Method for producing a monocrystalline body from a magnetic shape memory alloy
A kind of MSM-, single crystal technology, applied in the direction of material selection, crystal growth, single crystal growth, etc. for magnetostrictive devices, can solve the problems of difficult operation, expensive nucleation crystal cost, etc., to achieve the reduction of scraps, Examining the Effect of Placement Reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
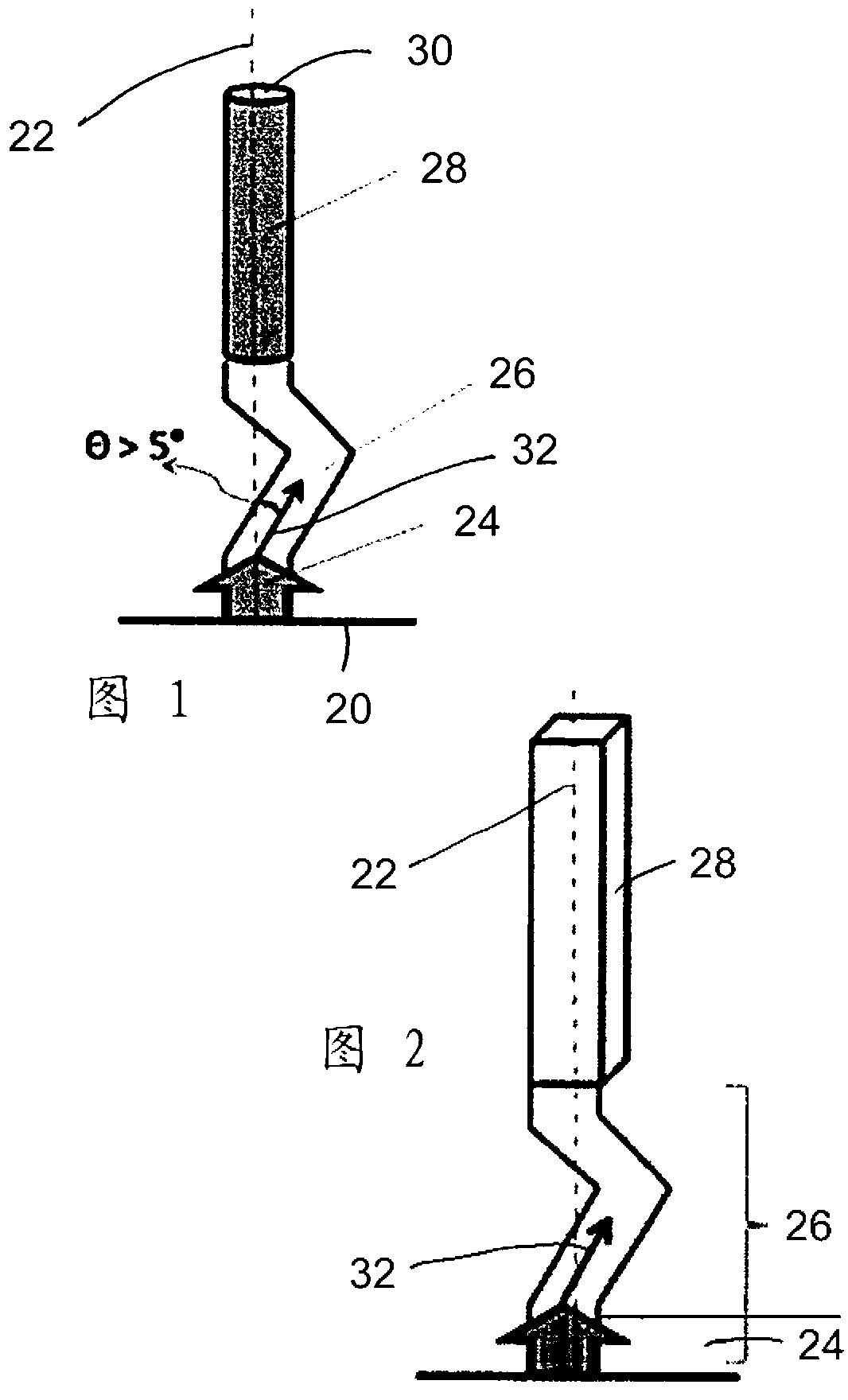
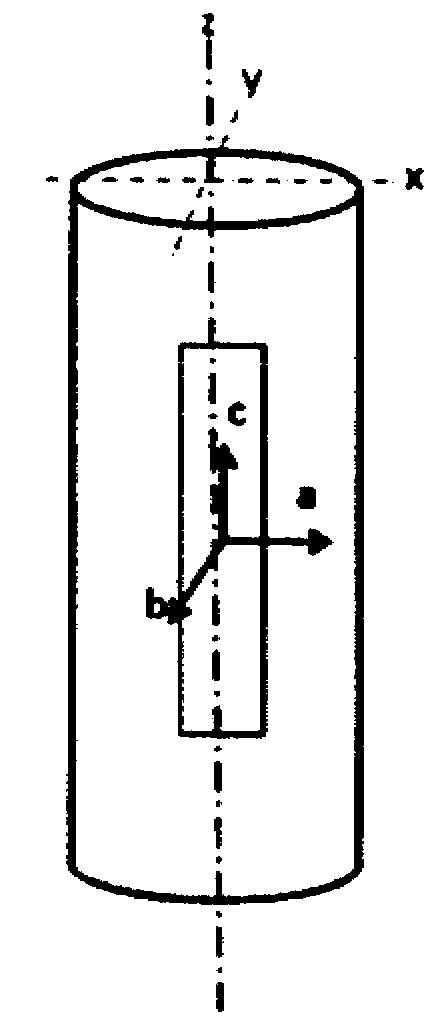
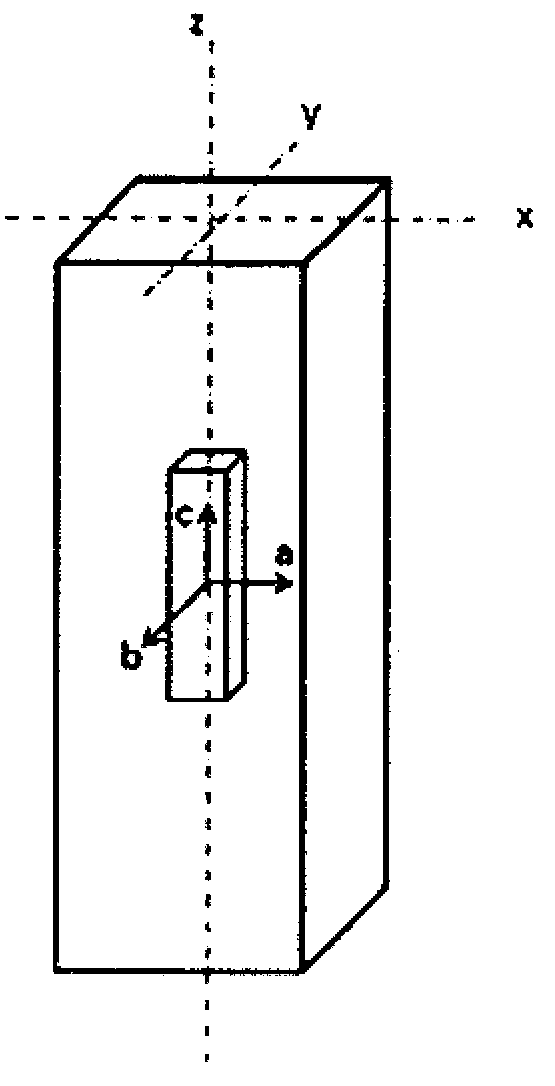
[0022] figure 1 This shows the principle with which the invention can be realized according to a first exemplary embodiment. The figure shows the so-called mold shell for producing single crystals according to the so-called Bridgman method (Bridgman-Verfahren), which mold shell extends perpendicularly from the cold plate 20 along the longitudinal axis (dashed line 22), forming a formation A core region (Ankeimbereich) 24 , a selector region (Selektorbereich) 26 following this nucleation region and a crystal region (Kristallbereich) 28 . The suitably melted alloy material is inserted into the device through the upper opening 30, and the liquid alloy material is then solidified from bottom to top (arrow 32) under the condition of forming a corresponding upwardly moving solidification front, the movement speed of the solidification front is controlled by a suitable Temperature affects reservations.
[0023] figure 1 (akin figure 2 ) shows how the solidification path accord...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com