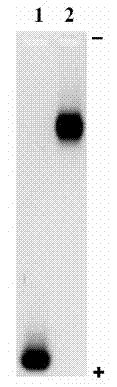
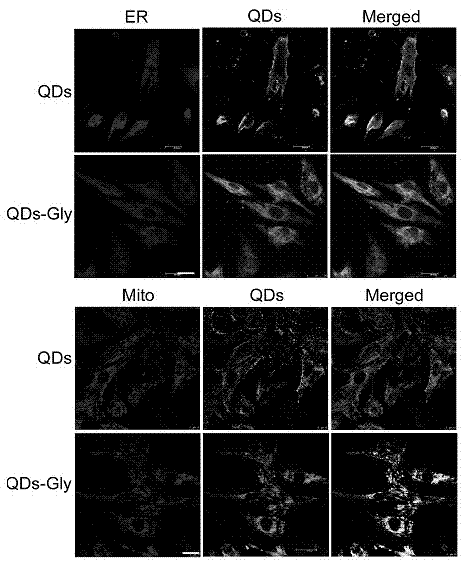
Method of using glycine modified quantum dot probes to mark living cell
A technology of quantum dots and glycine, which is applied in the field of glycine-modified quantum dot probes for labeling living cells, can solve problems such as the need for improvement of quantum dot probe modification methods, and achieves short reaction time, low requirements for experimental conditions, and short incubation time. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The quantum dot-glycine probe can be applied to the labeling of various living cells, and the usage method is similar. However, depending on the cell type and culture method (suspension, adherence), the labeling effect may be different, and the required probe concentration should also be adjusted as needed. And the quantum dot-glycine probe obtained by coupling the carboxyl group of the water-soluble quantum dot with the carboxyl functional group and the amino group of glycine, and the quantum dot-glycine probe obtained by coupling the amino group of the water-soluble quantum dot with the amino functional group and the carboxyl group of glycine obtained in different cells The results achieved may vary between experiments and experimental conditions. The following takes the primary cultured myocardium as an example for specific description.
[0025] (1) Reagents and instruments:
[0026] 1. Cells: primary cultured SD rat suckling rat cardiomyocytes
[0027] 2. Main re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com