Hydrothermal saccharification method and device for cellulose biomass
A cellulose and biomass technology, applied in sugar production, sugar production, food science and other directions, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of direct utilization of saccharification products, reducing the quality of the output material, and the complexity of the hydrolysis device. The effect of rapid chemical process, expansion of production scale, and elimination of detoxification process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
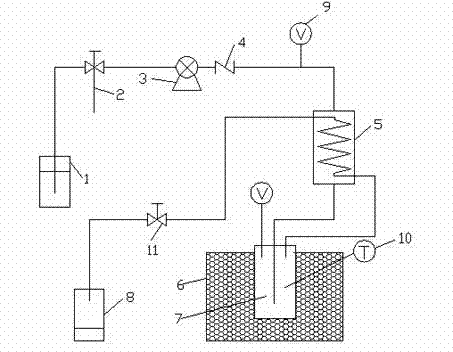
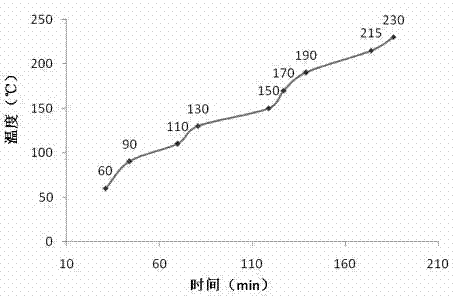
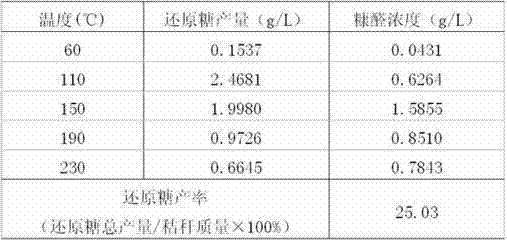
[0038] The collected wheat stalks were dried and crushed to a length of less than 1 cm for preservation. Weigh 25g of crushed wheat straw, put it into the reactor, seal the reactor, turn on the condensed water, turn on the metering pump, add 0.05wt% dilute sulfuric acid according to the ratio of solid to liquid ratio of 1:10, and control the flow rate of the metering pump at 15mL / min, stop adding acid after the dilute sulfuric acid in the reaction kettle reaches the required amount. Turn on the heating and stirring switch of the reaction kettle, start heating at a stirring speed of 80 r / min, the temperature is 60-230° C., and the pressure is kept at 1 MPa during the reaction. The temperature rise adopts a gradient temperature rise method, and the temperature is divided into nine nodes: 60°C, 90°C, 110°C, 130°C, 150°C, 170°C, 190°C, 215°C and 230°C. For the heating rate curve, see figure 2. When the temperature in the reactor rises to 60°C, open the pressure reducing valve a...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The collected wheat stalks were dried and crushed to a length of less than 1 cm for preservation. Weigh 25g of crushed wheat straw, put it into the reactor, seal the reactor, turn on the condensed water, turn on the metering pump, add 0.10wt% dilute sulfuric acid according to the ratio of solid to liquid 1:10, and control the flow rate of the metering pump at 15mL / min, stop adding acid after the dilute sulfuric acid in the reaction kettle reaches the required amount. Turn on the heating and stirring switch of the reaction kettle, start heating at a stirring speed of 80 r / min, the temperature is 60-230° C., and the pressure is kept at 2 MPa during the reaction. The temperature rise adopts a gradient temperature rise method, and the temperature is divided into nine nodes: 60°C, 90°C, 110°C, 130°C, 150°C, 170°C, 190°C, 215°C and 230°C. For the heating rate curve, see figure 2 . When the temperature in the reactor rises to 60°C, open the pressure reducing valve at the di...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The collected wheat stalks were dried and crushed to a length of less than 1 cm for preservation. Take by weighing the wheat straw of 25g pulverization, put into reactor, seal reactor, and open condensed water, open metering pump, add the dilute sulfuric acid of 0.50wt% according to the ratio of solid-liquid ratio 1:10, the flow velocity control of metering pump At 15mL / min, stop adding acid after the dilute sulfuric acid in the reactor reaches the required amount. Turn on the heating and stirring switch of the reactor, start heating at a stirring speed of 80 r / min, the temperature is 60-230° C., and the pressure is kept at 3 MPa during the reaction. The temperature rise adopts a gradient temperature rise method, and the temperature is divided into nine nodes: 60°C, 90°C, 110°C, 130°C, 150°C, 170°C, 190°C, 215°C and 230°C. For the heating rate curve, see figure 2 . When the temperature in the reactor rises to 60°C, open the pressure reducing valve at the discharge po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com