Metabolomic profiling of prostate cancer
A technology of prostate cancer and metabolites, applied in the field of cancer markers, can solve the problems of elevated serum PSA levels and the inability to know the invasiveness of cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
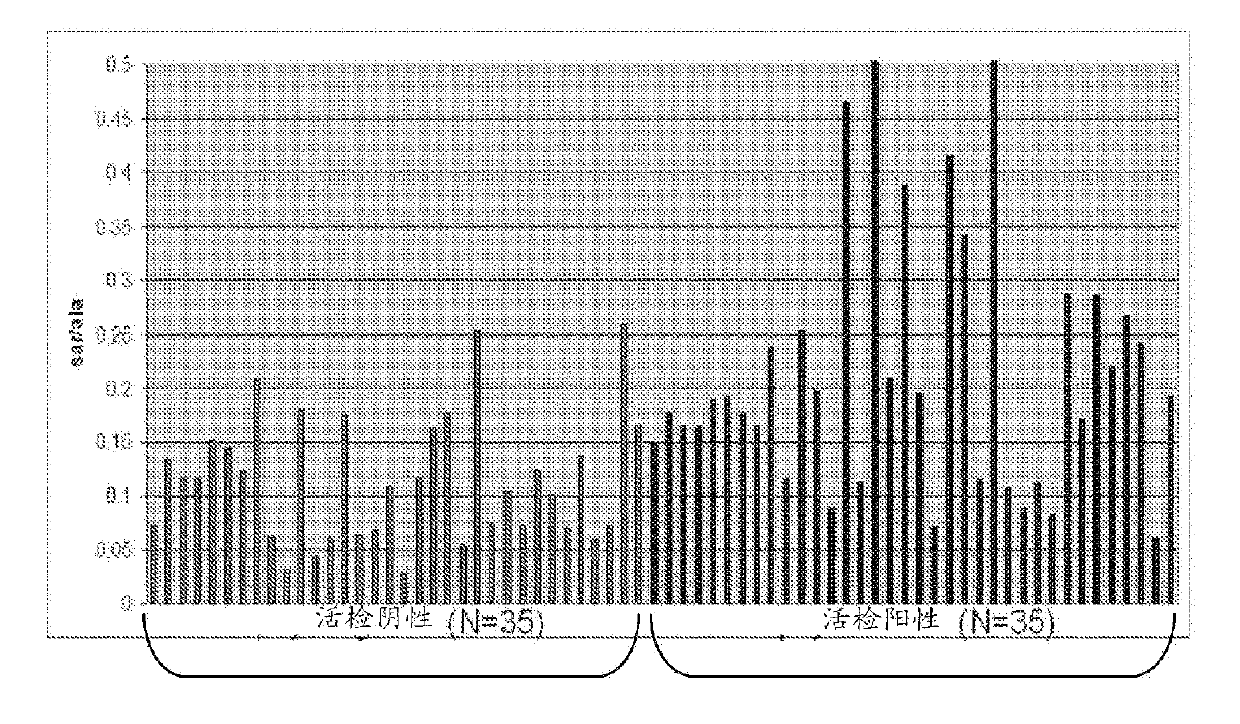
[0180] Biomarkers found in urine
[0181] general method
[0182] Identification of Metabolic Signatures in Prostate Cancer
[0183] Each sample was analyzed to determine the concentrations of several hundred metabolites. Analytical techniques such as GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) and UHPLC-MS (Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) are used to analyze metabolites. Multiple aliquots were analyzed in parallel simultaneously and after appropriate quality control (QC), the information obtained from each analysis was recombined. Each sample is characterized according to thousands of properties that ultimately boil down to hundreds of chemical species. The technique used enables the identification of new chemically unnamed compounds.
[0184] Statistical Analysis
[0185] The data were analyzed using t-tests to identify molecules (known named metabolites or unnamed metabolites) that were present at different levels in definable populatio...
