Non-partial regularization prior reconstruction method for low-dosage X-ray captive test (CT) image
A CT image, low-dose technology, applied in the field of image reconstruction of medical images, can solve problems such as inability to effectively distinguish edge information from noise, excessive smoothing or step-like effects in reconstructed images, failure to consider prior information of the same patient, etc. , to achieve the effect of improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
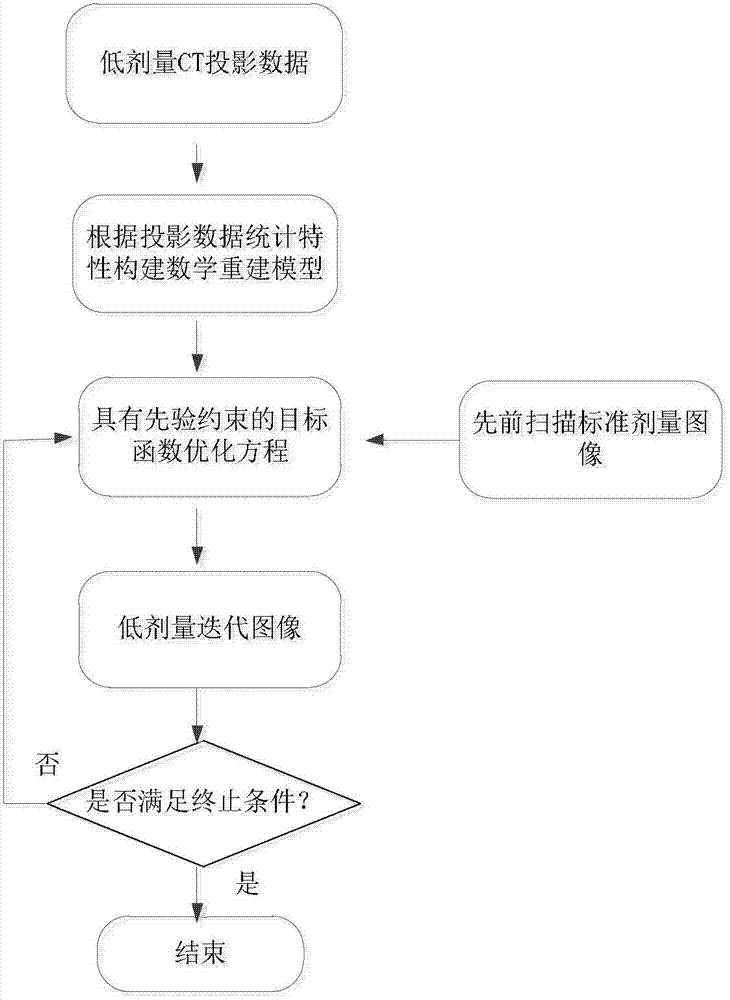
[0040] The non-local regularization prior reconstruction method of a low-dose X-ray CT image of the present invention, its specific implementation steps are as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
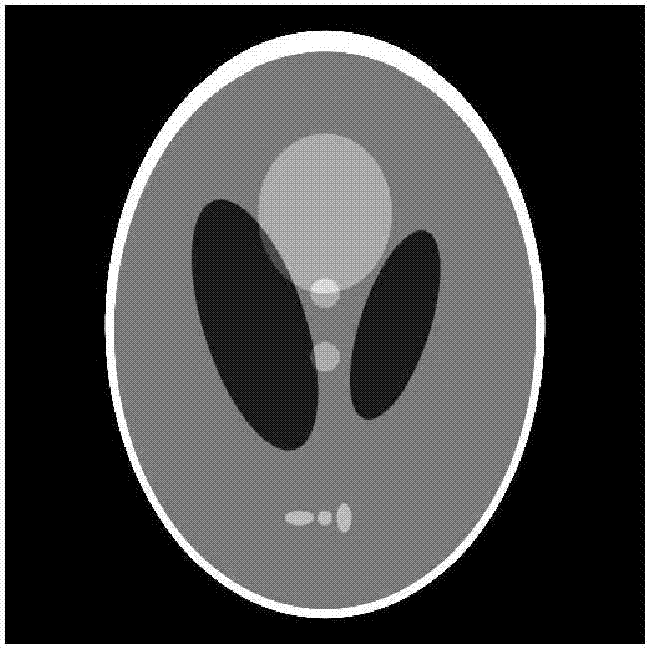
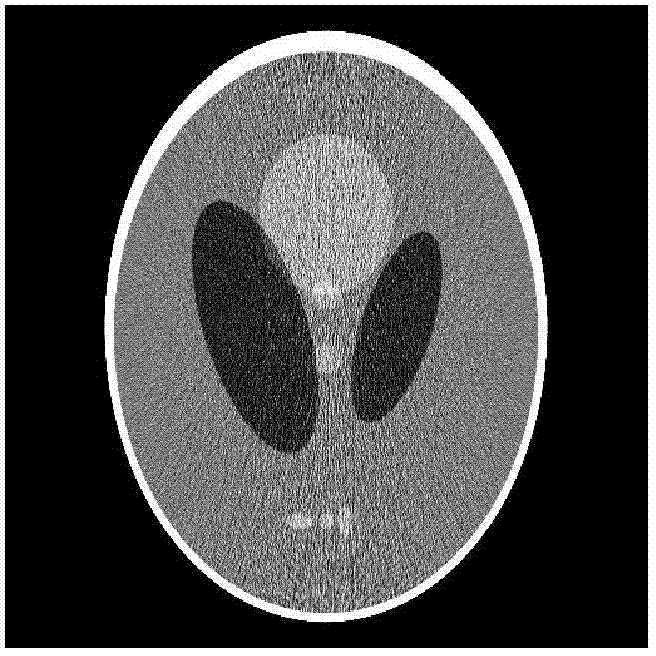
[0041] 1. Data acquisition: X-ray CT imaging equipment is used to collect CT medical images scanned by patients previously under standard dose radiation. The medical images under the standard dose radiation are medical images reconstructed by filtered back projection method under clinical standard milliampere-second scanning protocol. Image; use X-ray CT imaging equipment to collect the line integral projection data of the CT medical image of the low-dose radiation of the same patient under the low milliampere-second scanning protocol, and obtain the corresponding correction parameters and system matrix at the same time. Among them, the radiation of the low-dose radiation The dose is 1 / 7 to 1 / 20 of the radiation dose of the standard dose ray, which can be flexibly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com