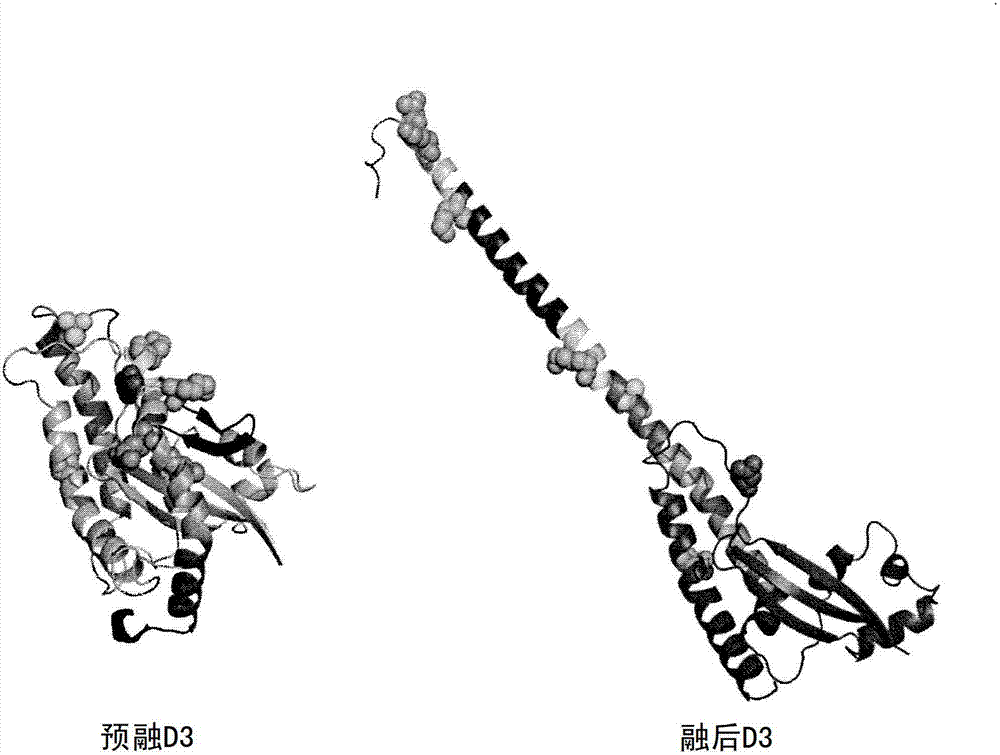
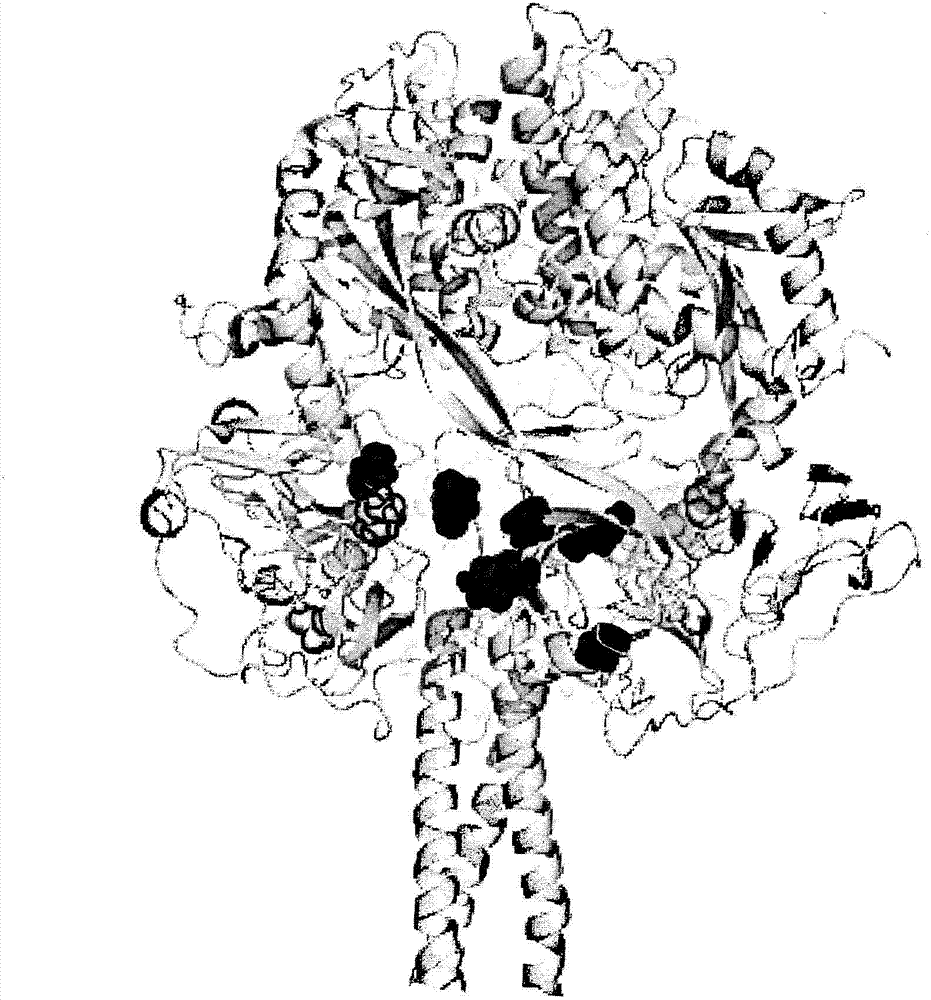
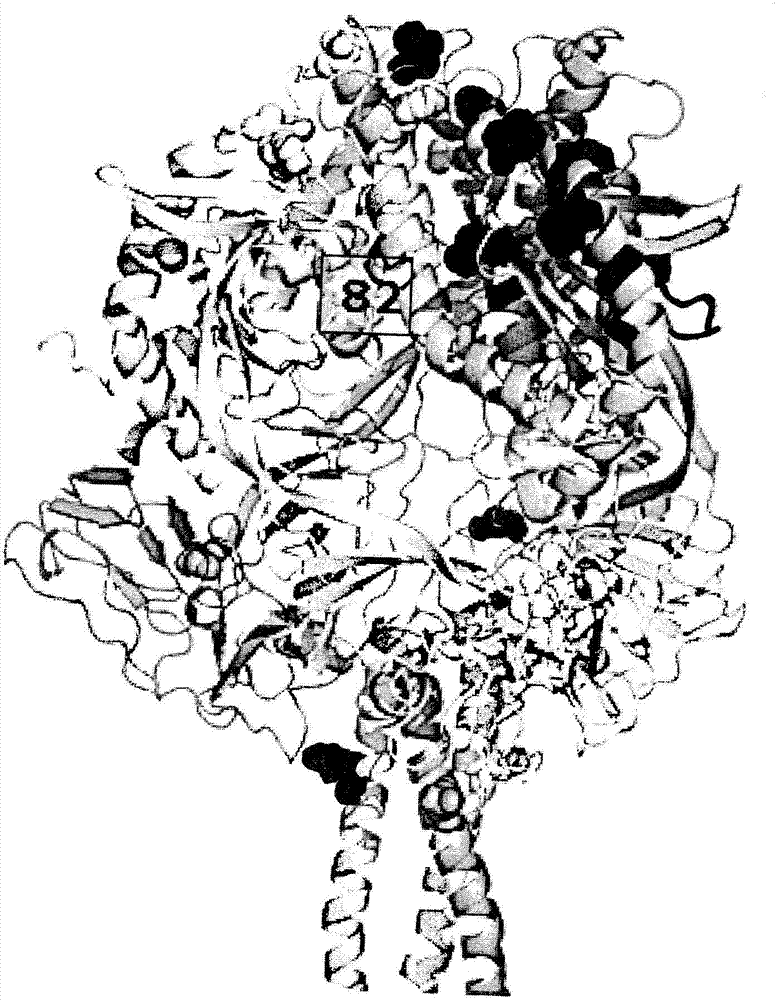Anti-human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) antibodies and methods of use
A technology of antibodies and viruses, applied in antiviral agents, respiratory diseases, viruses/bacteriophages, etc., can solve problems such as vaccine treatment without RSV
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0715] Expression of embodiment 1 RSV F protein
[0716] In this example, the RSV fusion protein (F protein) from RSV strain A2 was expressed and captured on an ELISA plate using anti-RSV monoclonal antibody clone 2F7, which recognizes the F0 and F1 subunits of the fusion glycoprotein. Purify. In a first example, recombinant RSV F protein was cloned and expressed in 293F cells. In a second example, the native RSV F protein was expressed by infecting HEp-2 cells with the RSV A2 strain.
[0717] A. Recombinant RSV F protein
[0718] In this example, the gene encoding the RSV F protein from the A2RSV strain was cloned and expressed. The RSV A2F gene (SEQ ID NO: 21 ) containing only the extracellular domain was synthesized according to standard DNA synthesis methods from GeneArt (Burlingame, CA). The RSV A2F gene was engineered to include a Kozak sequence (nucleotides 7-16 of SEQ ID NO:21), a c-myc sequence (nucleotides 1600-1629 of SEQ ID NO:21) and a 6X-His tag (SEQ ID NO : n...
Embodiment 2
[0724] Example 2 Isolation of anti-RSV Fab antibodies from EBV-transformed B cells
