Method of forming microstructures, laser irradiation device, and substrate
A structural and fine technology, applied in laser welding equipment, electrical connection formation of printed components, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the ease of etching (different etching speed, longer etching time, excessive etching, etc., to shorten the processing time , Fast etching speed, easy production management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0105]
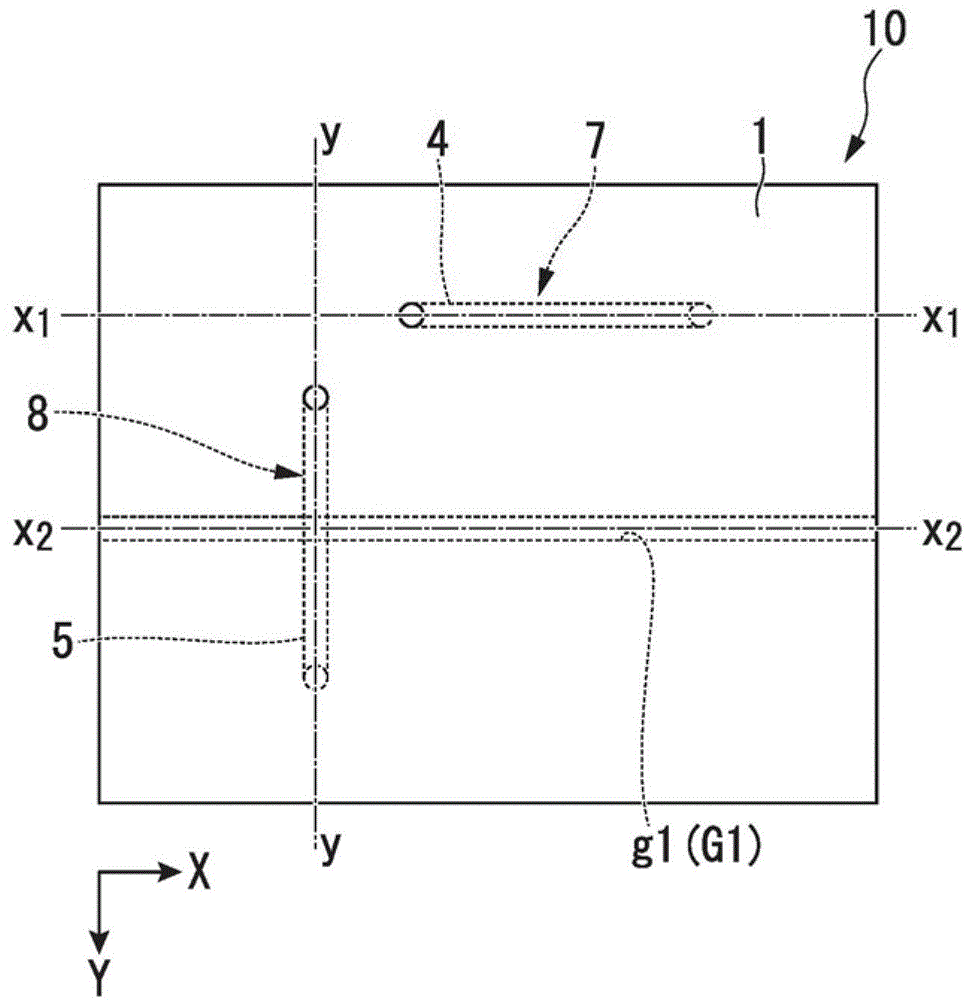
[0106] Figure 1A It is a plan view of interposer substrate 10 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Figure 1B is along Figure 1A The cross-sectional view of the line x1-x1. Figure 1C is along Figure 1A The cross-sectional view of the y-y line. Figure 1D is along Figure 1A The cross-sectional view of the x2-x2 line.
