Solid fermentation method of straw fermentation bio-additive and application
A technology for fermenting organisms and solid fermentation, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms and microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of high production cost, poor production stability, affecting the industrialization process, etc., to improve quality and effectiveness, reduce pH value, and simple fermentation method. easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
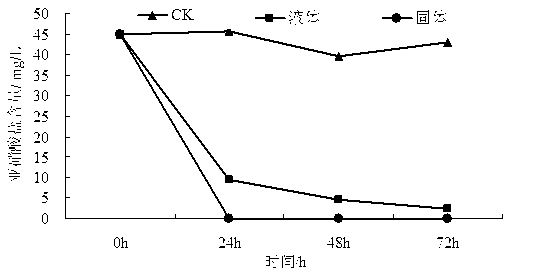
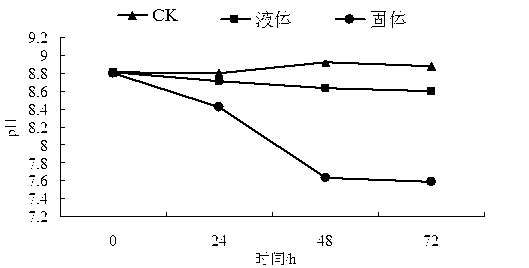
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Preparation of inoculum liquid:
[0021] (1) Take 1ml of each of Streptococcus faecalis, Pediococcus cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus daimeri and Bacillus licheniformis respectively inoculated in 100ml culture medium that has been sterilized by high temperature (20min, 121℃) cultured at 30°C for 48 hours. The formula of the culture solution is 4-6g of yeast extract, 8-15g of glucose, 5-10g of peptone, 1-3g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1000ml of water, and pH 6.0-7.0.
[0022] (2) Take a total of 600ml of six individually cultured bacterial solutions, add them to 11.4 L of the same high-temperature sterilized (20min, 121°C) culture solution (same formula as above) for mixed culture, and incubate at 30°C for 48h. Checked with a microscope, the number of bacteria in the culture solution reached 10 8 1 / ml is qualified, and 12L of mixed bacterial solution is obtained, which is the required liquid bacterial species.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Comparison of bacterial counts between liquid fermentation and solid fermentation of "Straw Fermentation Biological Additives"
[0025] (1) Liquid fermentation
[0026] Prepare 3L of culture medium (same formula as above), put it into a 5L fermenter, sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, add 300ml of mixed culture liquid strains, and put it at a temperature of 30°C, pH 5.0, stirring speed 300 r / min, ventilation volume 4 Under the optimal fermentation condition of L / min, the mixed bacterial liquid reached the end of fermentation in 24 hours, and the maximum concentration of bacterial liquid at the end of fermentation could reach 27.5×10 8 more than one / ml.
[0027] (2) Solid fermentation
[0028] Mix water: soybean meal powder: wheat bran powder: sucrose: urea at a ratio of 400:200:200:10:5, mix evenly and distribute, each bottle is 200-400g, sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes, and each bottle is filled with 20mL of liquid Bacteria were cultured statically at 35°C for 48...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Mix the solid medium and put it into jars, and sterilize it at 121°C for 15 minutes. The weight-to-number ratio of the solid medium is water: soybean meal powder: wheat bran powder: sucrose: urea Respectively 400:200:200:10:5;
[0039](2) Inoculate the liquid strains of the mixed culture according to 20% of the inoculum, and ferment and culture them in a constant temperature incubator at 35°C for 72 hours;
[0040] (3) After fermentation and natural drying at 30°C for 5 days, the number of bacteria reached 700×10 8 pcs / g; the liquid strain mentioned therein refers to: straw fermentation biological additive.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com