Embodiment 2
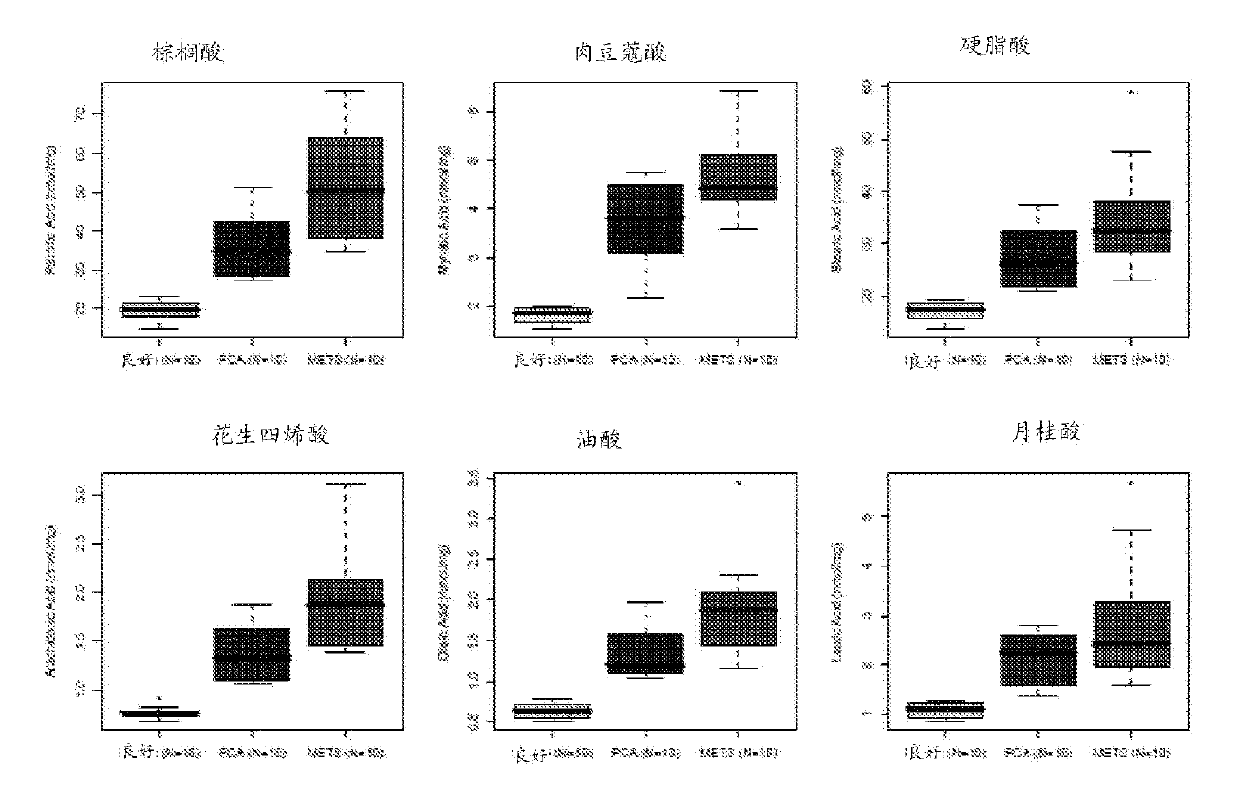
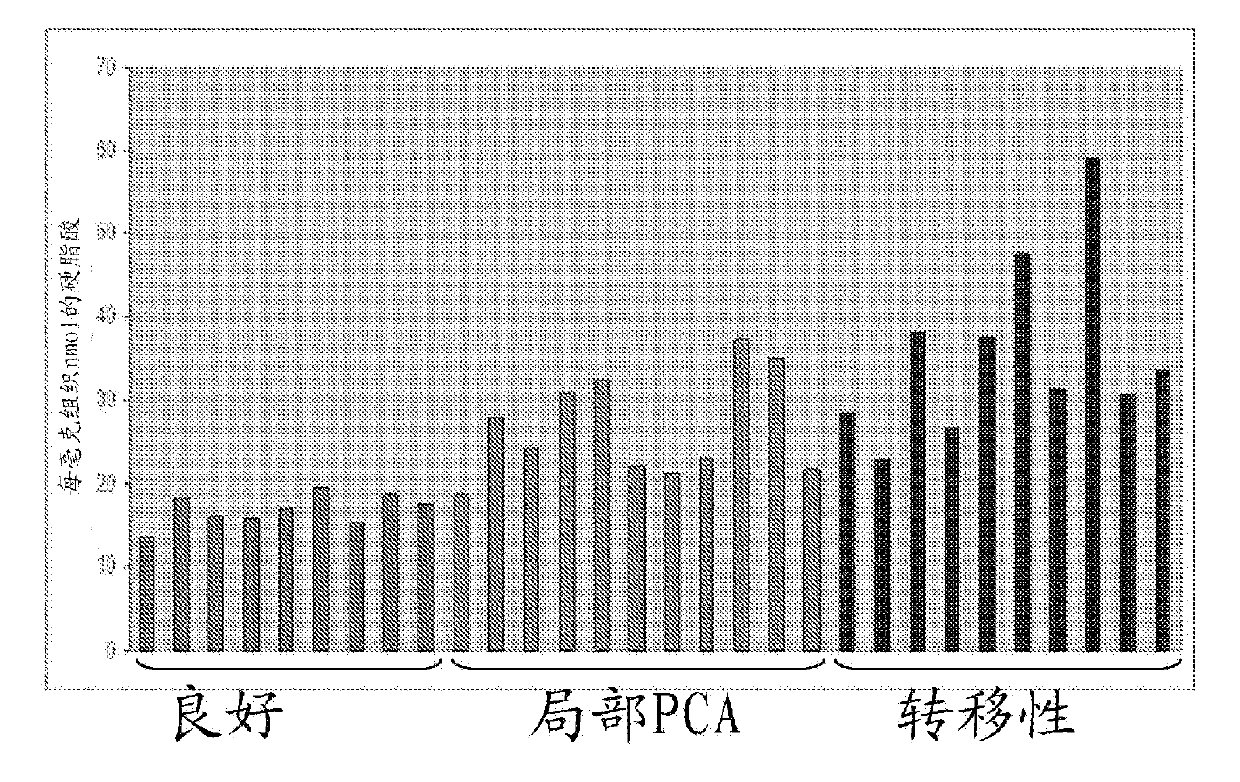
[0226] Validation of Multiple Metabolites in Prostate Cancer Tissues, Cell Lines, and Urinary Sediments
[0227] Materials and methods:
[0228] Amino acids were purchased from Sigma Corporation (St. Louis, MO, USA). Correspondingly labeled versions were purchased from Isotec Corporation (Miamisburg, OH, USA). Isobutanol, chloroform, methyl cyanide, dimethylformamide, ethyl acetate were purchased from Sigma. All other chemicals analyzed were reagent grade and purchased from Fluka and Sigma. n-methyl-N-(tert-butylmethylsilane trifluoroacetamide (MtBSTFA) + 1% tert-butyl-dimethylchlorosilane and heptafluorobutyrylic anhydride were purchased from Regis Technologies Inc, IL, USA.
[0229] clinical sample
[0230] Obtain benign prostate and localized prostate cancer tissue from radical prostatectomy series and metastatic prostate cancer biospecimens from expedited autopsy procedures at the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan Specialized Program of Research Excellence in P...
Embodiment 3
[0260] Validation of metabolites in breast cancer tissues and cell lines
[0261] Validation of sarcosine in breast cancer tissue:
[0262] Sarcosine was identified as a differential metabolite at high levels in the progression of prostate cancer. GC-MS studies indicate a progression from benign to localized and then metastatic disease in the progression of cancer. Levels of many metabolites were elevated. Analysis using cell lines supports this observation. The same approach was applied to breast cancer samples. 19 tissue samples (10 benign, 8 localized and 1 metastatic breast cancer tissue) were analyzed. Breast cancer tissues showed higher sarcosine levels than corresponding benign tissues (Figure 31).
[0263] Creatine validation in invasive and non-invasive breast cancer cell lines:
[0264] Sarcosine validation was performed using a range of invasive (MDA-MB-231, BT-549, T578, SVM-245) and non-invasive (HME) breast cancer cell lines. The invasive cell lines showed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com