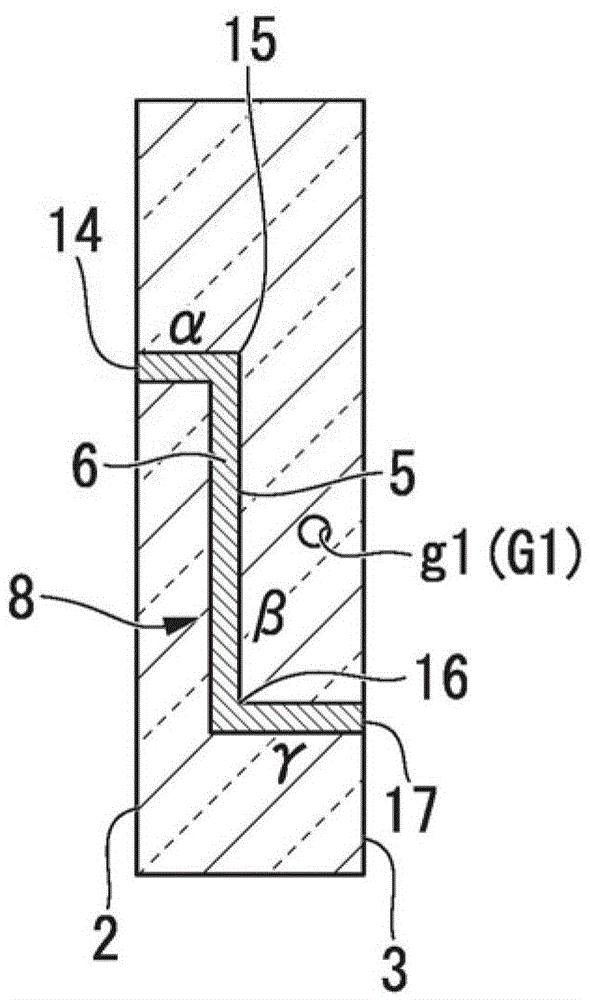
[0107] The through wiring substrate 10 includes a first through wiring 7 and a second through wiring 8 that connect one main surface 2 (first main surface) and the other main surface 2 (first main surface) of the substrate 1 in a connected manner. The first micropore 4 and the second micropore 5 are arranged so as to form the main surface 3 (second main surface), and the conductive substance 6 is filled or formed into a film in each micropore.
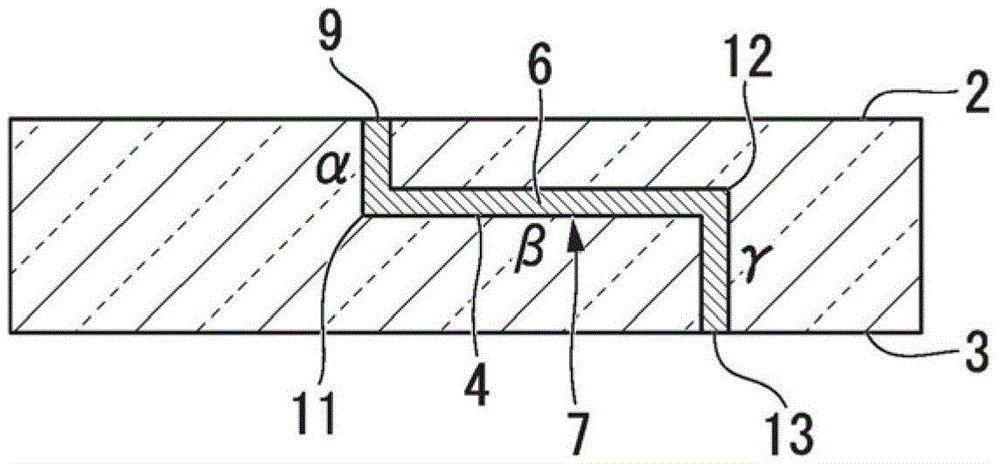
[0108] The first through wiring 7 includes: a region α extending from the opening 9 exposed on the main surface 2 to the bent portion 11 along the thickness direction of the substr...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0118]
[0119] Figure 2A It is a plan view of the surface wiring substrate 30 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 2B is along Figure 2A The cross-sectional view of the line x1-x1. Figure 2C is along Figure 2A The sectional view of the y1-y1 line. Figure 2D is along Figure 2A The cross-sectional view of the x2-x2 line. Figure 2E is along Figure 2A The sectional view of the y2-y2 line.
[0120] This surface wiring substrate 30 is provided with a first surface wiring 37 in which a first microgroove 34 is formed on the surface constituting one main surface 32 (first main surface) of the substrate 31 , and in the microgrooves 34 It is formed by filling or forming a film of a conductive substance 36 . In addition, the surface wiring board 30 is provided with a first flow path G2 constituted by the first fine hole g2 and a second flow path G3 constituted by the second fine hole g3.
[0121] The first surface wiring 37 includes a re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com