, a pore diameter of 0.4 μm, and a thickness of 10 μm) were placed on a 6-well cell culture plate;
[0037] The second group: 6 Transwell chambers (polycarbonate membrane at the bottom with a diameter of 24 mm, a pore diameter of 1.0 μm, and a thickness of 10 μm) were placed on a 6-well cell culture plate;
[0038] The third group: 6 Transwell chambers (polycarbonate membrane at the bottom with a diameter of 24 mm, a pore diameter of 3.0 μm, and a thick...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2. New Transwell co-culture induces UCMSCs to differentiate into epidermoid cells
[0051] 1. Group processing
[0052] 1. Human epidermal stem cells were treated with epidermal stem cell medium containing 10 mg / L mitomycin C and 10% calf serum for 3 hours, and then cells were washed with epidermal stem cell medium and suspended.
[0053] 2. Treat the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with a mesenchymal stem cell medium containing 10% calf serum for 3 hours, then wash the cells with the mesenchymal stem cell medium and suspend the cells.
[0054] 3. Group processing
[0055] The first group (flow chart see figure 2 A, co-cultivation of the front and back sides of the polycarbonate membrane at the bottom of the Transwell chamber): Under sterile conditions, take 6 Transwell chambers (the diameter of the polycarbonate membrane at the bottom is 24mm, the pore diameter is 0.4μm, and the thickness is 10μm), and the bottom is reversed. In a sterile 15cm petri d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com