A method of producing directionally solidified polycrystalline silicon ingots
A polycrystalline silicon ingot, directional solidification technology, applied in polycrystalline material growth, chemical instruments and methods, crystal growth, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the temperature and time of silicon ingots, reduce dislocation density, shorten production cycle, and reduce production Effect of Energy Consumption and Argon Consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
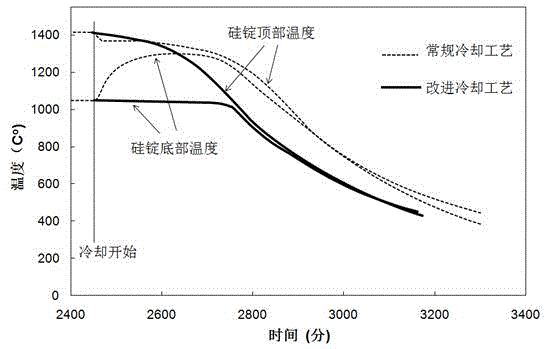
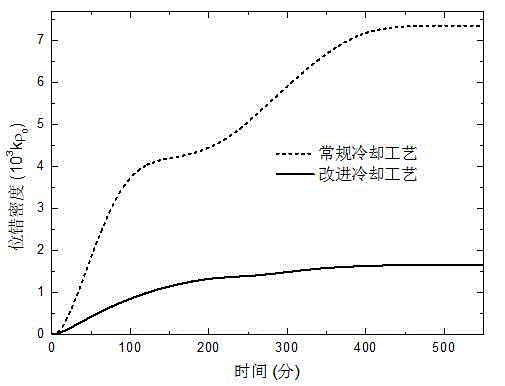
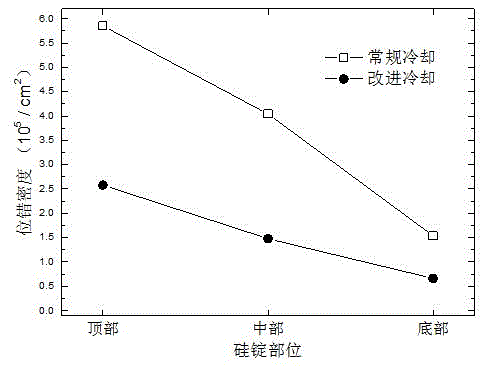
[0016] Polysilicon ingots are grown in a 450-kilogram directional solidification polysilicon furnace with an ordinary lifting and insulating cage type (such as produced by GT in the United States). The material of the crucible is high-purity quartz ceramics, the size is 840x840x350mm 3 . After the silicon ingot completes solidification and growth in the furnace, it enters the cooling stage. By adjusting and controlling the power of the furnace heater and the width of the heat dissipation channel below the bottom of the crucible, two cooling processes, conventional cooling and the improved cooling of the present invention, are realized respectively, and the conventional cooling polysilicon ingot and the improved cooling polysilicon ingot are obtained, and the cooling time of the latter is shortened by about 2 times compared with the former Hour.
[0017] After the two kinds of silicon ingots were sectioned, samples were sampled and polished at different parts and dislocations...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Polysilicon ingots are grown in a 450-kilogram directional solidification polysilicon furnace using an ordinary lifting and insulating base type (such as that produced by China Jinggong). The material of the crucible is high-purity quartz ceramics, the size is 840x840x350mm 3 . After the silicon ingot completes solidification and growth in the furnace, it enters the cooling stage. By adjusting and controlling the power of the furnace heater and the width of the heat dissipation channel below the bottom of the crucible, two cooling processes, conventional cooling and improved cooling, are realized respectively, and conventional cooling polysilicon ingots and improved cooling polysilicon ingots are obtained. The cooling time of the latter is about 2.5 hours shorter than that of the former.
[0024] After the two silicon ingots were cut, samples were polished at different parts and dislocations were etched. After that, the etched surface was randomly sampled under the con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com