Lithium ion secondary battery charging method
A secondary battery and charging method technology, which is applied in the direction of secondary battery charging/discharging, secondary battery repair/maintenance, battery electrodes, etc. The effect of shortening the time required for charging and suppressing heat generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
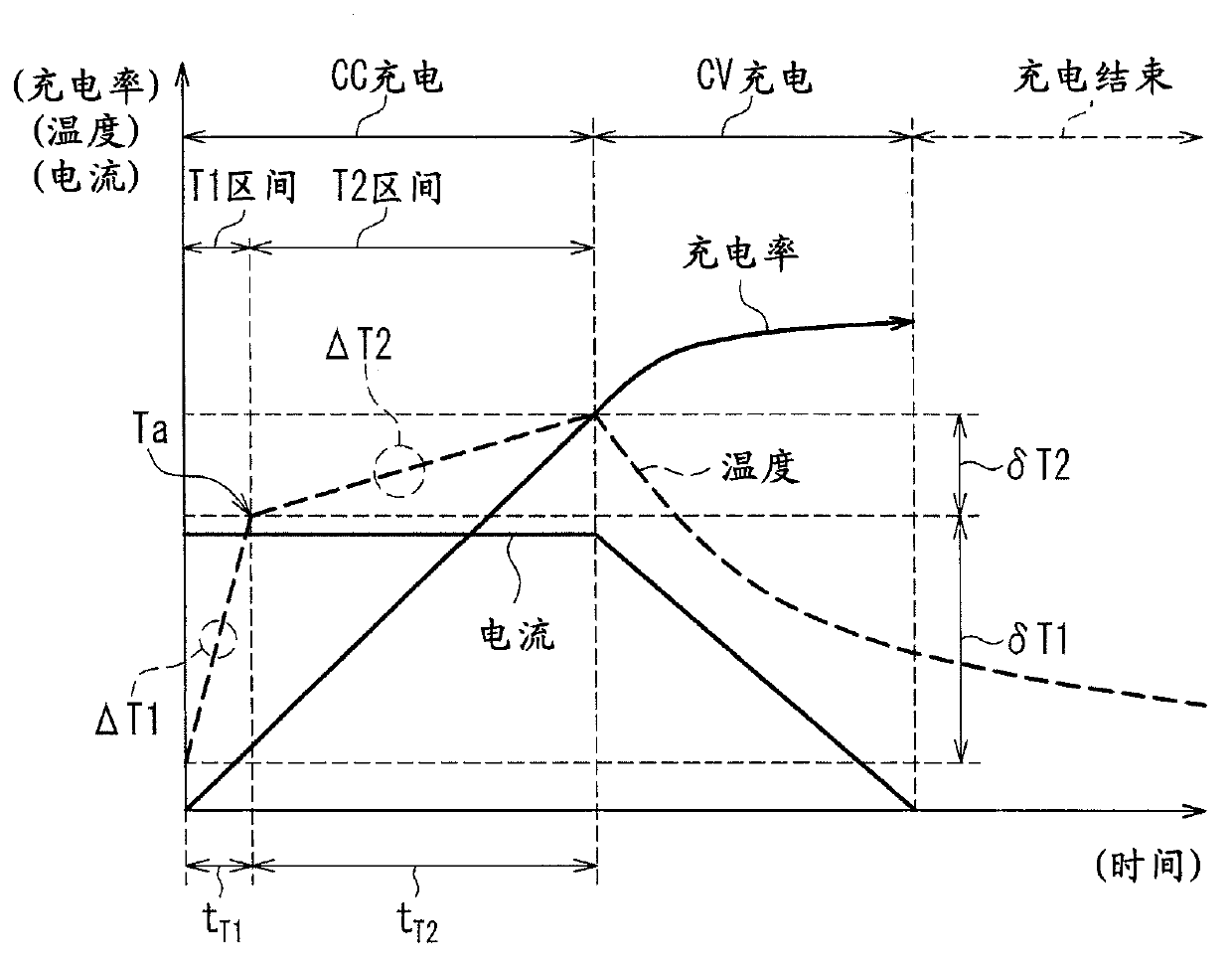
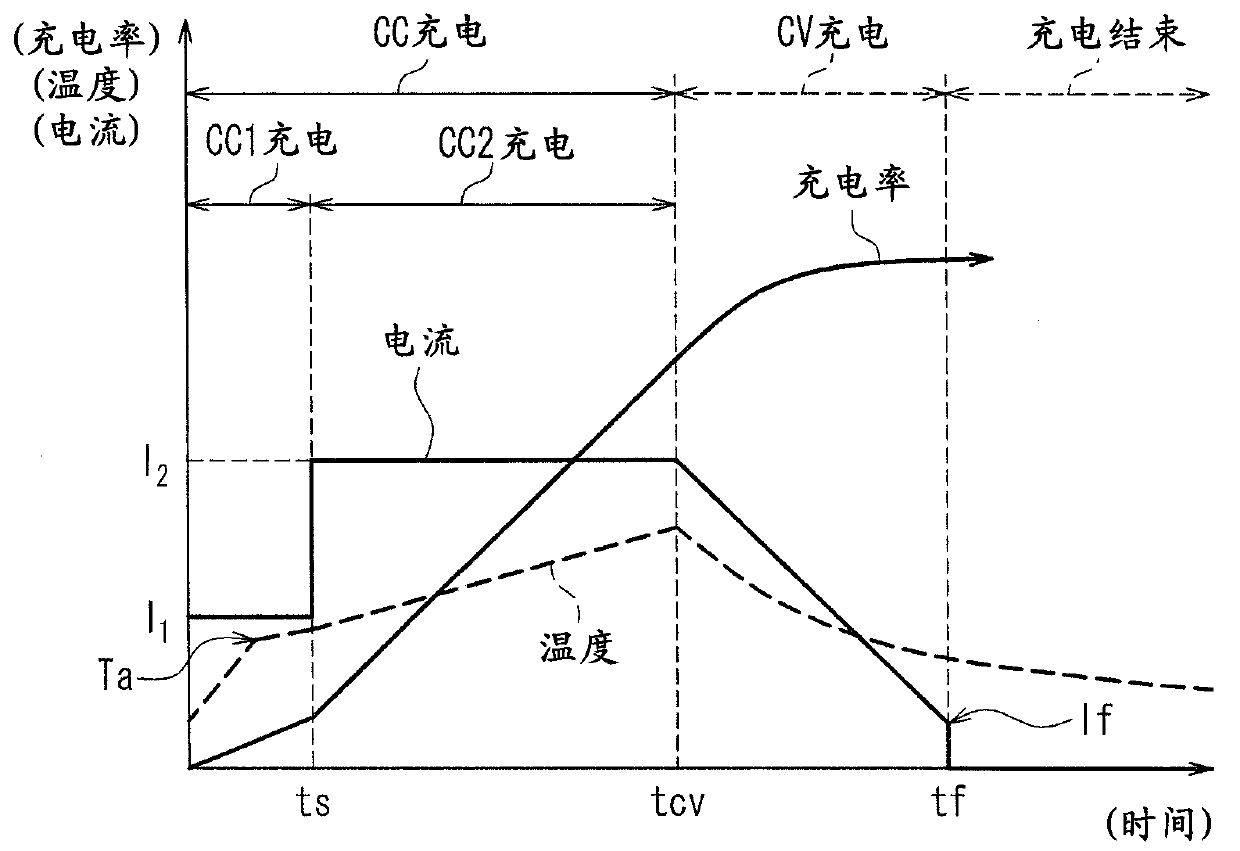
[0062] refer to figure 2 A charging method of the lithium ion secondary battery according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described. exist figure 2 In , the horizontal axis represents time, and the vertical axis represents current, charging rate, and temperature.
[0063] This charging method basically belongs to the CCCV charging method. That is, CV charging is performed up to a predetermined set voltage Vc (voltage illustration is omitted), and from the time (tcv) when the set voltage Vc is reached, CV charging is performed while reducing the charging current to maintain the set voltage. Charge. At time tf when the charging current reaches the set value If, the CV charging is stopped and the charging is completed.
[0064] This embodiment is characterized by the process of CC charging, such as figure 2 As shown, the time when the switching time ts has elapsed from the start of charging is set as the boundary, CC1 charging is performed at the initia...
Embodiment approach 2
[0082] The charging method of the lithium ion secondary battery of the second embodiment is substantially the same as that of the first embodiment. In this embodiment, the switching time ts1 of the first embodiment is replaced by the switching time ts2. therefore, figure 1 , figure 2 The content shown is common to this embodiment except for the switching time ts1, and the achieved effect is also the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0083] The switching time ts2 in this embodiment is set as follows. That is, for a lithium-ion secondary battery of the same specification as the charging target, charging is started from the state of charging rate 0%, and the charging time t until the change point Ta of the temperature rise gradient is detected is measured. TA .
[0084] If with charging time t TA The switching time ts2 is set correspondingly, and the switching time ts2 is set at the moment when the change point Ta appears. This makes it possible to switch from CC1 c...
Embodiment approach 3
[0091] The charging method of the lithium ion secondary battery of the third embodiment is substantially the same as that of the first embodiment. figure 1 , figure 2The contents shown are common to the present embodiment and are based on the same principle as that of the first embodiment. This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that it includes a step of determining the state of charge of the lithium-ion secondary battery before starting charging, thereby further improving the effect of shortening the charging time.
[0092] The state of charge of the lithium-ion secondary battery is determined in order to detect whether the battery is in a state before the change point Ta or a state beyond the change point Ta in the temperature rise gradient of the battery under CC charging. Then, if the state of charge is the state before the change point Ta, CC charging is performed at the first current value from the start of charging until the above-mentioned switching time ts el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com