High-frequency electro-optic position phase modulator
A phase modulator and electro-optic crystal technology, applied in the field of laser spectroscopy, can solve problems such as low Q value, lower crystal optical quality, and affect modulator efficiency, etc., achieve low half-wave voltage and improve microwave coupling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
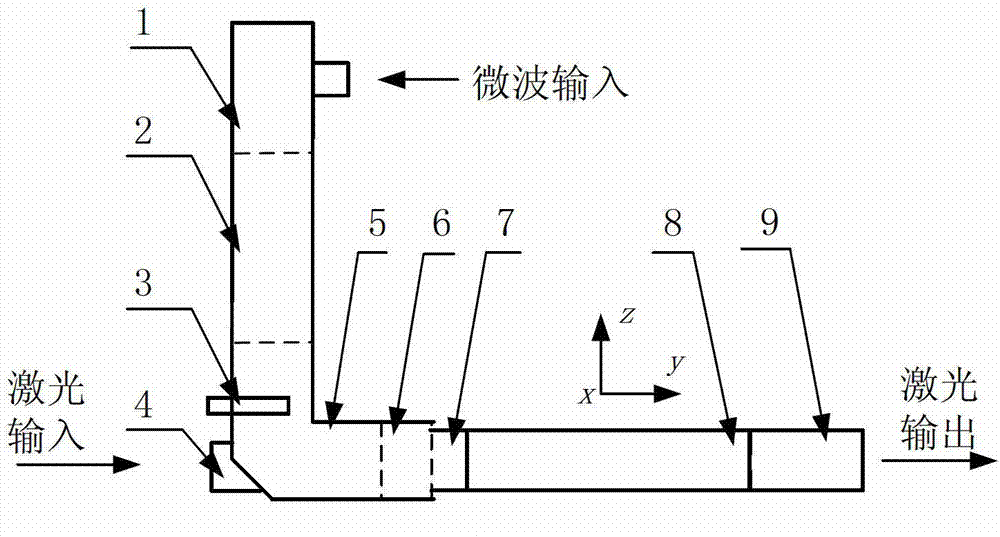
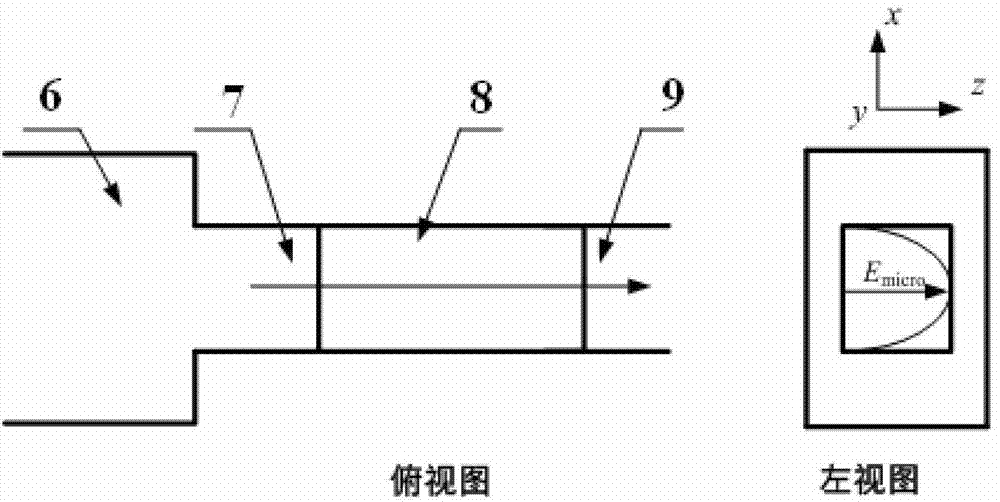
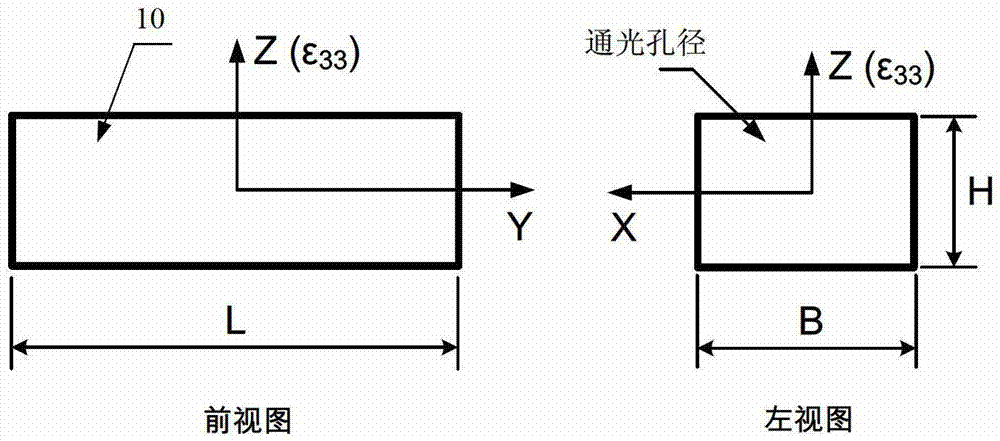
[0034] see first figure 1 , figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the high-frequency electro-optic volume phase modulator of the present invention. It can be seen from the figure that the high-frequency electro-optic volume phase modulator of the present invention is composed of a waveguide coaxial converter 1, a first waveguide 2, an E-plane curved waveguide 5, a second waveguide 6, first cut-off waveguide 7, electro-optic crystal 8 and second cut-off waveguide 9, the first waveguide 2, the E-plane bend waveguide 5 and the second waveguide 6 are integrated, the other end of the first waveguide 2 Connected to the waveguide coaxial converter 1 through a standard flange, the first cut-off waveguide 7 and the second cut-off waveguide 9 are integrated with the light-transmitting surface package at both ends of the electro-optic crystal 8, and the The four sides of the electro-optic crystal 8 are gold-plated, and the electro-optic crystal 8 forms a high-frequency microw...
Embodiment 2
[0046] see first figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of an embodiment of the present invention. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the waveguide described is a non-standard waveguide formed after the E-plane transition of the microwave band, such as Figure 4 As shown in the figure: GD_1-standard waveguide, GD_2-E-plane tapered transition waveguide, GD_3-non-standard waveguide.
[0047] The microwave operating frequency of the modulator, after the modulator is packaged, use a microwave network analyzer to test the TE of the modulator 10m Mode frequency, and as the actual microwave operating frequency of the modulator.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is that the E-plane curved waveguide 5 is provided with an adjusting screw 3 to adjust the microwave coupling efficiency.
[0050] for example:
[0051] Take the bulk modulator with a microwave operating frequency of ~10GHz as an example, in the figure: 1 is the waveguide coaxial converter of the X-band; the first waveguide 2 is the E-plane tapered transition waveguide of the X-band; the screw 3 is M2; The hole 4 is 3×3mm; the curvature of the E-plane curved waveguide 5 is 90 degrees; the second waveguide 6 is a non-standard height waveguide; the first cut-off waveguide 7; the electro-optic crystal 8 is a four-sided gold-plated lithium niobate crystal; the second cut-off waveguide 9. The microwave operating frequency of the modulator is 10.3GHz, and the aperture of the modulator is 3×2mm, S 11 The parameter is less than -15dB. Narrowband pulsed laser with a wavelength of 1053nm and a pulse width ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com