[0725] In this example, anti-RSV antibodies were isolated from stimulated Epstein-Barr virus-transformed donor memory B cells, the cells were screened for binding to the RSV F protein, and then subjected to in vitro antibody production. Sections A and B describe two slightly different methods for generating and cloning EBV-transformed B cells and screening for binding to RSV F protein. The differences are as follows: (1) the source of PMBC in step 1; (2) the isolation of IgG+B cells in step 2 (IgM, IgD and IgA expressing cells were removed in section A, and CD3 positive cells were additionally removed in section B); and (3) preparation of B-cell-depleted feeder cells irradiated in step 3.a.
[0726] A. Generation and cloning of EBV-transformed B cells and screening for binding to RSV F protein (Method A)
[0727] Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBC) were obtained from child care workers...
Embodiment 3
[0866] Embodiment 3 separates anti-RSV Fab antibody by single cell sorting
[0867] In this example, anti-RSV antibodies were isolated from CD19 / CD27 / IgG positive cells. CD19 / CD27 / IgG positive cells were obtained by 1) B cell isolation; and 2) FACS single cell sorting. The sorted cells are then used to isolate RNA that serves as a template for the production of Fab antibodies in vitro.
[0868] B cell isolation
[0869] B cells were isolated from PBMCs (harvested from anonymous blood bank donors) using a B cell isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Cat. No. 130-091-151). The kit is used to magnetically label and remove cells expressing CD2, CD14, CD16, CD36, CD43 and CD235a (activated B cells, plasma cells and CD5 + B-1a cells) and non-B cells (such as T cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, granulocytes and erythroid cells) to isolate highly pure B cells. By using biotin-conjugated monoclonal antibody (biotin-antibody mixture) as primary labeling reagent and anti-bioti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com