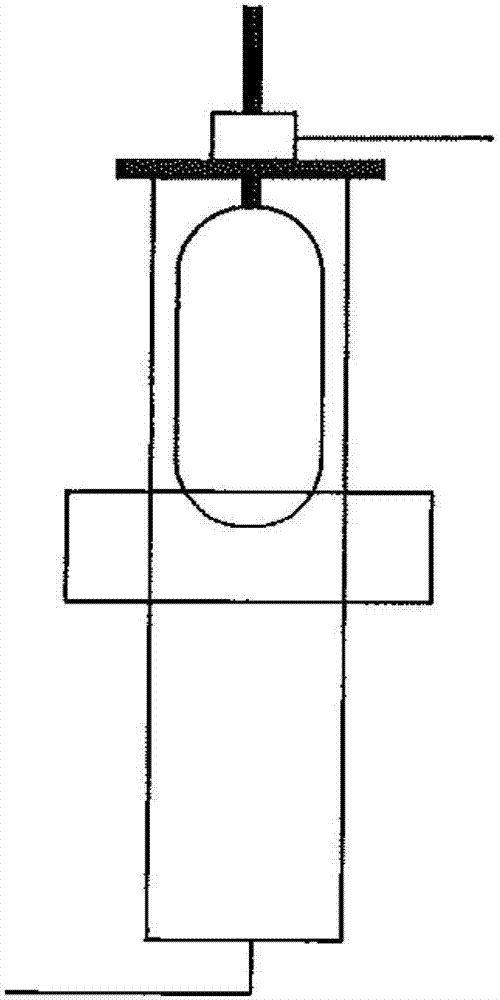
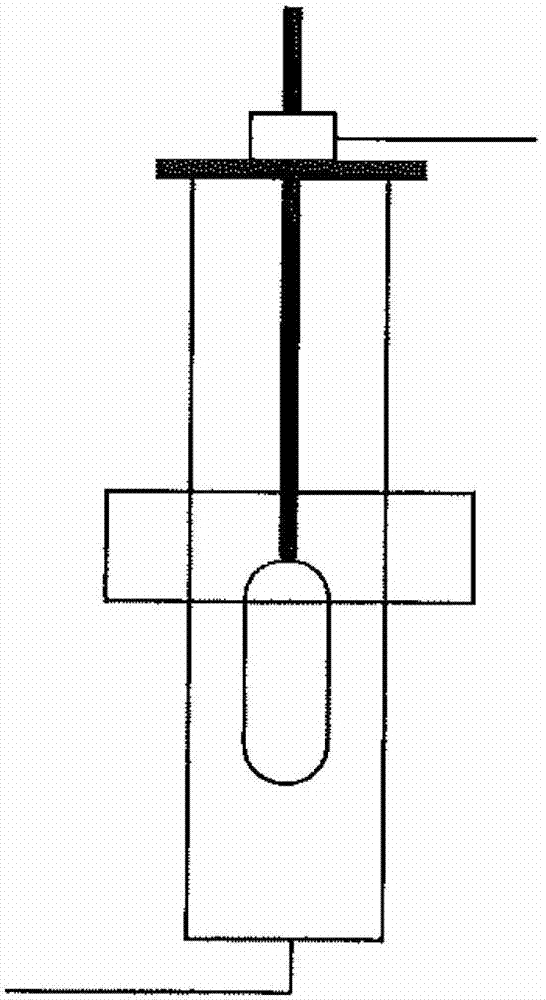
Manufacturing method of optical fiber base material possessing low refractive index portion distantly-positioned from core
A manufacturing method and base material technology, applied in manufacturing tools, glass manufacturing equipment, optics, etc., can solve problems such as smaller mode field diameter, disappearance of interchangeability, and rising manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Manufactured by the VAD method with an average density of 0.23g / cm 3 , The ratio of the core diameter to the shell diameter is 0.27, and the ash particle accumulation body is 150 mm in outer diameter. This soot accumulation body was inserted into a sintering furnace including an electric furnace and a quartz furnace core tube, while supplying He 16 [l / min], Cl 2 0.45[l / min], O 2 0.01 [l / min] while dehydrating at a temperature of 1100 [°C]. Thereafter, while supplying, He 20 [l / min], CF 4 0.03 [l / min] while vitrifying at a temperature of 1480 [°C]. Consider CF 4 When decomposed at high temperature in the furnace, the fluorine concentration becomes about 0.6 [mol%]. As a result, a core rod with an outer diameter of 65 mm was obtained in which the refractive index of the core portion was 0.40% higher than that of pure silica and the refractive index outside the shell portion was 0.10% lower than that of pure silica.
[0039] The core rod was heated and stretched with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com