Method for preparing arsenic adsorbent and method for treating waste water
An adsorbent and waste water technology, applied in the direction of adsorption water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of low recycling rate, low adsorption capacity, difficult regeneration, etc., and achieve mild synthesis conditions and synthesis The method is simple and easy to elute the regenerative effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041]Weigh 6.68 g (0.022mol) sodium lauryl sulfate into a 500 ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 99ml (5.5mol) water and stir until completely dissolved, then add 9.73ml (0.022mol) zirconium n-propoxide, adjust under stirring The pH of the solution reached 3, continued to stir for 30 min, stood still for 20 h, placed in an 80 °C oil bath for 120 h, filtered and washed with water and isopropanol, dried at 110 °C for 12 h, and then calcined at 550 °C for 3 h. In this embodiment, the zirconium oxide has a mesoporous structure of 2-50 nm through the structure-directing effect of the long-chain alkyl sodium sulfate. At the same time, sulfate ions and hydrogen ions were introduced into the pores of zirconia through long-chain alkyl sodium sulfate.
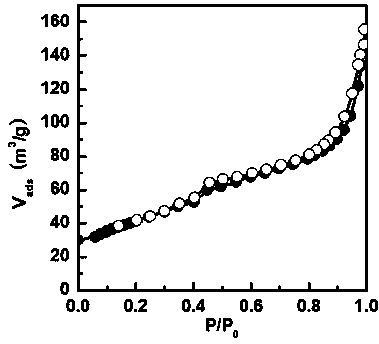
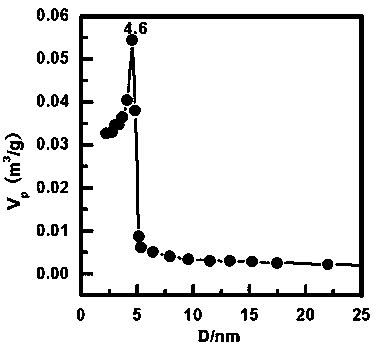
[0042] see figure 1 , this figure is the N of the material obtained in this example 2 Adsorption-desorption isotherm diagram. see figure 2 , which is the BJH pore size distribution of the material obtained in this example. From the figure a...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Weigh 7.66 g of sodium cetyl sulfate in a 500 ml conical flask, add 99 ml of water and stir until completely dissolved, then add 9.73 ml of zirconium n-propoxide, adjust the pH of the solution to 3 under stirring, continue stirring for 30 min, and let stand 20 h, placed in an 80°C oil bath for 5 days, filtered and washed with water and isopropanol, dried at 110°C for 12 h, and then calcined at 550°C for 3 h.
[0047] In the following examples, the materials of Example 1 and Example 2 were used respectively. Experiments have proved that the material prepared in Example 2 has the same performance as that in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Weigh 0.05 g of the arsenic adsorbent prepared in Example 1, and put it into 50 ml of water sample with arsenic concentration of 44.7 mg / L prepared with sodium arsenate. At this time, the initial pH of the arsenic solution was determined to be 9.8, that is, the solution was alkaline and there were no free hydrogen ions; at the same time, the SO 4 2- The concentration is 0mg / L. After the above water sample was stirred at 25°C for 24 hours, the adsorbent adsorbed arsenate ions, and ZrO 2 HSO 4 +H 2 AsO 4 - →ZrO 2 ·H 2 AsO 4 - +H + +SO 4 2- Reaction. Water sample is measured again, at this moment, the arsenic concentration in the recorded solution is 1.2mg / L, calculates that this adsorbent is 43.5mg / g to the adsorption capacity of arsenic (Ⅴ); Recorded solution pH is 4.1, measured Get SO 4 2- The concentration is 90.6 mg / L, which means that the solution is acidic due to the above-mentioned ion exchange.
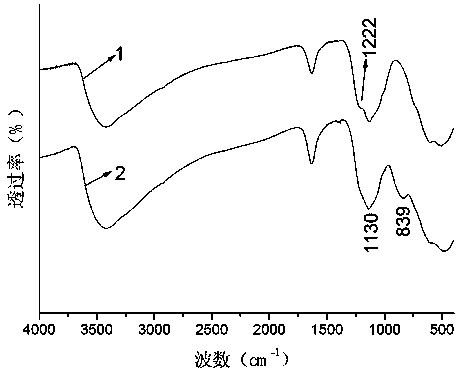
[0050] see image 3 1 among the figure is the infr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com